As we have learned, digestion is the simple process of breaking down food molecules into smaller components. This process begins from the mouth and is then carried on to the stomach, to the small intestine, large intestine and then to the anus. This is the physical process of digestion. Here, let us learn more in detail about the chemical process of digestion involved while digesting biomolecules.
Table of Contents
Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates
Digestion and Absorption of Proteins
Digestion and Absorption of Lipids
What is Digestion?
Digestion is the process of breaking large, insoluble food molecules into smaller molecules for absorption into the bloodstream. This process involves the use of many digestive fluids and enzymes such as saliva, mucus, bile and hydrochloric acid, among others.
There are four primary stages of food digestion in the human body that include:
- After the intake of food through the mouth, it makes its way through the stomach into the small intestine, where it is digested.
- The nutrients from the digested food get absorbed into the bloodstream through small pores in the small intestine.
- The remaining undigested food is sent to the large intestine, where any unprocessed water or nutrients are reabsorbed into the body.
- The remaining waste food product is passed out of the body in the form of stools.
What is Absorption?
Absorption is the process of the absorbing or assimilating substances into the cells or across the tissues and organs through the process of diffusion or osmosis. Also refer: Difference between Osmosis and Diffusion
Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrates
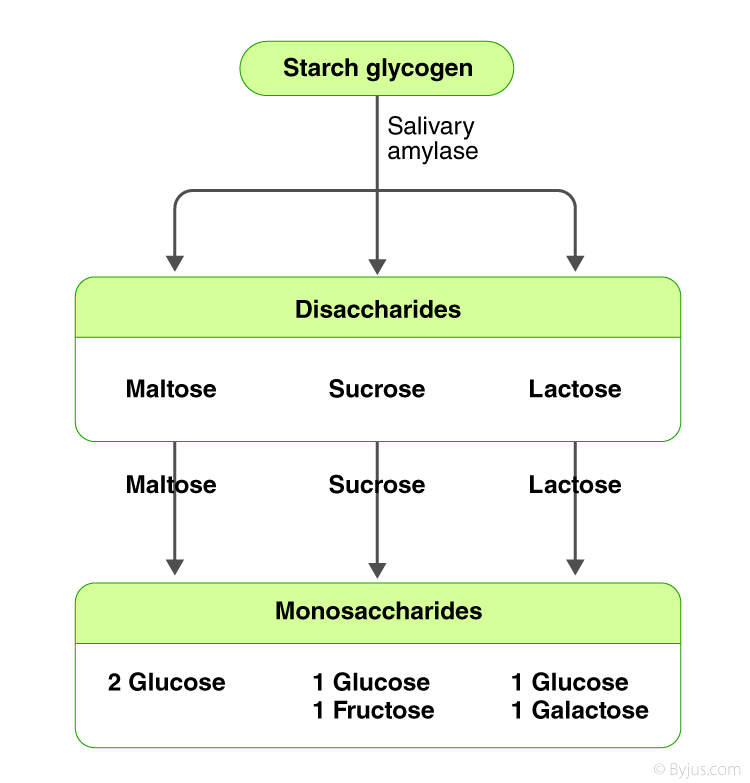
Carbohydrates are one of the essential nutrients in the human diet. There are two types of carbohydrates that can be digested by the human digestive system– sugar and starch.
Sugar is broken down in the gastrointestinal tract by the small intestine and three enzymes present in the mouth, namely, Lactase, Sucrase, and Maltase.
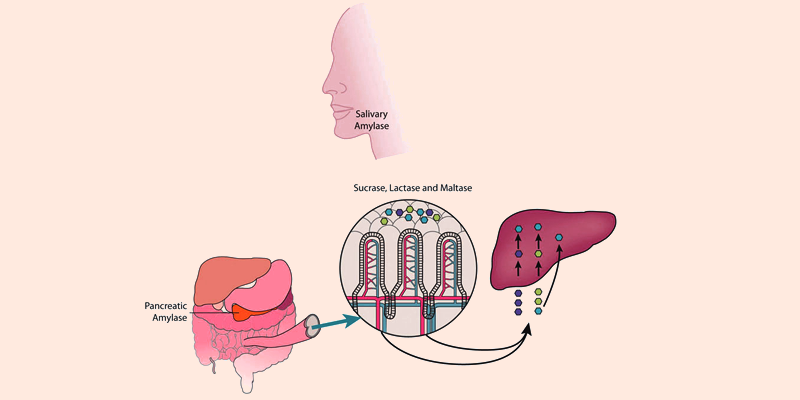 In the same way, starch is broken down with the help of the Amylase enzymes which are present in the mouth and the stomach. After digestion, carbohydrates are absorbed in the small intestine with the help of minute finger-shaped projections known as Villi. Also refer: Carbohydrates
In the same way, starch is broken down with the help of the Amylase enzymes which are present in the mouth and the stomach. After digestion, carbohydrates are absorbed in the small intestine with the help of minute finger-shaped projections known as Villi. Also refer: Carbohydrates
The chemical digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth. The below flowchart explains in detail about the series of steps involved in breaking down the carbohydrates into their monomers.
Recommended Videos


Digestion and Absorption of Proteins
 Proteins play a vital role in the growth and replenishment of body cells and tissues. The digestion of proteins takes place in the stomach with the help of protease and pepsin enzymes, which breaks down the proteins into amino acids. The process is facilitated by the hydrochloric acid present in the stomach. Amino acids are tiny elements which get absorbed into the blood system through the wall of the small intestine. Also refer: Proteins
Proteins play a vital role in the growth and replenishment of body cells and tissues. The digestion of proteins takes place in the stomach with the help of protease and pepsin enzymes, which breaks down the proteins into amino acids. The process is facilitated by the hydrochloric acid present in the stomach. Amino acids are tiny elements which get absorbed into the blood system through the wall of the small intestine. Also refer: Proteins
Digestion and Absorption of Lipids
Lipids are organic compounds comprising fatty acids, which are insoluble in water. Fats are the most common examples of lipids. The insoluble property of lipids makes the digestion and absorption of fats a complicated process.
Since they are hydrophobic, fats stick together as a large glob of insoluble mass after reaching the stomach. It is broken down with the help of bile juice, which contains bile salts. These broken molecules are then acted upon by pancreatic lipase, the major fat-absorbing enzymes in the body.
Pancreatic lipase breaks down fats into tiny molecules of free fatty acids and monoglycerides, which are small enough for the small intestine to push through into the bloodstream.
Also refer: Lipids
For more detailed information about Digestion and Absorption, its process or any other related topics and for digestion and absorption class 11 revision notes explore @ BYJU’S Biology.

I want note of absorption of protein.