Table of Contents:
A. GS1 Related:
B. GS2 Related:
2. Deciding issues of personal law
C. GS3 Related:
1. Now India has a nuclear triad
D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials : A Quick Glance
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
G. BILLS/ACTS/SCHEMES/ORGS IN NEWS
H. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
I. Archives
.
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Useful News Articles
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here today folks!
B. GS2 Related
Category: International Relations
Topic: Regional Grouping
Key Points:
- India hosted leaders of the five-nation BRICS as well as the seven-nation BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation), which together represent two-thirds of humanity and more than a quarter of the world’s growth
- While BIMSTEC has geographical moorings, BRICS is a unique organisation of countries that came together in 2006 not because of geography, history or wealth, but because of their promise as key “emerging economies”
- It is, therefore, unfortunate that the outcome of the BRICS summit and the outreach to BIMSTEC countries has been popularly condensed into what they had to say on a single issue: terrorism, with only a few paragraphs out of the 109-para Goa Declaration dominating the discourse
- New Delhi would have done better to bring the spotlight in Goa back to its own declared goals of building economies and bringing prosperity in the region
Category: Governance
Topic: Secularism
Key Points:
- The issue described as ‘triple talaq’ has unnecessarily been confused with the issue of a uniform civil code, thus thrusting India’s minority Muslim community into the defensive
- But this dilemma is essentially a question of whether the Supreme Court can pronounce on an issue of personal law
The Shah Bano case
- The last time that Supreme Court sought to rule in a matter concerning personal law was in 1985 resulting in what has come to be known as the Shah Bano amendment
- There was no doubt, held the apex court, that the Koran imposes an obligation on the Muslim husband to make provision for or to provide maintenance to the divorced wife
- Besides, Section 125 of the CrPC applies to all regardless of caste or creed. So Shah Bano had the right to be given maintenance money, similar to alimony
- The court also went on to discuss the desirability of bringing a uniform civil code in India, holding that a common civil code would help the cause of national integration by removing disparate loyalties to laws which have conflicting ideologies
- This judgment was vigorously criticised by the Muslim clergy
A setback for Muslim women
- The Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act was adopted in May 1986 and nullified the Supreme Court’s judgment in the Shah Bano case
- The Statement of Objects and Reasons of this Act clarifies that when a Muslim divorced woman is unable to support herself after the iddatperiod that she must observe after the death of her spouse or after a divorce, during which she may not marry another man, the magistrate is empowered to make an order for the payment of maintenance by her relatives who would be entitled to inherit her property on her death according to Muslim law
- But when a divorced woman has no such relatives, and does not have enough means to pay the maintenance, the magistrate would order the State Wakf Board to pay the maintenance
- The ‘liability’ of the husband to pay maintenance was thus restricted to the period of the iddatonly
Conclusion
In today’s vitiated communal environment it would be best if the apex court were to take on the responsibility of interpreting the law in light of the widely excoriated practice of triple talaq, which in the view of many practising Muslims is not the law
Category: International Relations
Topic: Regional Groupings
Key Points:
- With India announcing that all five BRICS member states are united in acknowledging the global threat posed by terrorism, and that those who support terror are as much a threat to us than those who perpetrate acts of terror, the eighth BRICS summit came to an end on Sunday in Goa. The BRICS agenda moved forward a bit with the BRICS leaders united in their “view to establish the BRICS Agriculture Research Platform, BRICS Railway Research Network, BRICS Sports Council, and various youth-centric fora” and agreeing “to fast track the setting up of a BRICS Rating Agency” based on market-oriented principles to “further bridge the gap in the global financial architecture.”
Focus on terrorism
- The Prime Minister’s focus, by and large, remained on the issue of terrorism. In more ways than one, he made it plain to his BRICS partners that this is an issue on which India feels rather strongly and that “BRICS needs to work together and act decisively to combat this threat.”
- This message was primarily aimed at China, a country with which India has had differences on the issue of Pakistan-sponsored terrorism against India
- China had recently put a technical hold once again at the United Nations and prevented Azhar from being designated a global terrorist, despite JeM being a UN-proscribed terror group
- The other change that India introduced to the BRICS agenda was also significant as it underscored India’s changing priorities. India used the summit to reach out to its neighbours by initiating the BRICS-BIMSTEC outreach
- Founded in 1997, the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) now includes Nepal and Bhutan apart from Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand
- Set up with the objective of enhancing technological and economic cooperation among South Asian and South-east Asian countries along the coast of the Bay of Bengal, it has been neglected so far by its members
Bilateral ties with Russia
- Finally, India used the Goa summit to re-galvanise its long-standing partnership with Russia, which was in danger of losing direction
- Russia’s decision to hold military exercises with Pakistan did not go down well with India at a time when it was seeking to diplomatically isolate Pakistan after the Uri terror attacks
- Russia, for its part, has been concerned about India’s tilt towards the U.S.
- In Goa, the two states reaffirmed the strategic nature of their friendship once again
- India signed three major deals worth billions of dollars with Russia: five S-400 Triumf air defence systems, four stealth frigates, and a joint venture to manufacture Kamov-226T utility helicopters in India
Recognising the limits of the BRICS mandate at a time of slowing economies and growing intra-BRICS political divergences, India has tried to reimagine the multilateral forum to serve its larger strategic ends.
