TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related GEOGRAPHY 1. 500 homeless in Bengal as Ganga swallows land B. GS2 Related POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. HC notice to Centre on OCIs entry into India 2. App for children to check cybercrimes: NCPCR 3. Publishing poll candidate’s propaganda is paid news 4. WhatsApp appoints grievance officer C. GS3 Related ECONOMY: HEALTH 1. PM launches Ayushman Bharat 2. States told to arm PHCs in fight against TB ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY 1. Study for solution to Ennore estuary sedimentation begins 2. Citizen science initiative helps save hornbills ECONOMY 1. Law tribunal directs insolvency proceedings against city builder 2. Full-service carriers face crosswinds from budget airlines DEFENCE 1. India looks to buy Israeli missiles D. GS4 Related E. Editorials ECONOMY 1. The primary anchor of a health-care road map POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. Governor’s discretion F. Tidbits H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
1. 500 homeless in Bengal as Ganga swallows land
Note to Students:
This particular news update deals with the Farakka Barrage and the issue of river bank erosion by the Ganges.
The News
- Due to severe river bank erosion by the Ganges, nearly 500 people have become homeless in the Hossainpur area of Murshidabad district.
- Over the past few days, the Ganga has swallowed large masses of land in the area.
Analysis:
This particular situation has generated severe discontent among the locals against
- the district administration and
- the Farakka Barrage Project authorities.
The local population has alleged that the project authorities “ignored” their warnings regarding the erosion.
A Note on the Farakka Barrage Project (FBP)

- The main objective of the Farakka Barrage Project complex is to divert adequate quantity of Ganga waters to Bhagirathi-Hoogly river system through 38.38 km long feeder canal for preservation and maintenance of Kolkata Port by improving the regime and navigability of the Bhagirathi-Hoogly river system.
- The increased upland supply from Ganga at Farakka into Bhagirathi reduces salinity and ensures sweet water supply to Kolkata and surrounding areas.
- The rail-cum-road bridge built across the river Ganga at Farakka establishes direct road and rail communication link to the North-Eastern Region with rest of the country.
B. GS2 Related
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. HC notice to Centre on OCIs entry into India
Note to Students:
The larger issue which students would need to read about would be that of citizenship. Students are advised to go through this chapter. BYJUs Tablet students can refer the chapter covered on citizenship.
The News:
- The Delhi High Court has directed the Centre to ensure that Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) card holders or foreigners are informed in advance if they are blacklisted and would be denied entry into the country.
Analysis:
- Recently, there have been a number of cases which have been filed in the High Court on account foreigners or OCI card holders not being permitted entry into India when they arrive here.
- Unfortunately, a common feature in each of them was that none of them had any prior intimation that they were blacklisted, despite having a valid visa.
Concluding Remarks:
- The High Court directed the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) to ensure that necessary directions are issued to all the officers, who are authorised to issue blacklisting orders.
- They are now to inform the foreigners/OCI card holders concerned that they have been blacklisted and their entry into the country would be denied.
2. App for children to check cybercrimes: NCPCR
The News:
- In a recent development, the government has launched the ‘cyber trivia’ app for children.
- This initiative has been taken up by the Government to counter incidents of cyber-crimes against children due to dangerous games like ‘Blue Whale’ and ‘Momo Challenge’.
A Note on the App
- This App will have multiple choice questions and children will be rewarded points based on their answers.
- This App is an attempt to teach these children in a fun way what should be done if they are contacted by a stranger on the Internet.
3. Publishing poll candidate’s propaganda is paid news
Note to Students:
This topic in the news relates to different chapters from the pages of Indian Polity. They include: a) the judiciary b) Elections c) Fundamental Rights (Part III) of the Indian Constitution.
The News:
- The Election Commission of India has told the Supreme Court that repeated publication of propaganda, lauding the achievements of a candidate in an election is nothing but “paid news”.
- The EC draws a distinction between “motivated propaganda” and the fundamental right to free speech. The EC adds that politicians cannot say that it is part of their fundamental right to free speech to spew out “motivated propaganda”.
