The periodic table is the tabular arrangement of all the chemical elements on the basis of their respective atomic numbers. In the periodic table, the vertical columns are called ‘groups’ and the horizontal rows are called ‘periods’. The modern periodic table is based on the modern periodic law put forward by the English physicist Henry Moseley, which states that “the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers”. Periodic trends in the properties of the elements can be observed down the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic table.
Table of Content
- Elements on the periodic table
- Related Videos on Periodic Table of Elements
- List of Chemical Elements
- Atomic Number of Elements
- FAQs
Elements on The Periodic Table
Every chemical element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus. All isotopes of an element fall under a single cell on the periodic table, since they all share the same atomic number.
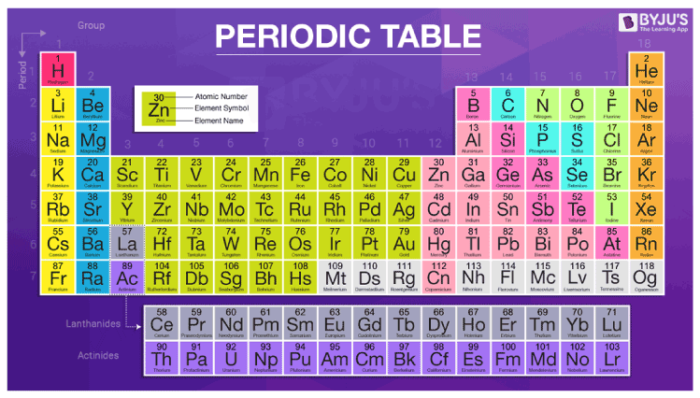
Periodic Table of Elements – Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Groups & Symbols
Also, Check ⇒
- Periodic Trends in Atomic Radii
- Periodic Trends in Ionic Radii
- Periodic Trends in Electronegativity
- Periodic Trends in Electron Affinity
- Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy
List of Chemical Elements
The table below consists of 118 elements of the periodic table, sorted by atomic number, atomic weight, symbols, density, discovered year and the group.
| Atomic Number | Atomic Mass | Chemical Element Name | Symbol | Discovery (Year) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0079 | Hydrogen | H | 1776 | 1 |
| 2 | 4.0026 | Helium | He | 1895 | 18 |
| 3 | 6.941 | Lithium | Li | 1817 | 1 |
| 4 | 9.0122 | Beryllium | Be | 1797 | 2 |
| 5 | 10.811 | Boron | B | 1808 | 13 |
| 6 | 12.0107 | Carbon | C | Ancient | 14 |
| 7 | 14.0067 | Nitrogen | N | 1772 | 15 |
| 8 | 15.9994 | Oxygen | O | 1774 | 16 |
| 9 | 18.9984 | Fluorine | F | 1886 | 17 |
| 10 | 20.1797 | Neon | Ne | 1898 | 18 |
| 11 | 22.9897 | Sodium | Na | 1807 | 1 |
| 12 | 24.305 | Magnesium | Mg | 1755 | 2 |
| 13 | 26.9815 | Aluminum | Al | 1825 | 13 |
| 14 | 28.0855 | Silicon | Si | 1824 | 14 |
| 15 | 30.9738 | Phosphorus | P | 1669 | 15 |
| 16 | 32.065 | Sulfur | S | Ancient | 16 |
| 17 | 35.453 | Chlorine | Cl | 1774 | 17 |
| 18 | 39.948 | Argon | Ar | 1894 | 18 |
| 19 | 39.0983 | Potassium | K | 1807 | 1 |
| 20 | 40.078 | Calcium | Ca | 1808 | 2 |
| 21 | 44.9559 | Scandium | Sc | 1879 | 3 |
| 22 | 47.867 | Titanium | Ti | 1791 | 4 |
| 23 | 50.9415 | Vanadium | V | 1830 | 5 |
| 24 | 51.9961 | Chromium | Cr | 1797 | 6 |
| 25 | 54.938 | Manganese | Mn | 1774 | 7 |
| 26 | 55.845 | Iron | Fe | Ancient | 8 |
| 27 | 58.9332 | Cobalt | Co | 1735 | 9 |
| 28 | 58.6934 | Nickel | Ni | 1751 | 10 |
| 29 | 63.546 | Copper | Cu | Ancient | 11 |
| 30 | 65.39 | Zinc | Zn | Ancient | 12 |
| 31 | 69.723 | Gallium | Ga | 1875 | 13 |
| 32 | 72.64 | Germanium | Ge | 1886 | 14 |
| 33 | 74.9216 | Arsenic | As | Ancient | 15 |
| 34 | 78.96 | Selenium | Se | 1817 | 16 |
| 35 | 79.904 | Bromine | Br | 1826 | 17 |
| 36 | 83.8 | Krypton | Kr | 1898 | 18 |
| 37 | 85.4678 | Rubidium | Rb | 1861 | 1 |
| 38 | 87.62 | Strontium | Sr | 1790 | 2 |
| 39 | 88.9059 | Yttrium | Y | 1794 | 3 |
| 40 | 91.224 | Zirconium | Zr | 1789 | 4 |
| 41 | 92.9064 | Niobium | Nb | 1801 | 5 |
