March 13th, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) 2. Cabinet approves scheme for “Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)” 3. Cabinet approves Minimum Support Price for Copra for 2020 season 4. Imparting new technologies to farmers through electronic media 5. Promoting use of bio pesticides and fertilizers 6. PM Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PM-KMY) 7. Formation of Farmer Produce Organizations 8. Implementation of PMFBY in States 9. Govt brings masks and hand sanitizers under the Essential Commodities Act 10. Wings India 2020 launched in Hyderabad 11. Foreign Investments and 'Make in India' Programme 12. Private Investment in Jammu and Kashmir 13. Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram 14. Average Life Expectancy 15. Organ Donation 16. Cancer Treatment 17. Ganga Aamantran Abhiyan 18. Amenities under Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan in Railways 19. Setting up of Railway Development Authority 20. Bhoomi Rashi portal 21. Groundwater affects Himalayan slip and climate as the mountains dance to its tune 22. Scientists pave way for potential new therapy for tongue cancer 23. New approach to speed up red blood cells generation in the lab 24. National Biopharma Mission 25. National Creche Scheme
1. South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
What’s in News?
The Prime Minister of India has called for SAARC nations to chalk out a strong strategy to fight Coronavirus.
SAARC
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation is an intergovernmental organization for the development of economic and regional integration.
Read more about SAARC.
2. Cabinet approves scheme for “Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP)”
What’s in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by Prime Minister, has given its approval for introducing the Scheme for Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP).
Details:
- Under the scheme, a mechanism would be created for reimbursement of taxes/ duties/ levies, at the central, state and local level, which are currently not being refunded under any other mechanism, but which are incurred in the process of manufacture and distribution of exported products.
- This scheme is going to give a boost to the domestic industry and Indian exports providing a level playing field for Indian producers in the International market so that domestic taxes/duties are not exported.
- Under the Scheme an inter-ministerial Committee will determine the rates and items for which the reimbursement of taxes and duties would be provided. In line with “Digital India”, refund under the Scheme, in the form of transferable duty credit/electronic scrip will be issued to the exporters, which will be maintained in an electronic ledger. The Scheme will be implemented with end to end digitization.
- The refunds under the RoDTEP scheme would be a step towards “zero-rating” of exports, along with refunds such as Drawback and IGST.
- This would lead to the cost competitiveness of exported products in international markets and better employment opportunities in export-oriented manufacturing industries.
Salient features:
- At present, GST taxes and import/customs duties for inputs required to manufacture exported products are either exempted or refunded.
- However, certain taxes/duties/levies are outside GST, and are not refunded for exports, such as, VAT on fuel used in transportation, Mandi tax, Duty on electricity used during manufacturing etc. These would be covered for reimbursement under the RoDTEP Scheme.
- The rebate would be claimed as a percentage of the Freight On Board (FOB) value of exports.
3. Cabinet approves Minimum Support Price for Copra for 2020 season
What’s in News?
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs, chaired by the Prime Minister has given its approval for the Minimum Support Prices (MSPs) for copra for 2020 season.
- The approval is based on recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- The increase in MSP for copra for 2020 season is in line with the principle of fixing the MSP at a level of at least 1.5 times the all India weighted average cost of production which was announced by the Government in the Budget 2018-19.
- It assures a minimum of 50% as a margin of profit as one of the important and progressive steps towards making possible doubling of farmers’ incomes by 2022.
- The National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Limited (NAFED) and National Cooperative Consumer Federation of India Limited (NCCF) will continue to act as Central Nodal Agencies to undertake price support operations at the MSP in the coconut growing states.
- India is number one in production and productivity of Copra in the World.
4. Imparting new technologies to farmers through electronic media
What’s in News?
Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare is taking various measures and initiatives in educating farmers through following use of electronic media:
- Kisan Suvidha mobile app facilitates the dissemination of information to farmers on critical parameters such as Weather; Market Prices; Plant Protection; Input Dealers (Seed, Pesticide, Fertilizer) Farm Machinery; Soil Health Card; Cold Storages & Godowns, Veterinary Centres and Diagnostic Labs.
- Crop related advisories are regularly sent to the registered farmers through SMSs on mKisan Portal.