- The EC has asked the Supreme Court court to declare whether it amounts to “paid news” if widely circulated daily newspapers cover statements issued by, and in the name of, a candidate that are
a) not only laudatory of his or her record and achievements but also are
b) a direct appeal to voters by the candidate.
Analysis
- It is important to note that if such motivated propaganda is allowed in the garb of free speech during the election period then there would be some serious consequences.
- For example, candidates with a strong network of connections and undefined relationships will exploit their sphere of influence in society, and as a consequence, will have the unequal advantage of encashing such silent services.
4. WhatsApp appoints grievance officer
Larger Background:
- In a recent development the Government of India said that the messaging platform will need to set up a local entity and find a tech solution to trace the origin of fake messages on its platform.
- Union minister of information technology Ravi Shankar Prasad, after meeting WhatsApp head Chris Daniels, said the Facebook-owned messaging application has contributed significantly to India’s digital story but it needs to find solutions to deal with “sinister developments” like mob lynching and revenge porn.
- Daniels’s visit to India and his meeting with Prasad follows more than a dozen killings across India this year in mob lynchings fuelled by rumours circulating on WhatsApp.
The News:
- In an attempt to clamp down on fake messages, WhatsApp has appointed a grievance officer for India and has detailed out the process for users to flag concerns and complaints, including those around fake news.
- Meeting one of the key demands that India had put forward to WhatsApp to curb fake messages that triggered mob killings, WhatsApp has updated its website to reflect the appointment of a grievance officer for India.
- This update mentions that users can seek help through the mobile app, send an e-mail or write to Komal Lahiri, who is based in the U.S.
C. GS3 Related
1. PM launches Ayushman Bharat
Note to Students:
Government Initiatives would come under the larger domain of Polity and Governance which is a GS Paper II topic. However, as this particular scheme pertains to Healthcare, it would come under the domain of GS Paper III.
It is important to relate this article to the concept of Universal Health Coverage.
Larger Background:
- The poor condition of healthcare in the country is not a secret, especially in India’s villages where infrastructure is in a dilapidated state. Government hospitals often fail to provide necessary health services to the poor, with private hospitals being out of the reach of most people. The country’s growing population and lack of resources has made matters worse. According to the 2011 census, India’s population is over 1.2 Billion, make it the second most populous nation in the world after, China.
- Many organizations, including the United Nations have estimated that by 2025, India would be the most populated nation in the world, surpassing China.
- More than 32% of total deaths in India are due to heart-related ailments. According to the Global Burden of Disease study, India is ranked low in the Healthcare index; India stands at a rank of 154. This index is out of 194 countries. But despite this, the budget allotment on healthcare services is extremely low.
- India spends less than 2% of her GDP on public healthcare. But now the Government is working on improving public healthcare services. The National Health Protection Mission or Ayushman Bharat Yojana, launched by the Government is the first major step in this direction. Ayushman Bharat Yojana is a program which aims to create a healthy, capable and content new India. It will also focus on the poor and weaker sections of the society. It aims to provide insurance of upto 5 lakh rupees to each family. The new scheme also intends to improve secondary and tertiary healthcare services for crores of Indians.
There are two flagship initiatives under Ayushman Bharat:
- The first is to create a network of health and wellness centres that will bring the healthcare system closer to the people. The centres will provide comprehensive healthcare, including treatment for non-communicable diseases and maternal and child health services. Besides this, they will also provide free essential drugs and diagnostic services; also Rs. 1200 crore have been allocated for this flagship programme. The scheme will cover more than 10 crore poor families, which is approximately 50 crore persons. It will also setup wellness centres which will give poor people OPD facility near their homes.
- The second flagship programme under ‘Ayushman Bharat’ is the ‘National Health Protection Scheme’. The National Health Protection Scheme will cover over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families. It will provide coverage up to 5 lakh rupees per family, per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
The News:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the healthcare scheme, Ayushman Bharat, also known as the Pradhan Mantri-Jan Aarogya Yojana (PM-JAY), from Ranchi on the 23rd of September, 2018.
