TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related Geography 1. ‘Recurving’ cyclones dried August rains B. GS2 Related Polity 1. BJP States tell police to push back Rohingya 2. Court suggests audit of NULM funds 3. How to make Indian courts more efficient 4. Provide relief in cases of unnatural jail death, SC tells Centre, States 5. Reservation charts on trains set to disappear 6. SC notice to Centre on plea to ban Blue Whale International Affairs/Bilateral Relations 1. ‘Gift from India’ sent in coordinated action 2. Three isn’t a crowd Health Issues 1. Under-five mortality rate highest in India: Report 2. India’s pharmaceutical research problem C. GS3 Related Economy 1. ‘Economy has to grow at 8-9% to get more people out of poverty’ 2. Centre plans to borrow for infra development 3. Exports climb 10.3% reversing 5-month slowdown 4. Rupee, gold widen current account gap 5. In a first, reserves hit $400 billion 6. External debt dips 2.7% to $471.9 bn as NRI deposits fall Internal Security and Defense 1. Indigenous artillery gun sets new record in range D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
1. ‘Recurving’ cyclones dried August rains
Context:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) had predicted normal monsoon rains in August.
- Re-curving of Western Pacific tropical cyclones may have played a role in reducing the August rainfall
In news:
- Reason for drying up if monsoon rains in August across India: A strange pattern of tropical cyclones (TC) noticed in the Western Pacific.
- Typically August will be the second most bountiful monsoon month after July.
- Process:
- Normal: During the monsoon months, cyclones in the Western Pacific move westwards towards India and aid rain-bearing systems over the sub-continent.
- Present scenario:
- But during some years they ‘recurve’, or start to swing north-east, and do not give as much of a push to the rains as they do in the good monsoon years.
- This re-curving frequently happens during the El Nino years but this time it inexplicably occurred when an El Nino hasn’t yet taken shape.
- What is El Nino? El Nino years are those when sea surface temperatures in the east equatorial Pacific rise, and often dampen the monsoon.
B. GS2 Related
1. BJP States tell police to push back Rohingya
Context:
- Rohingya’s issue.
- The union government has not yet taken any stance regarding the undocumented Rohingya refugees in India.
In news:
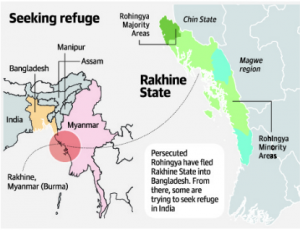
- BJP-led State governments in Assam and Manipur directed their police, especially in the border districts, to push back anyone who tries to cross the border.
- Key Fact:
- Assam shares a 262 km border with Bangladesh.
- Northeastern States — Manipur, Mizoram and Nagaland, are also front-line States.
- Intelligence inputs:
- Decision by state government based on Intelligence inputs from the center.
- What does the intelligence report say? terror groups could use the refugee crisis to sneak in their members and pose a security challenge to the country
2. Court suggests audit of NULM funds
In news:
- The SC has suggested an audit by the CAG of the funds disbursed under the National Urban Livelihood Mission (NULM) scheme
- The SC has questioned whether the money meant to build shelter homes for the urban homeless and poor across the country is was actually lying unspent or had been diverted for other purposes
- Questions posed by Supreme Court:
- The SC has asked, “How can Government ensure that the money is spent?”
- Court has said that the funds for NULM should not be diverted as the money has been given for a specific purpose
National Urban Livelihoods Mission
- National Urban Livelihoods Mission has be restructured and launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation (HUPA) which replaces earlier poverty alleviation programme for the urban poor titled Swarna Jayanti
- Shahari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY) The main reason is that urban poor have a strong desire to come out of their poverty and improve their quality of life which they are unable to do
- Social mobilization and strong institutional help are critical for them to come out ,they lack access to livelihood opportunities and capital
- It has also expanded the beneficiaries of urban poor to include the homeless and street vendors who are invariably ignored in government programmes
- A special provision has been made for the funding of all-weather 24/7 shelters with all essential facilities for the urban homeless. In addition, up to five per cent of the NULM budget has been earmarked to provide support to urban street vendors which will include skill upgradation and development of vendor markets.
