TABLE OF CONTENT
A. GS1 Related History 1. Mysore Lancers’ tryst with Haifa B. GS2 Related Polity 1. SC open to liquor sale on city highways 2. Allow people with genuine reasons to deposit banned notes: SC to govt 3. Centre may partially lift AFSPA 4. ‘Make registration of marriages compulsory International Relations 1. Moving beyond security ties 2. Incursions by PLA rose in 2017 3. Vietnam for greater Indian role in SE Asia 4. North Korea claims it tested intercontinental missile C. GS3 Related Economics 1. Tap GST for jobs data: PM-appointed panel Science & Technology 1. Drug-resistant TB higher among children than expected: report E. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn F. Bills/Acts/Schemes/Orgs in News G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
UPSC Current Affairs 2017: News Analysis
1. Mysore Lancers’ tryst with Haifa
Context:
- A long forgotten slice of martial history related to Mysuru will be revisited when Prime Minister Narendra Modi pays tribute to fallen Indian soldiers at the Haifa cemetery in Israel.
The Mysore Imperial Service and the liberation of Haifa:
- The Mysore Imperial Service played a big role in the liberation of Haifa on September 23, 1918, from Ottoman Turks and Germans, by allied forces.
- This is seen as one of the fiercest battles in the west Asian theatre of World War I in which India, as a British colony, fought German and the Ottoman troops.
- The Mysore Lancers were in the 15th Imperial Service as the forces sent by the princely states of Mysore, Jodhpur and Hyderabad.
- The then Mysuru Maharaja Nalwudi Krishnaraja Wadiyar sent his troops to defend the empire and even gave nearly ₹50 lakh to the India War Fund.
1. SC open to liquor sale on city highways
Context:
- December 15, 2016 Supreme Court order: prohibited the sale of liquor within a distance of 500 metres from the outer edge of national and State highways.
- March 2017 order: the ban was not restricted to just liquor shops alongside the highways but also to other larger establishments, including pubs and hotels.
- Intention: to prevent drunken driving on high-speed thoroughfares.
- Many states started de-notifying highways in order to circumvent the December 15th
Petition: filed by NGO Arrive Safe Society challenging the Chandigarh administration’s move to de-notify certain roads.
In news:
The Supreme Court observations
- nothing wrong in de-notifying particular stretches of highways running inside city limits as city roads and such de-classification does not violate its earlier order of banning liquor sales near National and State highways.
Reasons given:
- Traffic inside city limits is usually slow and heavy, and stretches de-notified fall within the city limits.
- .The goal of the liquor ban was to prevent drunken driving in fast-moving traffic.
- The pace of traffic with the city is very different from traffic outside city limits.
- Purpose of the ban is to avoid drivers getting inebriated while driving on highways inter-linking cities.
Widespread relief: especially to pubs and restaurants in the metros, which were forced to shut down
2. Allow people with genuine reasons to deposit banned notes: SC to govt
Context: demonetization
In news:
- The Supreme Court asked the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to come up with a policy to offer a window to people who could not deposit their demonetised notes for legitimate reasons before last year’s December 30 deadline.
3. Centre may partially lift AFSPA
In news:
- As per the inputs from a senior Home Ministry official: The Centre is considering partial removal of the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) from Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. There was no proposal to withdraw it in Jammu and Kashmir.
- In Arunachal Pradesh, complete withdrawal, except two districts in the east bordering Myanmar and Nagaland.
- Views sought: The Ministry has asked the two States for their views on AFSPA withdrawal and said that it was open to reviewing the stringent law in other States like Manipur.
Basics of AFSPA :
- Armed Forces (Special Powers) Acts (AFSPA), are Acts of the Parliament of India that grant special powers to the Indian Armed Forces in what each act terms “disturbed areas”.According to The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976 once declared ‘disturbed’, the area has to maintain status quo for a minimum of 3 months.
- The AFSPA gives powers to the Army and Central forces deployed in “disturbed areas” to kill anyone acting in contravention of law, arrest and search any premises without a warrant.
- It provides cover to forces from prosecution and legal suits without the Centre’s sanction.
Active AFSPA:
- Whole of Nagaland, Assam, Manipur (excluding the seven Assembly constituencies of Imphal).