- He further declared that the scheme would be a “game changer” globally in health insurance.
2. States told to arm PHCs in fight against TB
Note to Students:
Government Initiatives would come under the larger domain of Polity and Governance which is a GS Paper II topic. However, as this particular scheme pertains to Healthcare, it would come under the domain of GS Paper III.
Larger Background:
- The Union Government had earlier set an ambitious target to eradicate tuberculosis (TB) by 2025.
- This is an effort five years ahead of the target fixed by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- Pursuant to this, the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has directed all States to expand TB diagnostics services to all primary health centres (PHCs).
A Note on the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme:
- The Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program is the state-run tuberculosis control initiative of the Government of India.
- Under the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP), Government is committed to end tuberculosis by 2025.
- The strategies adopted for this purpose include:
- strengthening and improving quality of basic TB services,
- addressing TB HIV co-infection, other co-morbidities and MDR-TB.
- Further, targeted interventions in the vulnerable population, integrating newer molecular diagnostics for TB in the health system for early diagnosis of TB, Information Communication Technology (ICT), Enhanced Private Sector Engagement, Nikshay and E Nikshay etc. have also been leveraged as part of the strategies under RNTCP.
TB diagnosis:
- Currently, TB diagnosis under the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP) is done primarily using sputum smear microscopy.
- This is done in more than 14,000 Designated Microscopy Centres (DMCs) spread across the country.
The Problem:
- It is important to note that while at least 25,650 Primary Health Centres (PHCs) have been established in the country (as on March 31, 2017), most don’t offer the service of sputum smear microscopy.
- The samples from such Primary Health Centres (PHCs) are sent to the nearest facility that has a DMC. Because of this, there might be a significant loss of presumptive TB cases.
- It is believed that establishing microscopy centres will prevent sample loss owing to lack of referral links for sputum examination. As a consequence, this would lead to improved case detection.
- Further compounding India’s burdens, India has an estimated 27 lakh TB patients, of which only 13 lakh have been captured in government data.
- According to the Global TB Report of 2017, the estimated incidence of TB in India is 28 lakh. This amounts to about a quarter of the world’s TB cases.
Concluding Remarks:
- All States have been directed to map the non-DMC PHCs and designate all PHCs, including those in urban areas, as microscopy centres.
- In PHCs where a laboratory technician is already available, microscopes should be provided and, if required, the technician trained.
- In PHCs that do not have laboratory technicians, recruitment should be urgently carried out, and microscopes and training provided subsequently.
Category: ENVIRONMENT AND ECOLOGY
1. Study for solution to Ennore estuary sedimentation begins
Context
- Sand deposits have been clogging the Ennore estuary for some time now.
- This has become a major environmental concern.
- Pursuant to this development, the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) has initiated a survey.
- The objective of this survey is to find remedial measures that would ensure smooth fresh water exchange with sea.
- The Water Resources Department (WRD) manages the Ennore estuary.
- The Water Resources Department (WRD) has sought the NIOT’s assistance for a technical study on ways to minimise siltation and have the mouth open for free flow of water throughout the year.
The Threat
- The are various threats which one needs to be cognisant about. For example:
- Prolonged clogging of the estuary:
- This happens due to sand depositions. This makes the surrounding areas vulnerable to flooding during the monsoon season.
- This also affects the livelihood of fishermen. These fishermen have only limited access to the sea because of siltation. It is important to note that the Ennore estuary must be free of siltation for a length of a minimum of 200 m.
In conclusion, working towards providing a permanent solution to the issue, the team from NIOT has started a bathymetric survey that would mea

sure the depth of the sea and estuary and water level in estuary.
What is a Bathymetric survey?
Bathymetric surveys allow us to measure the depth of a water body as well as map the underwater features of a water body.
2. Citizen science initiative helps save hornbills
Context
- A recent citizen science initiative of documenting Indian hornbills is providing valuable inputs for the conservation of this unique bird.
What is this initiative?