3. How to make Indian courts more efficient
Context:
- Problem of ‘Pendency’ in Indian Judicial System
Clearing out of Long Pending Cases
- Lower courts in Kerala, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, and Chandigarh have disposed of almost all cases that had been pending for a decade or more
- Key Fact:
- A total of 11,000 cases pending for over 10 years in these four states and the Union territory of Chandigarh
- National pendency count is at around 2.3 million cases
- Delhi, Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka are also close to clearing out long-pending cases
Lessons to be learnt from lower Courts:
- The high court of Punjab and Haryana has jurisdiction over the lower courts of Punjab, Haryana and Chandigarh
- Case management system—i.e. a mechanism to monitor every case from filing to disposal, setup a decade ago.
- It also began to categorize writ petitions based on their urgency
- In addition, it set annual targets and action plans for judicial officers to dispose of old cases.
- And began a quarterly performance review to ensure that cases were not disposed of with undue haste
- All these measures ushered in a degree of transparency and accountability in the system, the results of which are now apparent
Judicial Case Management:
- In this system, the court sets a timetable for the case and the judge actively monitors progress
- This marks a fundamental shift in the management of cases—the responsibility for which moves from the litigants and their lawyers to the court
Law Commission of India’s Report suggestions :
- The Law Commission of India in its 230th report has also offered a long list of measures to deal with the pendency of cases
- These include
(1) Providing strict guidelines for the grant of adjournments
(2) Curtailing vacation time in the higher judiciary
(3) Reducing the time for oral arguments unless the case involves a complicated question of law
(4) And framing clear and decisive judgements to avoid further litigation
Way Forwards:
- The courts should also seriously consider incorporating technology into the system
- Digitizing courts records has been a good start in this context
- Just like automation powered by Artificial Intelligence is already helping doctors, it can also be leveraged to assist judges and lawyers
4. Provide relief in cases of unnatural jail death, SC tells Centre, States
Context:
- Unnatural Jail deaths.
- The judgment came on a letter addressed to the apex court in 2013 by its former Chief Justice R.C. Lahoti on the deplorable conditions of 1382 prisons across the country.
In news:
- Supreme Court directive:
- Directed the Chief Justices of all High Courts to suo motu register petitions to identify the kin of prisoners who died unnatural deaths from 2012 and order the States to award them compensation.
- This judgment is significant as the high court will now directly award compensation and ensure compliance by the States.
- For first time offenders: Appoint counselors and support persons for counselling prisoners.
- Extend family visits of prisoners and use phones and video-conferencing not only between a prisoner and family, but also his lawyers.
- Supreme Court quotes: Nelson Mandela Rules passed by the UN General Assembly says “merely because a person is in prison, it does not mean that he or she should be cut off from the outside world”.
- State Legal Services Authorities (SLSAs) to conduct a study and performance audit of prisons.
- Constitute a Board of Visitors which includes eminent members of society to initiate prison reforms.
- Encourage open prisons. Semi-open prison in Delhi are extremely successful.
- Key Facts:
- CAG in 2014: Hospital in Tihar Jail has a shortage of doctors and other medical staff ranging from 18% to 62%.
- NHRC monograph: From 2007–2011, prisoners’ suicides formed 71% of the total number of unnatural deaths.
- Present Scenario:
- The National and States Human Rights Commissions decide and award compensations in cases of custodial torture, deaths, etc.
- However, compliance by State governments is low as these commissions do not exercise any power of contempt.
- Besides, the States go for a long-drawn appeal in the high courts and later on in the Supreme Court, if necessary.
- Why from 2012? National Crimes Records Bureau has records of unnatural deaths from that year.
5. Reservation charts on trains set to disappear
In news:
- The Ministry of Railways has decided to discontinue pasting of reservation charts on reserved coaches of all trains originating from some railway stations on an experimental basis for three months.
- The stations are New Delhi, Hazrat Nizamuddin, Mumbai Central, Mumbai Chatrapati Shivaji Terminus, Chennai Central, Howrah and Sealdah.