- The Indian Council of Agriculture Research (ICAR) has compiled more than 100 mobile apps in the areas of crops, horticulture, veterinary, dairy, poultry, fisheries, natural resources management and integrated subjects.
- Awareness is being created among farmers through various electronic mass media mediums like DD Kisan Channel, Doordarshan, All India Radio etc.
- Apart from the above, Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube are being used to educate farmers, across the country.
The Government is implementing the following schemes aimed at imparting training to farmers in the agriculture and allied sectors:
- A Centrally Sponsored Scheme on ‘Support to State Extension Programmes for Extension Reforms’ popularly known as Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA) Scheme is under implementation. The extension activities under ATMA, inter-alia, include Farmers’ Training.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) with its network of Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) has mandate of technology assessment, demonstration and capacity development of farmers. KVKs are imparting training to farmers for getting higher agricultural production and income.
- Four Farm Machinery Training & Testing Institutes (FMTTIs) are engaged in imparting training to various categories of trainees including farmers, in the field of Farm Mechanization.
- National Food Security Mission (NFSM) is being implemented in identified districts of 28 States and 2 UTs viz. Ladakh and J&K of the country to increase the production and productivity of rice, wheat, pulses, coarse cereals and nutri- cereals (millets) through area expansion and productivity enhancement.
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH), a Centrally Sponsored Scheme is being implemented for holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root and tuber crops, mushrooms, spices, flowers, aromatic plants, coconut, cashew, cocoa and bamboo. All States and UTs are covered under MIDH.
5. Promoting use of bio pesticides and fertilizers
- To promote the use of bio pesticides in agriculture, Central Insecticide Board & Registration Committee has formulated simplified guidelines for registration of bio pesticides as compared to chemical pesticides.
- During provisional registration granted under The Insecticides Act, 1968, the applicant is allowed to commercialize the bio-pesticides, unlike chemical pesticides.
- Government of India through organic farming schemes of Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North Eastern Region (MOVCDNER) and Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme (CISS) aims for sustainable agriculture production with eco-friendly process in tune with nature, promoting organic inputs and chemical free agriculture produce for improving the health condition of the people.
- Under PKVY, assistance of Rs. 50,000 per hectare for 3 years is provided, out of which 62% is given to the farmers directly through DBT, for inputs (bio-fertilizers, bio-pesticides, vermicompost, botanical extracts, etc.), production/ procurement, post-harvest management etc.
- Under MOVCDNER, the farmers are given assistance of Rs. 25000 per hectare for 3 years for both on-farm & off-farm organic inputs, and seeds/ planting material.
- Under, CISS, the Government promotes production of bio-fertilizers by providing 100% assistance to State Government / Government Agencies upto a maximum limit of Rs.160.00 lakh/ unit for setting up of state of art liquid/ carrier-based Bio-fertilizer units of 200 Tonnes Per Annum capacity.
Similarly, for individuals/ private agencies assistance upto 25% of cost limited to Rs.40 lakh/unit as capital investment is provided through National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD).
6. PM Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana (PM-KMY)
- PM Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana is a voluntary and contributory pension scheme.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme which is administered by the Cooperation & Farmers Welfare, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare and Government of India in partnership with Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC).
- It was launched with a view to provide social security to Small and Marginal Farmers in their old age.
- Under this scheme, a minimum fixed pension of Rs.3,000/- is provided to the small and marginal farmers, subject to certain exclusion criteria, on attaining the age of 60 years.
- Small and Marginal Farmers between the age of 18 to 40 years are eligible to join this scheme.
- The eligible farmer is required to contribute to a Pension Fund between Rs.55 to Rs.200 per month depending on the entry age. The Central Government also contributes in equal amount to the Pension Fund.
Read more about PM Kisan Maan Dhan Yojana
7. Formation of Farmer Produce Organizations
What’s in News?
- Government of India has approved a Central Sector Scheme titled “Formation and Promotion of Farmer Produce Organizations (FPOs)” to form and promote 10,000 new FPOs.
- Under the scheme, a total number of 2000 FPOs have been proposed to be formed in 2020-21.
Farmer Producer Organisation has been covered in 27th February 2020 PIB Summary and Analysis.
8. Implementation of PMFBY in States
What’s in News?