- In Arunachal Pradesh, it is in force in 16 police stations and in Tirap, Longding and Changlang districts bordering Assam.
- Tripura withdrew AFSPA in 2015.
- It is not in force in Meghalaya (except 20 kilometre area along Assam border) and Mizoram.
Supreme court ruling:
- On July 8, 2016, in a landmark ruling, The Supreme Court of India ended the immunity of the armed forces from prosecution under AFSPA, saying,“It does not matter whether the victim was a common person or a militant or a terrorist, nor does it matter whether the aggressor was a common person or the state. The law is the same for both and is equally applicable to both… This is the requirement of a democracy and the requirement of preservation of the rule of law and the preservation of individual liberties.”
- Supreme Court said that any encounter carried out by armed forces in the garb of AFSPA should be subjected to thorough inquiry.
4. ‘Make registration of marriages compulsory
In news:
- The Law Commission of India- the commission headed by former Supreme Court judge Justice B.S. Chauhan, has recommended compulsory registration of marriages.
Why?
- To protect gullible women who become victims of fake marriages.
- The lack of provisions for compulsory registration of marriages had proven disastrous for women and deprived them of societal recognition and legal security.
Key fact: Fraudulent marriages are on the rise especially among non-resident Indians. Compulsory registration can serve as a means to ensure that conditions of a valid marriage have been performed.
Minor amendment:
- Minor amendment to the Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969, including a provision for compulsory registration of marriage, would serve the purpose.
- And there was no need to amend any of the personal laws of religious communities.
2006 Supreme Court in Seema vs Ashwani case:
- Marriages of persons who are citizens of India belonging to various religions should be registered compulsorily in their States.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. Moving beyond security ties
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to Israel
In news:
The leaders to focus on a “non-security” strategic partnership involving agriculture, water, tourism, science technology and space.
2. Incursions by PLA rose in 2017
In News:
- Incidents of transgression by the People’s Liberation Army(PLA) has increased marginally this year along the disputed Sino-Indian border compared to 2016.
- Key Fact: 20-25% increase in transgressions by the Chinese PLA till May this year, particularly in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh. On an average around 300 transgressions are reported along the China border due to “difference in perception.
Sovereignty claims:
- Over the years both sides have developed a strategy of sending long patrols into disputed areas in summer months to assert their claims for sovereignty.
- These patrols are undertaken at eight of the key disputed locations, mostly in Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh and are believed to enjoy political sanction.
Reasons for increased transgression:
- Indian troops have improved their observation of the presence of Chinese patrols in disputed areas.
- The Chinese have stepped up border patrols as part of an aggressive posture along the border.
Ladakh border: 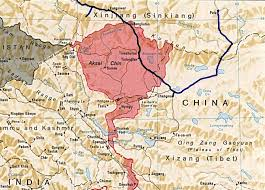
- Along the Ladakh border, India sticks mostly to a boundary drawn by British civil servant H. Johnson in 1865, which showed Aksai Chin as part of J&K.
- China disputes this claim and in the 1950s and built a road connecting Xinjiang and Tibet which ran through Aksai Chin.
- In northeast India, New Delhi sticks to the McMahon Line. China claims that McMahon Line has no legal standing and claims Arunachal Pradesh as part of Tibet.
3. Vietnam for greater Indian role in SE Asia
Delhi Dialogue IX:
- A platform for discussion between ASEAN and India.
- The Delhi Dialogue IX marks the beginning of the celebrations to mark the 25th anniversary of India-ASEAN diplomatic ties
- Vietnam on asked:
- India to play a greater role in ASEAN’s strategic and security affairs.
- India should support freedom of navigation in the South China Sea on the basis of international law and conventions.
India and ASEAN: India’s tie with ASEAN is at the centre of India’s Act East Policy.
4. North Korea claims it tested intercontinental missile
In news:
- North Korea claimed it successfully test-launched its first intercontinental ballistic missile
- North Korea’s Academy of Defence Science said the test of an ICBM the Hwasong-14 marked the “final step” in creating a “confident and powerful nuclear state that can strike anywhere on Earth.”
- Test a direct rebuke to U.S. President Donald Trump’s earlier declaration that such a test “won’t happen!”
Capability:
- A U.S. scientist examining the height and distance said the missile could potentially be powerful enough to reach Alaska.