| 42 | 95.94 | Molybdenum | Mo | 1781 | 6 |
| 43 | 98 | Technetium | Tc | 1937 | 7 |
| 44 | 101.07 | Ruthenium | Ru | 1844 | 8 |
| 45 | 102.9055 | Rhodium | Rh | 1803 | 9 |
| 46 | 106.42 | Palladium | Pd | 1803 | 10 |
| 47 | 107.8682 | Silver | Ag | Ancient | 11 |
| 48 | 112.411 | Cadmium | Cd | 1817 | 12 |
| 49 | 114.818 | Indium | In | 1863 | 13 |
| 50 | 118.71 | Tin | Sn | Ancient | 14 |
| 51 | 121.76 | Antimony | Sb | Ancient | 15 |
| 52 | 127.6 | Tellurium | Te | 1783 | 16 |
| 53 | 126.9045 | Iodine | I | 1811 | 17 |
| 54 | 131.293 | Xenon | Xe | 1898 | 18 |
| 55 | 132.9055 | Cesium | Cs | 1860 | 1 |
| 56 | 137.327 | Barium | Ba | 1808 | 2 |
| 57 | 138.9055 | Lanthanum | La | 1839 | 3 |
| 58 | 140.116 | Cerium | Ce | 1803 | 101 |
| 59 | 140.9077 | Praseodymium | Pr | 1885 | 101 |
| 60 | 144.24 | Neodymium | Nd | 1885 | 101 |
| 61 | 145 | Promethium | Pm | 1945 | 101 |
| 62 | 150.36 | Samarium | Sm | 1879 | 101 |
| 63 | 151.964 | Europium | Eu | 1901 | 101 |
| 64 | 157.25 | Gadolinium | Gd | 1880 | 101 |
| 65 | 158.9253 | Terbium | Tb | 1843 | 101 |
| 66 | 162.5 | Dysprosium | Dy | 1886 | 101 |
| 67 | 164.9303 | Holmium | Ho | 1867 | 101 |
| 68 | 167.259 | Erbium | Er | 1842 | 101 |
| 69 | 168.9342 | Thulium | Tm | 1879 | 101 |
| 70 | 173.04 | Ytterbium | Yb | 1878 | 101 |
| 71 | 174.967 | Lutetium | Lu | 1907 | 101 |
| 72 | 178.49 | Hafnium | Hf | 1923 | 4 |
| 73 | 180.9479 | Tantalum | Ta | 1802 | 5 |
| 74 | 183.84 | Tungsten | W | 1783 | 6 |
| 75 | 186.207 | Rhenium | Re | 1925 | 7 |
| 76 | 190.23 | Osmium | Os | 1803 | 8 |
| 77 | 196.9665 | Iridium | Ir | Ancient | 11 |
| 78 | 192.217 | Platinum | Pt | 1803 | 9 |
| 79 | 195.078 | Gold | Au | 1735 | 10 |
| 80 | 200.59 | Mercury | Hg | Ancient | 12 |
| 81 | 204.3833 | Thallium | Tl | 1861 | 13 |
| 82 | 207.2 | Lead | Pb | Ancient | 14 |
| 83 | 208.9804 | Bismuth | Bi | Ancient | 15 |
| 84 | 209 | Polonium | Po | 1898 | 16 |
| 85 | 210 | Astatine | At | 1940 | 17 |
| 86 | 222 | Radon | Rn | 1900 | 18 |
| 87 | 223 | Francium | Fr | 1939 | 1 |
| 88 | 226 | Radium | Ra | 1898 | 2 |
| 89 | 227 | Actinium | Ac | 1899 | 3 |
| 90 | 232.0381 | Thorium | Th | 1829 | 102 |
| 91 | 231.0359 | Protactinium | Pa | 1913 | 102 |
| 92 | 238.0289 | Uranium | U | 1789 | 102 |
| 93 | 237 | Neptunium | Np | 1940 | 102 |
| 94 | 244 | Plutonium | Pu | 1940 | 102 |
| 95 | 243 | Americium | Am | 1944 | 102 |
| 96 | 247 | Curium | Cm | 1944 | 102 |
| 97 | 247 | Berkelium | Bk | 1949 | 102 |
| 98 | 251 | Californium | Cf | 1950 | 102 |
| 99 | 252 | Einsteinium | Es | 1952 | 102 |
| 100 | 257 | Fermium | Fm | 1952 | 102 |
| 101 | 258 | Mendelevium | Md | 1955 | 102 |
| 102 | 259 | Nobelium | No | 1958 | 102 |
| 103 | 262 | Lawrencium | Lr | 1961 | 102 |
| 104 | 261 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 1964 | 4 |
| 105 | 262 | Dubnium | Db | 1967 | 5 |
| 106 | 266 | Seaborgium | Sg | 1974 | 6 |
| 107 | 264 | Bohrium | Bh | 1981 | 7 |
| 108 | 277 | Hassium | Hs | 1984 | 8 |
| 109 | 268 | Meitnerium | Mt | 1982 | 9 |
| 110 | 261.9 | Darmstadtium | Ds | 1994 | 10 |
| 111 | 271.8 | Roentgenium | Rg | 1994 | 11 |
| 112 | 285 | Copernicium | Cn | 1996 | 12 |
| 113 | 286 | Ununtrium | Uut | 2003 | 13 |
| 114 | 289 | Flerovium | Fl | 1998 | 14 |
| 115 | 288 | Ununpentium | Uup | 2010 | 15 |
| 116 | 293 | Livermorium | Lv | 2000 | 16 |
| 117 | 260.9 | Ununseptium | Uus | 2010 | 17 |