- Based on the experience of past crop insurance schemes and with a view to include more risks under crop insurance and making it more affordable to the farmers etc., Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) has been introduced for implementation from Kharif 2016 season.
- The scheme also aims to cover the risk of crop yield losses of insured farmers against all non-preventable natural risks from pre-sowing to post-harvest and to provide adequate claim amount and timely settlement of claims.
Details:
- PMFBY is the government sponsored crop insurance scheme that integrates multiple stakeholders on a single platform.
- As the scheme is voluntary for the States/Union Territories (UTs), only 27 States/UTs have participated in the scheme in one or more seasons.
- Further, the scheme was compulsory for loanee farmers obtaining operational agricultural/Kisan Credit Card loans for crops/areas notified by the concerned State Governments and is optional for other farmers.
- However, Government has recently revamped the PMFBY and made the scheme optional for all farmers for its implementation from Kharif 2020.
Read more about Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
9. Govt brings masks and hand sanitizers under the Essential Commodities Act
What’s in News?
Government has notified an Order under the Essential Commodities Act to declare masks and hand sanitizers as Essential Commodities up to 30th June, 2020 by amending the Schedule of the Essential Commodities Act, 1955.
Details:
- It has also issued an advisory under the Legal Metrology Act (LM Act).
- Under the E.C Act, after discussions with the manufacturers, States can ask them to enhance their production capacity of these items, to make the supply chain smooth, while under the L.M. Act the States can ensure the sale of both the items at MRP.
- An offender under the EC Act may be punished with imprisonment upto 7 years or fine or both.
Significance:
- The decision would empower the Government and States/UTs to regulate the production, quality, distribution etc. of masks (2 ply & 3 ply surgical masks, N95 masks) and hand sanitizers and to smoothen the sale and availability of these items and carry out operations against orders speculators etc. and those involved in over pricing, black-marketing etc.
- It will enhance the availability of both the items to the general people at reasonable prices or under MRP.
10. Wings India 2020 launched in Hyderabad
What’s in News?
Wings India 2020 was launched today at Begumpet Airport in Hyderabad.
Details:
- Wings India is a biennial civil aviation and aerospace event.
- The theme of Wings India 2020 is ‘Flying For All’.
- The event is being organised by Ministry of Civil Aviation along with Airports Authority of India and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI).
11. Foreign Investments and ‘Make in India’ Programme
- Make in India initiative has made significant achievements and presently focuses on 27 sectors under Make in India 2.0.
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade is coordinating action plans for 15 manufacturing sectors, while the Department of Commerce is coordinating action plans for 12 service sectors.
- At the same time, investment promotion and facilitation activities under the Make in India initiative are being undertaken by several Central Government Ministries/ Departments and various State Governments from time to time.
Read more about Make in India.
12. Private Investment in Jammu and Kashmir
In order to facilitate investments in Union Territory (UT) of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), the following incentives are offered to attract entrepreneurs by the UT:
- Allotment of land at a subsidized rate.
- Cheaper Power Tariffs.
- Subsidy on purchase & installation of DG set.
- Subsidy on the installation of Quality Control/Testing Equipments.
Additionally Department for Promotion of Industry & Internal Trade is also implementing different Packages for providing incentives to industries in UT of Jammu & Kashmir.
13. Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) has been launched with the objective to eliminate out of pocket expenses for both pregnant women and sick infants accessing public health institution for treatment.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram (JSSK) entitles all pregnant women delivering in public health institutions, to absolutely free delivery including Caesarean section, post-natal care and treatment of sick infants till one year of age.
- The initiative was estimated to benefit more than 1 crore pregnant women access public health institutions every year in both urban and rural areas.
Key features of the scheme:
- The initiative entitles all pregnant women delivering in public health institutions to absolutely free and no expense delivery, including caesarean section.
- The entitlements include free drugs and consumables, free diet up to 3 days during normal delivery and up to 7 days for C-section, free diagnostics, and free blood wherever required.
- This initiative also provides for free transport from home to institution, between facilities in case of a referral and drop back home.
- Similar entitlements have been put in place for all sick newborns accessing public health institutions for treatment till 30 days after birth. This has now been expanded to cover sick infants.