1. Tap GST for jobs data: PM-appointed panel
Task force led by NITI Aayog vice chairman Arvind Panagariya recommends:
- The task force to improve India’s data on jobs was set up by Prime Minister Narendra Modi
- The Centre could use lakhs of firms registered under the new Goods and Services Tax (GST) as the sample frame to capture employment data through a new Annual Survey of Enterprises.
- The traditional Employment-Unemployment Surveys carried out by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) every five years must be scrapped.
New definition of formal employment:
- The task force has called for a fresh definition of formal employment to include any person who gets a Form 16 reflecting income tax deductions at source.
- Workers covered under any one of the The Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 or EPF and miscellaneous Provision Act 1952, government and other public sector employees, workers having coverage under private insurance or pension schemes of PFs,” be considered formal workers
Labour force survey
- A new periodic labour force survey (the first one has already begun this April) will be conducted annually to provide estimates of labour force, employment, unemployment, nature of employment and industry.
- To get more frequent employment trends data, an urban module of this survey will be updated every quarter.
Category: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1. Drug-resistant TB higher among children than expected: report
In news:
- Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) TB is higher among children than expected.
- This trend has been described as a “worrying trend” by the Union Health Ministry.
Who conducted the tests?
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) conducted the tests in collaboration with the Central TB Division under the Revised National TB Control Programme (RNTCP).
Key fact:
- Detection of tuberculosis (TB) in children remains a challenge.
- 5,500 of over 76,000 children tested in nine cities have been diagnosed with TB.
- Nine per cent of these paediatric TB cases have been diagnosed to have MDR TB
Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND)
- FIND initially started a unique initiative for diagnosing paediatric TB in four cities of Delhi, Chennai, Hyderabad and Kolkata from April 2014 with funding from the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
- The aim of the project is to provide rapid access to quality TB diagnosis for all presumptive paediatric TB patients in the project intervention areas.
Challenges associated with paediatric TB case detection
- Absence of appropriate samples coupled with decentralised capacity to get good samples from children to test for TB remains a challenge in paediatric TB case detection.
- Poor sensitivity of tests like the Acid fast bacilli (AFB) smear
- Children were more prone to primary MDR infection as they were in close contact with their parents and grandparents
Basic Information:
The Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND)
- The Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) is a global health non-profit based in Geneva, Switzerland. FIND functions as a product development partnership, engaging in active collaboration with over 150 partners to facilitate the development, evaluation, and implementation of diagnostic tests for poverty-related diseases. The organisation’s Geneva headquarters are in Campus Biotech. Country offices are located in New Delhi, India; Cape Town, South Africa; and Hanoi, Viet Nam.
- Priorities: The organization focuses on improving diagnosis in several disease areas, including hepatitis C, HIV, malaria, neglected tropical diseases (sleeping sickness, Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, buruli ulcer), and tuberculosis. Alongside this, FIND works on diagnostic connectivity, antimicrobial resistance, acute febrile illness, and outbreak preparedness.
GeneXpert MTB/RIF
The Xpert MTB/RIF is a cartridge based nucleic acid amplification test, automated diagnostic test that can identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) DNA and resistance to rifampicin (RIF) by nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT)
N A nucleic acid test (NAT) or nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) is a molecular technique used to detect a particular pathogen (virus or bacterium) in a specimen of blood or other tissue or body fluid. It does so by detecting and amplifying the RNA or DNA of the pathogen, that is, making extra copies of its nucleic acids.
Nothing here for Today!!!
Nothing here for Today!!!
Nothing here for Today!!!
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1:The Navegaon National Park is located in which state?
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
Question 2: The Supreme Court’s power to hear Inter-State Water Disputes can be
classified under its
- Original Jurisdiction
- Appellate Jurisdiction
- Writ Jurisdiction
- Advisory Jurisdiction
Question 3: What is/are the eligibility criteria’s that needs to be fulfilled, in order to
be the member of a G7 group?
- A very high net national wealth
- A very high Human Development Index
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
Question 4: The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority is a
- Statutory body
- Constitutional body
- Body set up as per executive order
- None of the above
Question 5: VAJRA (Visiting Advanced Joint Research) Faculty scheme is being implemented
by which agency?
- The Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB)
- Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
- Indian Institute of Science
- None of the above
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series


Comments