“Decomposition is the process by which the complex organic substances breakdown into simpler substances by the action of microorganisms.”

What is Decomposition?
The term decomposition means “to break down”. It typically corresponds to the disintegration or rupture of complex organic matter into a simpler inorganic matter. It is one of the significant and essential processes of the ecosystem. Hence, decomposition is a metabolic process, taking up raw materials in the form of complex compounds, processing it and then converting it into simpler compounds.
Bacteria, fungi and a few other microorganisms initiate the process of decomposition and are known as decomposers. They feed on dead organisms to survive.
The decaying and dead animals and plants serve as the raw materials which, on the breakdown, produces nutrients, carbon dioxide, and water, etc. Detritus are the raw materials such as dead animals, plants and their remains. Microbes then process this detritus which are collectively known as saprophytes.
Also refer: Putrefaction
Let us know more in detail about its process and the major factors affecting the process of decomposition.
Factors Affecting Decomposition
Following are the important factors affecting the rate of decomposition:
Litter Quality
The rate of decomposition depends on the structural and chemical properties of litter. For eg., the litter of bryophytes are decomposed at a slower rate due to the presence of lignin like complex chemicals.
Temperature
Temperature regulates the growth and activity of microorganisms. The temperature is different at different elevations. The species diversity and the microorganism count is affected by environmental changes.
Aeration
The oxygen present in the pores of the soil helps in the growth of microorganisms. In the water-logged soils, the aerobic microorganisms are absent. Here only anaerobic microorganisms can grow and initiate decomposition.
Soil pH
The presence of cations and anions governs the pH of the soil, which in turn affects microbial growth.
Inorganic Chemicals
After decomposition, the elements like potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium are released into the soil. Some of these are used by the microorganisms for their growth. Thus, it affects the rate of decomposition.
Moisture
The water present in the soil is responsible for various physiological processes of microorganisms present in the soil. The growth of microorganisms is thus governed by the presence of moisture in the soil.
Process of Decomposition
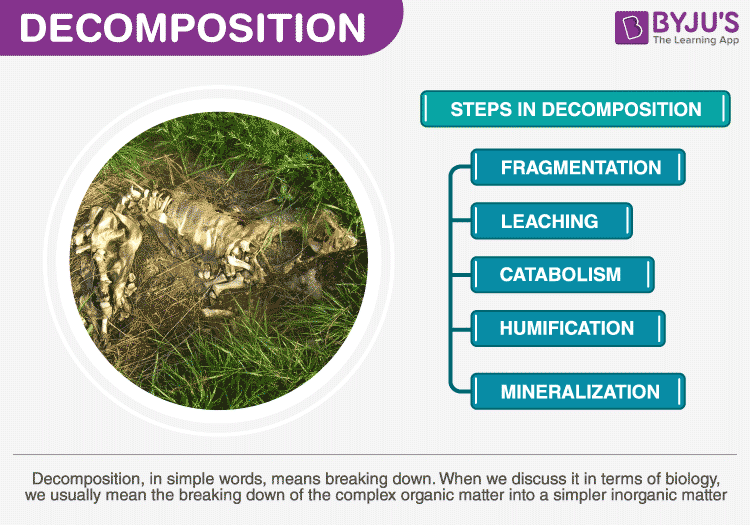
Process of Decomposition
Death and decomposition are an essential part of all life cycles on earth. In order to permit a successful continuation of life and growth of new plants and animals, older specimens must die and decompose. This process provides essential nutrients for plants and also for the growth and development of new organisms.
A complete process of decomposition takes place in five different steps or phases:
Fragmentation
It is the initial stage of decomposition. Fragmentation means the breakdown of detritus into smaller pieces by the detritivores.
Leaching
The fragmented particles may contain a lot of water-soluble nutrients which are inorganic in nature. These nutrients get dissolved in the water and seep into the soil and get precipitated in the process of leaching.
Catabolism
Once the complex material is broken down into smaller particles and the inorganic nutrients are removed, it is time to convert the detritus into simpler inorganic compounds. This process is carried out by various fungal and bacterial enzymes by the process of catabolism.
Humification
It is the process of formation of a dark-coloured layer of amorphous substance on the soil called humus. It cannot be decomposed easily as it is highly resistant to the action of microbes. The layer of humus is very rich in nutrients as it provides high fertility to the soil.
Mineralization
It is the final step in the process. Mineralization is the process of the degradation of the hummus to release inorganic nutrients.
Also Read: Rigor Mortis
For more information on Decomposition and the process of decomposition, keep visiting BYJU’S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions on Decomposition
Which of the following condition Will inhibit decomposition? A. Low temperature B. High temperature C. Moderate temperature D. Aerobic conditions
The process of decomposition requires living entities as their decomposers. These decompose the degraded complexes in the ecosystem and could be bacteria or fungi. The decomposers attack organic or degraded complexes thus transforming them into simpler forms, thereby initiating the process of degradation. In this process, temperature plays an important role and has a great influence. If the temperature is increased, the process is smoothly carried out and if the temperature is low, the process of decomposition is slow. The colder temperature decreases the rate of decomposition while warmer temperature increases the rate of decomposition. For this process, moisture is required. Hence, the correct option is option A – low temperature, it inhibits the process of decomposition.

Comments