- The Hornbill Watch initiative (www.hornbills.in) is an interactive web interface that allows a person to report on hornbills anywhere in India. People can record the observation of a live hornbill, note its call or report a dead, hunted or captive bird.
How will this data help?
- The data on the presence of hornbills outside protected areas would be crucial in identifying and protecting their habitats from possible threats and development projects.
Species Distribution in India
- There are nine hornbill species in India.
- States from where the most sightings were recorded are Karnataka, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Hornbills were reported from across 70 protected areas in the country. While 41% of the observations were made within protected areas, 59% were made outside.
Some Important Hornbills:
- The endangered Narcondam hornbill is restricted to an area of 6 sq.km. of the Narcondam Island in the Andamans.
- The rufous-necked hornbill is a vulnerable or near threatened species.
- Further, the Austen’s brown hornbill and the great hornbill were observed in several States in northeastern India.
- Other important species of hornbill include the oriental pied hornbill and the Indian grey hornbill.
1. Law tribunal directs insolvency proceedings against city builder
Background
- A case was filed by a group of flat owners against Green Peace Construction Private Limited.
- Following this, the Chennai Bench of National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) has directed commencement of insolvency proceedings against Green Peace Construction Private Limited.
The Issue:
- In its petition, members of Ajanta Flat Owners Association had claimed non-payment of outstanding dues of Rs.1.15 crore, in addition to an interest of about Rs. 31 lakh by the builder.
- The members represented themselves as operational creditor of the company.
- In the year 2010, the members of the Ajanta Flat Owners Association had entered into joint development agreement with the firm for construction of 54 flats.
- This joint development agreement included a clause that if any structural defect is found in the building within 18 months of possession, the developer has to fix it without any monetary liability on the part of house owners.
- The Association also claimed that the builder failed to complete substantial work relating to other facilities including provision for two gensets, lift, external paintings, provision of the reticulated gas connection and gym equipment, among others.
- Despite repeated reminders and assurances, the work was not completed and the owners took upon themselves to finish the work.
- They allege that the builder agreed to pay for it but failed to do so.
Note to Students:
From a UPSC point of view, students must be aware of the larger issue concerning insolvency. We at BYJUs have recorded a YouTube video on the same which one can use as a reference.
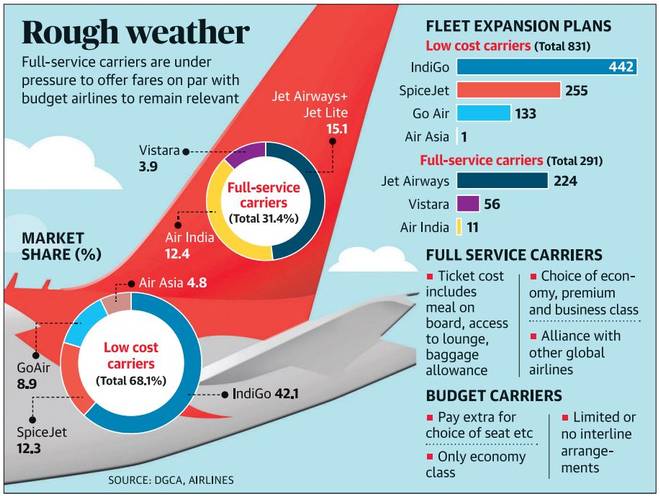
2. Full-service carriers face crosswinds from budget airlines
Note to Students: This news update underscores the need for aspirants to study the issue of profitability of full-service carriers. There has been a lot of debate in the recent months regarding this issue.
Analysis:
- The domestic aviation market in India is highly competitive.
- This is a market where passenger is the king and airlines attempt at attracting them with the lowest ticket prices.
- However, full-service carriers (FSCs) which seek to stand out with the promise of higher level of services and global connectivity are increasingly under pressure.
- They are under pressure to cut costs and offer fares on par with the budget airlines for travel within the country to remain relevant.
Recent Developments
- Recently, Jet Airways decided to do away with the complimentary meal on-board.
- For certain fare categories on domestic routes, this complimentary meal on-board is the single-most distinguishing feature for a full service carrier in the country.
