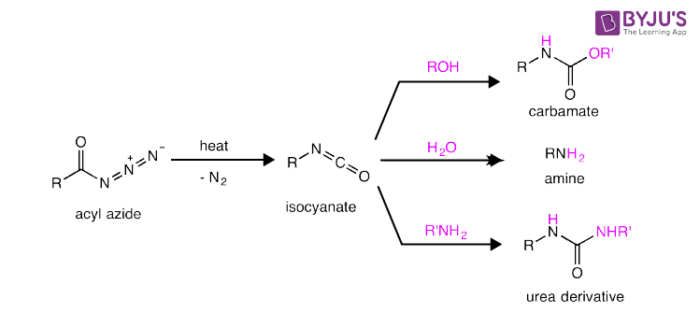
What is Curtius Rearrangement?
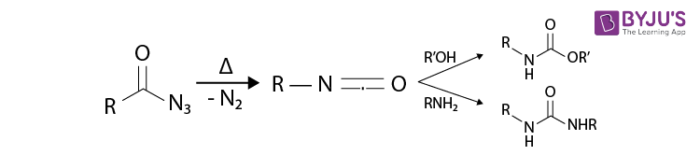
Curtius Rearrangement is also called Curtius degradation or Curtius reaction. Curtius Rearrangement is a thermal decomposition of acyl acid to form isocyanate with a loss of nitrogen as stated by Theodor Curtius in the year 1885. It is also known as Curtius degradation or Curtius reaction. This reaction is identical to Schmidt Reaction.
Isocyanates are subjected to attack by various nucleophiles namely alcohols, water, and amines which in turn outputs urea derivative or carbamate and essential amines.
Mechanism of Curtius Rearrangement
- Acyl azide preparation
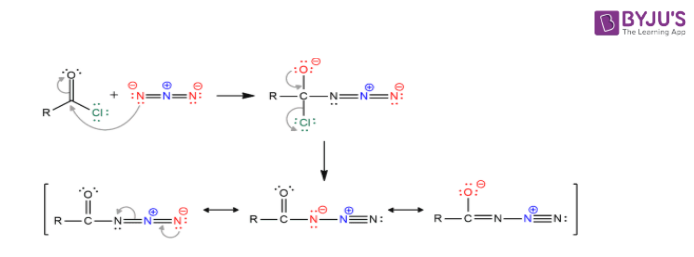
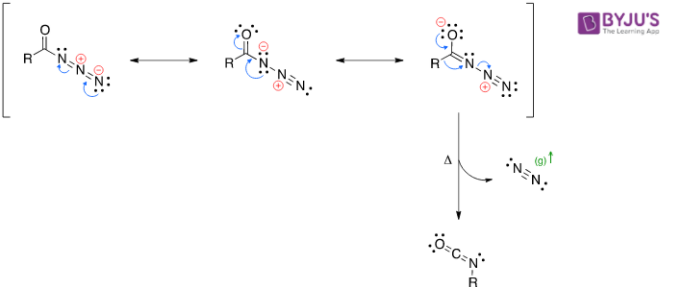
- Decomposition
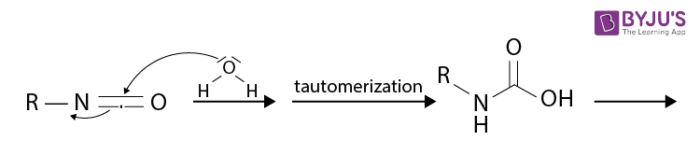
- Reacts with water to form an unstable carbamic acid derivative. It further undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation.
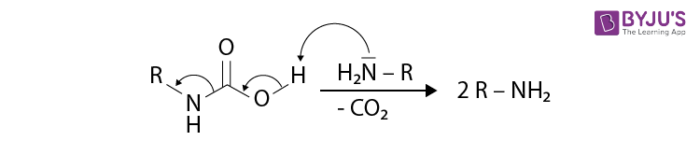
- Isocyanates are versatile starting materials. Isocyanates play a vital role in polymerization work and in the derivatization of biomacromolecules.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more interesting topics in Chemistry. Also, get various engaging and video lessons to learn more effectively.


Comments