- Why such a move?
- This follows a green initiative by South Western Railway’s Bengauru Division (SBC) that is saving about ₹60 lakh on papers.
- The measure is expected to save substantial money to the national exchequer.
6. SC notice to Centre on plea to ban Blue Whale
In news:
- The Supreme Court asked the government to respond to a petition for an immediate direction to ban online game ‘Blue Whale’.
- Blue Whale is suspected to be behind the deaths or attempted suicides of teenagers and young adults hooked to it.
- Petition filed by: advocate C.R. Jaya Sukin, representing another lawyer N.S. Ponnaiah, who wanted the government to take immediate steps to spread awareness about the dangers of playing the game and end its availability online.
Category: INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS
1. ‘Gift from India’ sent in coordinated action
In News:
- India dispatched one of the largest relief consignments to southeast Bangladesh for the refugees streaming in from violence-hit Myanmar.
- Family packs: Food grains, pulses, sugar, salt, cooking oil, tea, milk powder, biscuits and noodles were put together in jute bags, with ‘Gift from People of India’ stitched on it. Each small jute pack contains food grains, besides soaps and a mosquito net.
Context:
- India-Japan Special Strategic and Global partnership summit, and the highlights of the Joint statement between India and Japan
Concerns about China
- Even though the Doklam issue is resolved, it can happen again on the long unsettled border between the two countries, at a place and time of China’s choosing.
- Japan, which has its own troubles with China over territory, was the only country that openly articulated its support for India during those two troubled months
- Shinzo Abe recalled Japan’s own experience with China’s claims over the Senkaku (Diaoyu) islands as “very challenging”
- BRICS summit in Xiamen, China, where two Pakistan-based terror groups with animus toward India, Lashkar and Jaish, were named in the resolution
Highlights of the joint-statement:
- It calls for a “rules-based order” in the Indo-Pacific region where “sovereignty and international law are respected, and differences resolved through dialogue
- And all countries, large or small, enjoy freedom of navigation and overflight, sustainable development, and a free, fair and open trade and investment system
- It took a swipe at China’s OBOR initiative by calling for transparency in the development of connectivity and infrastructure development in the region
- It reaffirmed the India-Japan project to connect Africa and Asia
- The statement condemns North Korea, but for the first time, includes “the importance of holding accountable all parties” that helped that country develop its nuclear programme.
The defence and security co-operation
- Malabar joint exercise the most high-profile representation of this.
- A new chapter of co-operation in relations in all spheres, from terrorism, defence, the bullet train, infrastructure development to nuclear co-operation
1. Under-five mortality rate highest in India: Report
In News:
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 : In 2016, 9 million children under the age of five died in India — the highest globally
- National Family Health Survey-4:
- The under-five mortality rate in India stands at 50 per 1000 live births down from 74 in the 10 years between 2005-06 and 2015-16.
- It ranges from 78 in Uttar Pradesh to 7 in Kerala, one of the best states in the country when it comes to effective health systems.
- Globally, mortality rates have decreased across all age groups over the past five decades, with the largest improvements occurring among children younger than five years
- At the national level, heterogeneity remains in terms of both level and rate of changes in age-specific mortality; increases in mortality for certain age groups occurred in some locations.
- GBD 2016 has shown that, non communicable diseases constitute seven of the top ten causes of death in India. The leading cause of mortality was ischemic heart disease.
2. India’s pharmaceutical research problem
Context:
- Issues which are halting the progress of Pharmaceutical Sector in India
Biggest Challenge
- Lack of sufficient funding and inadequate allocations by the government
- At 0.83% of GDP, India is among the countries with the lowest investment in scientific research
An industry study of 2016
- It examined the extent to which public investment, IPRs and drug pricing policies in 56 countries actively contribute to or detract from innovation in global life-sciences.