- Mean Machines
Category: International Relations Topic: India-Russia

C. GS3 Related
Category: Internal Security
Topic: Coastal Security
Key Points:
- India has quietly completed its nuclear triad by inducting the indigenously built strategic nuclear submarine INS Arihant into service
- INS which stands for ‘Indian Naval Ship’ is affixed to a ship only after it is inducted into service
No-first-use doctrine
- Arihant is capable of carrying nuclear tipped ballistic missiles, the class referred to as Ship Submersible Ballistic Nuclear (SSBN). SSBNs are designed to prowl the deep ocean waters carrying nuclear weapons and provide a nation with an assured second strike capability — the capability to strike back after being hit by nuclear weapons first.
- Second strike capability is particularly important for India as it had committed to a ‘No-First-Use’ policy as part of its nuclear doctrine
- With this India joins the select group of countries which have a nuclear triad, i.e. capable of delivering nuclear weapons by aircraft, ballistic missiles and submarine launched missiles
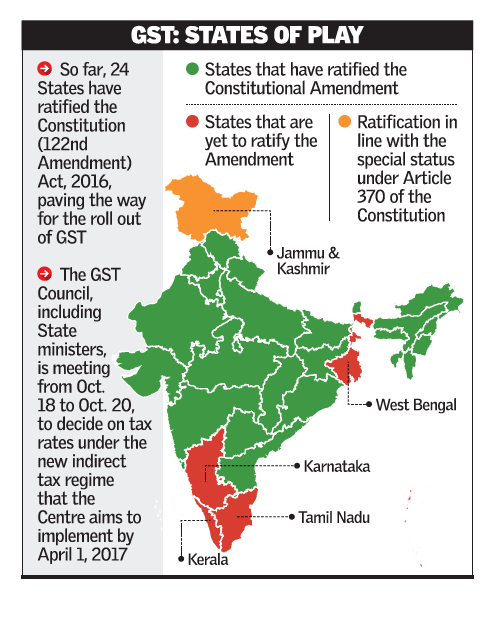
- GST: States of Play
Category: Indian Economy
Topic: Taxation
D. GS4 Related
E. Important Editorials: A Quick Glance
Category: Environment
Topic: Climate change
Key Points:
- On October 15, at the Rwandan capital of Kigali, 197 countries arrived at an accord to phase out a planet-warming chemical used in air conditioners and refrigerators
- The agreement amends the Montreal Protocol of 1989 to allow it to eliminate HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons)
- These gases comprise a small part of the greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere and do not harm the ozone layer
- But their heat-trapping capacity is more than a thousand times that of carbon dioxide, making HFCs far more destructive to the climate than the more well-known GHG
- The Kigali accord divides the world into three groups
- The richest countries, including the US and European Union nations, will freeze the production and consumption of HFCs by 2018 and reduce their use to about 15 per cent of 2012 levels by 2036
- A group of developing countries, including China, Brazil and South Africa, are mandated to freeze HFC use by 2024 and reduce it to 20 per cent of their average value in 2020-22 by 2045
- India, Iran, Iraq, Pakistan and oil economies like Saudi Arabia and Kuwait will have the most lenient schedule
- They will freeze HFC use by 2028 and reduce it to about 15 per cent of 2025 levels by 2047
- This phase-out will avert the equivalent of about 70 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions by 2050
- In 2011, the EU banned the use of HFCs in cars and is phasing out the chemical in other industries
- Industries in the US have started replacing CFCs with climate-friendly refrigerants
F. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn:
- Montreal Protocol amendment
- BIMSTEC
- BRICS
- Nuclear Warfare
- GST
- India-Russia
G. BILLS/ACTS/SCHEMES/ORGS IN NEWS
Companies Amendment Bill
H. Fun with Practice Questions 🙂
Question 1: Which of the following is true regarding BIMSTEC?
- Members of Bimstec include Bangladesh, Pakistan, Thailand and Bhutan
- This sub-regional organization came into being in 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration
a) Only 1 b) Only 2 c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question 2: The words ‘socialist’ and ‘secular’ were added to the preamble by:
Question 3: Which of the following statement/s is are true?
- BRICS includes India, Brazil and South Africa only
- Ufa, Fortaleza and Goa are declarations of the BRICS summits
a) Only 1 b) Only 2 c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question 4: Which of the following is true?
- GST will result in the mitigation of double taxation
- For consumers, it will result in uniform prices throughout the country
a) Only 1 b) Only 2 c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
Question 5: Which of the following is true?
- Hydrofluorocarbons, are also known as super greenhouse gases because their high global warming potential could undercut the benefits expected from the reduction of other greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide
- Recently delegates meeting in Rwanda accepted a complex amendment to the Montreal Protocol to include HFCs under the protocol too
a) Only 1 b) Only 2 c) Both 1 and 2 d) Neither 1 nor 2
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
I. Archives:
You can check out some more recent News Analysis sections to build even more context
17th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
16th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
15th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
14th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
13th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
12th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
11th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
10th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
9th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
8th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
7th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
6th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
5th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
4th October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
3rd October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
2nd October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
1st October 2016: Daily News & Current Affairs Analysis
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series

Comments