What’s in News?
As per the report titled SRS Based Life Table 2013-17 published by the Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, Government of India, the average life expectancy at birth has increased from 49.7 during 1970-75 to 69.0 in 2013-17, registering an increase of 19.3 years during this period.
Details:
- A cross-sectional multi-centric community based study of elderly population aged 60 years and above conducted jointly by the Government of India and WHO Country Office in India has revealed that diseases like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischaemic heart disease, poor vision, difficulty in hearing, anaemia, arthritis, fall/fractures, bowel complaints, urinary complaints, depression, weight loss, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, TB etc. are common among older patients.
- Recognizing the need for specialized accessible health care for the elderly, the Government of India has launched various programmes, including the National Programme for Health Care of Elderly (NPHCE) and Integrated Programme for Older Persons such as Ayushman Bharat. These programmes aim to provide health care facilities to senior citizens (aged 60 years and above) at primary, secondary and tertiary health care delivery system and to further increase the average life expectancy of people.
- The Government of India has also enacted ‘Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007’.
The measures taken for providing better health services to ensure a healthy life and to further improve the average life expectancy:
- Mobilization of public health action at multiple levels.
- The Ayushman Bharat effort, with its two components of Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), addresses the disparity in access and reduces out of pocket expenditure for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization for 40% of India’s population.
- National Health Mission (NHM) is creating a network of 1,50,000 HWCs by upgrading existing Sub Centres (SCs) and Primary Health Centres (PHCs) to provide Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC), which is universal and free to all those who access public health facilities.
- The CPHC basket of services cover 12 key service areas, which go beyond the Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A) services to include screening and care for NCDs (diabetes, high blood pressure, oral, breast, cervical cancers etc.), elderly care, palliative and rehabilitative care, Oral, Eye and ENT care, mental health and first level care for emergencies and trauma etc.
- Continuum of care is being provided to all elderly citizen of age above 60 years under the National Programme for Healthcare of Elderly (NPHCE).
- Palliative care is being provided to terminal cases of Cancer, AIDS etc. under the National Programme for Palliative Care (NPPC).
- Government is providing financial support in the form of untied funds, annual maintenance grants and Rogi Kalyan Samiti (RKS) funds for development of health facilities and ensuring services.
- It is providing infrastructural support to State/UTs in constructing new health facilities and/or for up-gradation of infrastructure, Mother & Child Health (MCH) wings, up-gradation of the trauma centres & First Referral Units, Operationalization of the blood banks etc.
- It is operationalizing health facilities in rural areas (through placement of human resources in difficult areas, supply of equipment, drugs and diagnostics).
- In addition, certain new initiatives have been undertaken, like the Screening for Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs), Mothers Absolute Affection (to promote exclusive breastfeeding), Pradhan Mantri Shurakshit Matratva Abhiyan (to improve access to specialist maternal care through voluntary participation of private providers), Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Program, Mission Indradhanush (to immunise partially or uncovered population), Rashtriya Swasthya Bal Karyakram (RBSK), Kayakalp (to promote cleanliness, hygiene and Infection Control Practices in public Health Care Facilities), Labour room quality improvement initiative- LAQSHYA (Initiative to reduce preventable maternal and new-born mortality, morbidity and stillbirths associated with the care around delivery in Labour room and Maternity OT and ensure respectful maternity care), Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan (SUMAN) (to end all preventable maternal and neonatal deaths) etc.
15. Organ Donation
Government of India enacted the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994. The Act was amended in 2011. Further, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India has notified Transplantation of Human Organs and Tissues Rules, 2014. The aforesaid Act and Rules provide for the policy regarding organ donation.
- The Act is for the purpose of regulation and removal, storage and transplantation of human organs and tissues for therapeutic purpose and for prevention of commercial dealing in human organs and tissues and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- Health being a State subject, the States are required to adopt the Act before it may become applicable.
16. Cancer Treatment
- The objectives of National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS), includes awareness generation for cancer prevention, screening, early detection and referral to an appropriate level institution for treatment.
- It is being implemented by Central Government under National Health Mission (NHM) for interventions upto the district level.
- For cancer, the focus is on three cancers, namely breast, cervical and oral.
