Ether is an organic compound containing an oxygen atom bonded to two same or different alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula for ethers can be R-O-R, R-O-Ar or Ar-O-Ar, where R represents an alkyl group and Ar represents an aryl group.
Ethers are generally classified into two categories on the basis of substituent groups attached: symmetrical ether (when two identical groups are attached to the oxygen atom) and asymmetrical ether (when two different groups are attached to the oxygen atom). Ethers exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties.
Some physical and chemical properties of ethers are discussed below:
Physical Properties of Ethers
- An ether molecule has a net dipole moment due to the polarity of C-O bonds.
- The boiling point of ethers is comparable to the alkanes but much lower than that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass despite the polarity of the C-O bond. The miscibility of ethers with water resembles those of alcohols.
- Ether molecules are miscible in water. This is attributed to the fact that like alcohol, the oxygen atom of ether can also form hydrogen bonds with a water molecule.
Chemical Properties of Ethers
Ethers generally undergo chemical reactions in two ways:
1. Cleavage of C-O bond
Ethers are generally very unreactive in nature. When an excess of hydrogen halide is added to the ether, cleavage of C-O bond takes place leading to the formation of alkyl halides. The order of reactivity is given as HI>HBr>HCl
R-O-R + HX → RX + R-OH
2. Electrophilic Substitution
The alkoxy group in ether activates the aromatic ring at ortho and para positions for electrophilic substitution. Common electrophilic substitution reactions are halogenation, Friedel Craft’s reaction etc.
3. Halogenation of Ethers
Aromatic ethers undergo halogenation, for example, bromination, upon the addition halogen in the presence or absence of a catalyst.

4. Friedel Craft’s Reaction of Ethers
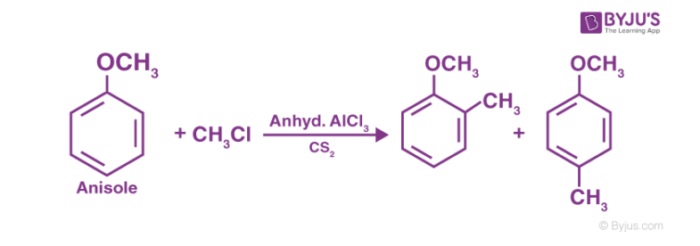
Aromatic ethers undergo Friedel Craft’s reaction for example addition of alkyl or acyl group upon the reaction with alkyl or acyl halide in the presence of a Lewis acid as catalyst.
To learn more about physical and chemical properties of ethers download BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Comments