| 118 | 294 | Ununoctium | Uuo | 2006 | 18 |
Atomic Number of Elements
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is atomic number?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s2 2p2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the atomic number and mass number?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly different mass numbers, it calculates the atomic mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
Can two different elements have the same atomic number?
Atoms from two different elements may have the same neutron count, but never the same proton count. The number of protons is unique to the element and it represents the number of atoms.
How do we calculate atomic mass?
Add the mass of protons and neutrons to compute the atomic mass of a single atom of an element. Example: Find the atomic mass of a carbon isotope which has 7 neutrons. From the periodic table you can see that carbon has an atomic number of 6, which is its proton number.
Why is atomic number important?
Atomic number is called the number of protons in an atom. This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element’s atoms. An element’s atoms all have the same number of protons and each element has a different number of protons in its atoms.


Good
ITS AWESOME
Wow awesome ???????????? this message is so super and useful ?????????????????
Good
Excellent
Very good
Very useful
nice
very important
thank u
thank u.
Good
Thanks a lot??
Same here it is very helpfull
For me also
Excellent work
I did fall in love with learning
And all credits goes to Byju’s the learning app
Thanks a lot ?????????????
It’s really helpful
Thanks a lot
its useful
Very help full
Nice
Thanks ?
Thankyou sir or mam for this table and video, This is so helpfull for me ???????????✌️✌️✌️✌️✌️
what is the unit for atomic mass number?
How to calculate number of atoms an element has?
Atomic mass is an absolute mass, relative isotopic mass is a number without proportions and without units.
To measure the number of atoms in a sample you will figure out how many moles the sample element contains. A mole is the choice of unit chemists. It’s equal to Avogadro’s number (6.02 X 1023) of atoms. For each element the atomic weight is on the periodic table right under the symbol of the element. The carbon atomic weight is 12 units of atomic mass (amu), so the weight of one mole is 12 grams.
A sample consisting the atoms of a single element, weights the sample in grams and separates the element by its atomic weight. The quotient shows you how many moles it has. Multiply this by the amount of Avogadro, and you can figure out how many atoms the sample contains.
Who discover hydrogen ?
Hydrogen was discovered by the English physicist Henry Cavendish in 1766.
Explain the following and give suitable examples with balanced chemical equations.
a. Reaction of metals with oxygen
b. Reaction of non-metals with oxygen
c. Reaction of metals with water
d. Reaction of metals with acid
Click here to learn more about Reaction of metals and Non-metals.
Very benefit for me
Excellent
It very useful and I learned it.
It benefits to students ??
thanks
good for students
who discovered krypton and what is its valency?
Krypton was discovered in Britain in 1898 by William Ramsay, a Scottish chemist, and Morris Travers, an English chemist, in residue left from evaporating nearly all components of liquid air.