- In August 2018, Vistara, which is the only full-service domestic carrier in the world, had done the same by introducing a basket of fare options where one can pay extra for additional services such as meal on-board, additional baggage allowance, seat selection as well as free rescheduling and cancellation.
The threat of low-cost carriers (LCCs)
- Low-cost carriers (LCCs) offer competitive airfares.
- They have new and modern planes, an aggressive fleet expansion plan, wider domestic network with higher frequencies and often better punctuality.
- Low-cost carriers (LCCs) have ensured decline in domestic market share of full-service carriers to close to 30%.
- Aviation industry experts believe that unlike low-cost carriers in other countries which offer bare-bone facilities to their passengers, better services by low-cost carriers in India mean there is very little difference between them and full-service carriers.
1. India looks to buy Israeli missiles
Note to Students:
- This topic in the news relates to both GS Paper II and GS Paper III. It is relevant from a GS Paper II point of view as some of these points can be used in an answer while elaborating on the nature of the bilateral relationship between India and Israel.
- It is relevant from a GS Paper III point of view as it deals with the acquisition of defence technology.
The News:
- Recently, a deal has been brought before the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) for approval.
- This deal is essentially about the procurement of the Spike anti-tank guided missiles from Israel through the government-to-government route.
- However, some validation trials have to be held before the deal is signed.
- These validation trials pertain to that of the infrared seeker (IR).
- The validation trials would be held once the DAC accords approval.
- Currently, the Indian Army is faced with a huge shortage of anti-tank guided missiles.
A Note on the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC):
Objective:
- The objective of the Defence Acquisition Council is to ensure expeditious procurement of the approved requirements of the Armed Forces in terms of capabilities sought and time frame prescribed by optimally utilizing the allocated budgetary resources.
Composition:
The composition of the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) is as follows:
- Defence Minister: Chairman
- Minister of State for Defence: Member
- Chief of Army Staff: Member
- Chief of Naval Staff: Member
- Chief of Air Staff: Member
- Defence Secretary: Member
- Secretary Defence Research & Development: Member
- Secretary Defence Production: Member
- Chief of Integrated Staff Committees HQ IDS: Member
- Director General (Acquisition): Member
- Dy. Chief of Integrated Defence: Staff Member Secretary
Functions:
The functions of the DAC include:
- in-principle approval of 15 Year Long-Term Integrated Perspective Plan for Defence Forces;
- accord of Acceptance of Necessity to acquisition proposals;
- categorization of the acquisition proposals relating to ‘Buy’, ‘Buy & Make’ and ‘Make’;
- issues relating to Single vendor clearance;
- decision regarding ‘offset’ provisions in respect of acquisition proposals above Rs. 300 crores;
- decisions regarding Transfer of Technology under the ‘Buy & Make’ category of acquisition proposals; and
- Field Trial evaluation.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
1. The primary anchor of a health-care road map
Note to Students: It is important to relate this article to the concept of Universal Health Coverage. Pursuant to this, we have taken the liberty towards giving a broader context to the larger issue which needs to be understood by students.
Larger Background:
- The poor condition of healthcare in the country is not a secret, especially in India’s villages where infrastructure is in a dilapidated state. Government hospitals often fail to provide necessary health services to the poor, with private hospitals being out of the reach of most people. The country’s growing population and lack of resources has made matters worse. According to the 2011 census, India’s population is over 1.2 Billion, make it the second most populous nation in the world after, China.
- Many organizations, including the United Nations have estimated that by 2025, India would be the most populated nation in the world, surpassing China.
- More than 32% of total deaths in India are due to heart-related ailments. According to the Global Burden of Disease study, India is ranked low in the Healthcare index; India stands at a rank of 154. This index is out of 194 countries. But despite this, the budget allotment on healthcare services is extremely low.
- India spends less than 2% of her GDP on public healthcare. But now the Government is working on improving public healthcare services. The National Health Protection Mission or Ayushman Bharat Yojana, launched by the Government is the first major step in this direction. Ayushman Bharat Yojana is a program which aims to create a healthy, capable and content new India. It will also focus on the poor and weaker sections of the society. It aims to provide insurance of upto 5 lakh rupees to each family. The new scheme also intends to improve secondary and tertiary healthcare services for crores of Indians.