- India ranked among the lowest (in the bottom five) due to weak IP protection, lack of data protection for biologics, low investment in R&D and price regulations
- All of these contribute to reduced revenue and therefore reduced future investment in biopharmaceuticals
Investment Attractiveness:
- India ranked No.19 in this 28-nation survey
- Five metrics were used to determine these rankings
(1) scientific capabilities and infrastructure
(2) clinical research conditions and framework
(3) regulatory system
(4) market access and financing
(5) effective intellectual property protections
- India scored low on almost all metrics except for partial step-ups on scientific capabilities and infrastructure, and clinical research conditions and framework
Chances ahead:
- Rising cardiovascular problems and other chronic diseases, make India a strong candidate to become a future powerhouse of R&D and manufacturing in pharmaceuticals
- In addition, clean water, rising incomes and better health infrastructure for the nation are contributing to an ageing population
- This population will cause a greater demand for different types of pharmaceutical drugs
Low R&D investment:
- The R&D investment as a percentage of sales has been rising for several years and now stands at 6% for some Indian companies
- But it is still well short of the 20% typical of Western pharma companies
- Moreover, innovation in chronic diseases and rare diseases has not yet taken off
Issues with Indian Education System
- The education system is to blame as well, imparting theoretical knowledge with no emphasis on product development and application of theory
- This leads to the deterioration of the knack(capability) for problem-solving and innovation
- Those who manage to keep their enthusiasm alive for research have to deal with the lack of facilities or face delayed funding issues
- Educational and academic institutions should be encouraged to participate in research programmes with funding from both the government as well as the private sector
Need of the hour:
- Four pillars for strengthening the innovation environment in the biopharmaceutical industry
(1) human resources
(2) finances
(3) infrastructure
(4) legal and regulatory framework
- Each of these pillars needs a concerted focus and a long-term commitment from industry as well as the government
- The environment to support the development of these verticals could emerge through our various government-led initiatives such as Skill India, Make in India, Atal Innovation Mission, etc.
Way Forward:
- In order to support consistent innovation, investment has to increase substantially before any tangible outcomes can be envisioned
- A strong patent system and robust IPRs environment is required to encourage research and to enable foreign pharma companies to bring new products to the market
- Without the requisite investment and enabling policy environment, patients in India will continue to suffer due to lack of access to cutting-edge medicines and new diagnostics
C. GS3 Related
1. ‘Economy has to grow at 8-9% to get more people out of poverty’
In news:
- Rangarajan, former chairman, Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council and former Governor, Reserve Bank of India in his speech at the International Conference on Finance and Economics organised by Loyola Institute of Business Administration on the topic ‘Current Trends in Finance and Economics highlights:
- If economy can grow up to 8-9% for a decade or so, the number of people below the poverty line will come down.
- The vulnerable and poor do need to be given special treatment, we need two-fold approaches: letting the economy grow fast and directly addressing the problems of the poor.
- The rural employment guarantee scheme, extension of food security were all done when the economy was strong.
- A policy intervention is needed to divert the surpluses that are generated to development.
- Growth cannot be sustained for a long time unless the population is healthy and educated. For sustained development, you need an educated population
- The challenges ahead is to maintain a tolerable level of inflation
2. Centre plans to borrow for infra development
In news:
- The Urban Affairs Ministry is planning to go for market borrowings to incentivise good performance by the States.
- This move is a bid to break the vicious cycle of low performance leading to low budgetary allocation.
3. Exports climb 10.3% reversing 5-month slowdown
In news:
- India’s merchandise exports grew 10.3% year-on-year to $23.8 billion in August, reversing a declining trend witnessed for five straight months.
- Data released by Commerce Ministry
- The jump in shipments was driven mainly by engineering goods, petroleum products and chemicals as well as an improvement in demand in overseas markets.
4. Rupee, gold widen current account gap
In news:
- April-June period: Current account deficit (CAD) widened to $14.3 billion, 2.4% of GDP.
- In the year earlier period, the CAD was $0.4 billion, which was 0.1% of GDP.
- Reasons:
- Stronger Rupee, one of the best-performing Asian currencies in 2017 encouraged imports and
- Gold imports prior to the introduction of GST.