There are two flagship initiatives under Ayushman Bharat:
- The first is to create a network of health and wellness centres that will bring the healthcare system closer to the people. The centres will provide comprehensive healthcare, including treatment for non-communicable diseases and maternal and child health services. Besides this, they will also provide free essential drugs and diagnostic services; also Rs. 1200 crore have been allocated for this flagship programme.
The scheme will cover more than 10 crore poor families, which is approximately 50 crore persons. It will also setup wellness centres which will give poor people OPD facility near their homes.
- The second flagship programme under ‘Ayushman Bharat’ is the ‘National Health Protection Scheme’. The National Health Protection Scheme will cover over 10 crore poor and vulnerable families. It will provide coverage up to 5 lakh rupees per family, per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
Analysis:
- Universal health coverage is getting prioritised as a part of political reform with the launch of two pillars.
The pillars are the
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY): Ayushman Bharat (AB)
Under this scheme, 1.5 lakh health sub-centres are being converted into health and wellness centres. - The National Health Protection Mission (NHPM)
This aims to provide health cover of Rs. 5 lakh per family, per annum, reaching out to 500 million people.
- It is important to note that the “best health care at the lowest possible cost” should be: a) inclusive
- make health-care providers accountable for cost and quality
- achieve a reduction in disease burden, and
- eliminate catastrophic health expenditures for the consumer.
A Critical Analysis:
- Currently, the NHPM is pushing for hospitalisation at secondary, and at tertiary-level private hospitals, while disregarding the need for eligible households to first access primary care, prior to becoming ‘a case for acute care’.
- Thus, we are in danger of placing the cart (higher-level care) before the horse (primary care).
- It is important to note that without the stepping stone of primary health care, direct hospitalisation is a high-cost solution.
- Recently, the Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare, J.P. Nadda, said that while the PMJAY would help improve availability, accessibility, and affordability for the needy 40% of the population, the Prime Minister was looking for one additional requirement.
- This requirement is that the PMJAY must continue to maintain credibility.
Problem of constraints:
- Public sector health capacities are constrained at all levels.
- Further, forward movement is feasible only through partnerships and coalitions with private sector providers.
- It is important to note that these partnerships are credible only if made accountable.
- It has been suggested that Health-care providers (public/private) should be accredited without any upper limit on the number of service providers in a given district.
Further, the annual premium for each beneficiary would be paid to those service providers, for up to one year only (renewable), as selected by beneficiaries.
- It is believed that the resultant competition would enhance quality and keep costs in check.
- Further, upgrading district hospitals to government medical colleges and teaching hospitals will enhance capacities at the district level.
- Service providers will become accountable for cost and quality if they are bound to the nuts and bolts of good governance.
A look at primary care:
Experts believe that the elimination of health expenditures for the consumer can come about only if there is sustained effort to modernise and transform the primary care space.
It is believed that one must bring together all relevant inter-sectoral action, linking health and development, so as to universalise the availability of:
- clean drinking water,
- sanitation,
- garbage disposal,
- waste management,
- food security,
- nutrition and
- vector control.
Further, the Swachh Bharat programme must be incorporated in the PMJAY. These steps put together will reduce the disease burden.
The Way Forward
- It is believed that at the 1.5 lakh health and wellness clinics, one must register households to provide them access to district-specific, evidence-based, integrated packages of community, primary preventive and promotive health care.
- Further, a public education media campaign could highlight the merits of personal hygiene and healthy living.
- The States of Kerala and Tamil Nadu have demonstrated that high-performing, primary health-care systems do address a majority of community/individual health needs.
- The health and wellness clinics must connect with early detection and treatment.
- It is believed that robust delivery of preventive, clinical and diagnostic health-care services will result in early detection of cancers, diabetes and chronic conditions, mostly needing long-term treatment and home care.
- This would further minimise the demand for hospitalisation.
- In conclusion, investment in primary care would very quickly reduce the overall cost of health care for the state and for the consumer. Technology and innovation are further reducing costs. AI-powered mobile applications will soon provide high-quality, low-cost, patient-centric, smart wellness solutions. Currently, the scaleable and inter-operable IT platform being readied for the Ayushman Bharat is encouraging. Finally, as we integrate prevention, detection and treatment of ill-health, the PMJAY will win the hearts of people.
But this is only if we receive a well-governed ‘Health for All’ scheme.
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
Note to the Students:
This issue is important as it re-looks a the whole issue surrounding The discretionary powers of the Governor. The issue surrounding the discretionary powers of the Governor have been in the news for quite some time now.
The News:
- Currently, the discretionary powers of the Governor are once again at the centre of controversy. This assumes importance based on the recent decision on the remission of seven convicts in the Rajiv Gandhi assassination case.
Analysis:
- It is important to note that Article 161 of the Constitution provides the Governor with the power to “remit or commute the sentence of any prisoner”.
- However, the Governor’s decision will be subject to judicial review by the constitutional courts.
- Currently, the immediate question is whether there is an independent, discretionary power vested with the Governor with regard to Articles 161 and 163 of the Constitution.
Prior Precedents:
- In the Nabam Rebia and Bamang Felix v. Deputy Speaker (2016) case, the Supreme Court, speaking through a five-judge Bench, viewed that the discretionary power of the Governor is extremely limited and entirely amenable to judicial review.
- As a matter of fact, time and again, the courts have spoken out against the Governor acting in the capacity of an “all-pervading super-constitutional authority”.
- Pertaining to the exercise of discretion, in Samsher Singh v. State of Punjab (1974), a seven-judge Bench of the Supreme Court had held that the Governor may do so only “in harmony with his Council of Ministers”.
- In an effort to do so, the Governor is prevented from taking a stand against the wishes of the Council of Ministers.
Concluding Remarks:
- Currently, the domain being traversed in this case is alien to the Constitution of India, not having envisaged a situation where the Governor exercises his power under Article 161 against the express recommendation of the Council of Ministers.
- As a matter of fact, such a decision may drastically alter the Constitution and its founding principles such as
a) the federal structure,
b) Cabinet responsibility and
c) accountable governance.
- This might also be interpreted as the Governor having lost faith in the State government with regard to the performance of its executive functions.
- Either which way, it is believed that to stay true to the spirit of the Constitution, the Governor should desist from conferring discretionary powers to his office where there are none.
F. Tidbits
Nothing here for today!!!
G. Prelims Fact
Nothing here for today!!!
H. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. What happens during National Emergency?
-
State Governments are suspended.
-
Legislative power of the State Legislatures is suspended.
Options:
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
See
Question 2. Which of the following statement/s is/are incorrect with respect to the National
Human Rights Commission?
-
It is a statutory body established under the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993.
-
It can regulate its own procedure.
-
It has no powers to punish the violators of human rights.
Options:
- Only 1
- Only 1 and 3
- Only 2
- None of the above
See
Question 3. Consider the following statements in relation to Bhagat Singh:
-
He was the first secretary of Punjab Naujawan Bharat Sabha.
-
He was firmly opposed to colonialism.
-
He was a socialist with a secular outlook.
Which of the above statement/s is/are correct?
- i) and ii) only
- i) and iii) only
- ii) and iii) only
- All of the above
See
Question 4. Which of the following were a part of Sher Shah Suri’s administration?
-
Measurement of the sown land was done for revenue collection.
-
Shiqdar was in charge of the general administration of a Pargana.
-
Customs duty was imposed on the goods only at two places to promote trade and commerce.
Options:
- i) only
- i) and ii) only
- i) and iii) only
- All of the above
See
I. Practice Questions for UPSC Mains Exam
-
Discuss the issues related to public healthcare infrastructure in India. Suggest ways to address these challenges.
- Citizens play the most important role in realization of a successful and vibrant democracy. Discuss.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series

Comments