- Data released by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The widening of the CAD on a year-on-year basis was primarily on account of a higher trade deficit ($41.2 billion) brought about by a larger increase in merchandise imports relative to exports.
What is a ‘Current Account Deficit’?
- Current account deficit is a measurement of a country’s trade where the value of the goods and services it imports exceeds the value of the goods and services it exports.
- The current account also includes net income, such as interest and dividends, as well as transfers, such as foreign aid, though these components make up only a small percentage of the current account when compared to exports and imports.
- The current account is essentially a calculation of a country’s foreign transactions and, along with the capital account, is a component of a country’s balance of payment
5. In a first, reserves hit $400 billion
In news:
- The country’s foreign exchange reserves have touched $400 billion for the first time.
- Usage of reserve: The reserves act as a buffer to be used in challenging times (assets to boost the import cover).
FOREX:
- Definition: Forex reserves are foreign currency assets held by the central banks of countries.
- Description: These assets include foreign marketable securities, monetary gold, special drawing rights (SDRs) and reserve position in the IMF. The main purpose of holding foreign exchange reserves is to make international payments and hedge against exchange rate risks.
6. External debt dips 2.7% to $471.9 bn as NRI deposits fall
Key Stats:
- India’s total external debt for the financial year 2016-17 stood at $471.9 billion, declining 2.7% from the previous year’s level.
- The decline in external debt was due to the decrease in long-term debt particularly NRI deposits and commercial borrowings.
- International Debt Statistics 2017’: An inter-country comparison by the World Bank, , which presents the debt data for 2015, shows that India continues to be among the less vulnerable countries with its external debt indicators comparing well with other indebted developing countries
Category: INTERNAL SECURITY AND DEFENSE
1. Indigenous artillery gun sets new record in range
In news:
- Setting up World record: The advanced towed artillery gun system (ATAGS) has set a world record in range by hitting targets at a distance of 48 km
- ATAGS is being jointly developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation and the private sector
- During trial firings, ATAGS registered the longest ever distance of 48.074 km, surpassing the maximum ranges of 35-40 km fired by any artillery gun system in this category
Development of the Gun
- The development is being done through a consortium based model
- It was designed by DRDO’s Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE)
- In addition, Bharat Forge Limited of Kalyani Group, Tata Power Strategic Engineering Division and Mahindra Defence Naval System are involved in a big way, along with the Ordnance Factory Board
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. PRELIMS FACT
Astra missile: Indigenously developed beyond visual range air to air missile, successfully completed developmental trails over the Bay of Bengal.
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Over the last decade, the country that is the World’s largest receiver
of remittances is
- USA
- India
- Russia
- Canada
See
Question 2. The Indian constitution prohibits discrimination between individuals on the
basis of
- Gender and caste only
- Gender, caste, religion, race and place of birth
- Gender, education, caste and place of birth
- Caste, education, religion and race only
See
Question 3. Under the SMARTGRAM initiative of Rashtrapati (President)
Bhavan, what is considered as a ‘smart gram (village)’?
- A village that is on the transition to become a municipal area
- A village where a majority of the population is digitally literate
- A village having required physical and social infrastructure governed with a layer of smart information and communication systems
- A village that is close to sub-urban areas of smart cities
See
Question 4. The National Mission on Cultural Mapping of India intends to
- Create repository of information about cultural assets.
- Launch massive cultural awareness campaigns.
- Open a direct channel of communication of artists with the Government.
- Hold talent hunt competitions from Block level to National level.
Select the correct answer using the codes below.
- 1 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Question 5. Consider the following about The Energy Resources Institute (TERI).
- It is a non-profit policy research organisation.
- It is an attached agency of the International Centre for Climate Governance (ICCG).
Which of the above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- None
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
GS Paper I
-
“Merely because a person is in prison, it does not mean that he or she should be cut off from the outside world”. Evaluate.
GS Paper II
-
Discuss the major irritant in Indo-China relations and highlight the latest move to overcome these.
GS Paper III
-
Adaptation of PPP model for infrastructure development of the country has not been free from criticism. Critically discuss the pros and cons of the model.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series

Comments