- A population level initiative for prevention, control and screening for common Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) i.e. diabetes, hypertension and common cancers viz. oral, breast and cervical cancer has been rolled out as a part of comprehensive primary healthcare.
- Screening of common NCDs including three common cancers i.e. oral, breast and cervical is also an integral part of service delivery under Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres.
- Cancer is diagnosed and treated at various levels in the health care system. In Government hospitals, treatment is either free or highly subsidized.
- Treatment of cancers is also available under Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan ArogyaYojana (PMJAY).
- Besides this, Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal outlets have been opened with an objective to make available drugs and implants at discounted prices to the patients.
- Under the umbrella scheme of Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi, financial assistance is provided to families living below the threshold poverty line for their treatment, including treatment of cancer, in Government hospitals.
What’s in News?
Union Minister for Home Affairs presided over the Flag-in ceremony of the Ganga Aamantran Abhiyan, organized under the National Mission for Clean Ganga.
- Under the Ganga Aamantran Abhiyan, a month-long research expedition and awareness campaign would be conducted on the river, which would play a big role in rejuvenating it.
- It is a part of the river conservation efforts National Mission for Clean Ganga.
Read more about National Mission for Clean Ganga.
18. Amenities under Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan in Railways
What’s in News?
Recently in February, 2020 the guidelines for accessibility of Railways have been circulated for implementation over Indian railways.
- As per these guidelines, Indian Railways endeavor to provide comprehensive facilities and services to Divyangjan which inter-alia include an easy use of information system, accessible infrastructure, various concession to passengers travelling on Divyangjan concession Tickets, Human Assistance, Wheel Chairs, Signages, etc.
- Railways also aim to make the railway coaches and stations accessible by retrofitting the existing infrastructure as well as integration of accessibility in new infrastructure for planning at design stage itself.
- Indian Railways is committed to make its railways stations and trains accessible for Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan) as part of “Sugamya Bharat Mission” or Accessible India Campaign of Government of India.
Read more about Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan.
19. Setting up of Railway Development Authority
What’s in News?
Government approved the constitution of Rail Development Authority (RDA) in April, 2017. It is responsible for recommending passenger fares, setting performance standards for rail operations and creating level playing policy for private sector participation.
The role/mandate of RDA includes providing expert advice to the Government to make an informed decision on:
- Pricing of services commensurate with costs;
- Measures for enhancement of non-fare Revenue;
- Protection of consumer interests, by ensuring quality of service and cost optimization;
- Promoting competition, efficiency and economy;
- Encouraging market development and participation of stakeholders in the rail sector and for ensuring a fair deal to the stakeholders and customers;
- Creating positive environment for investment;
- Promoting efficient allocation of resources in the Sector;
- Benchmarking of service standards against international norms and specify and enforce standards with respect to the quality, continuity and reliability of services provided them;
- Providing framework for non-discriminatory open access to the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) infrastructure and others in future;
- Suggesting measures to absorb new technologies for achieving desired efficiency and performance standards; and
- Suggesting measures for human resource development to achieve any of its stated objectives.
What’s in News?
- Bhoomi Rashi portal of Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has significantly expedited error free and transparent land acquisition for National Highways.
- In order to overcome the issues of delays and avoid parking of public funds with the Competent Authority for Land Acquisition (CALA), the Ministry developed a web based Utility –Bhoomi Rashi to fully digitize and automate the entire process of land acquisition.
- The portal has been integrated with the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) for depositing the compensation in the account of affected/ interested persons on real-time basis. This integration has resulted in avoiding the parking of huge public funds in the account of the Competent Authority for Land Acquisition.
- The Bhoomi Rashi portal model is replicable and can be used by state governments as well as by Ministries which directly acquire land under their relevant legal provisions.
21. Groundwater affects Himalayan slip and climate as the mountains dance to its tune
What’s in News?
Researchers from Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG) have found the mighty Himalayas subside and move up depending on the seasonal changes in groundwater. Since Himalayas play a very important role in influencing climate in the Indian subcontinent, the study funded by DST will help in understanding how hydrology affects climate.
- The Himalayan foothills and the Indo-Gangetic plain are sinking because its contiguous areas are rising due to tectonic activity associated with landmass movement or continental drift.
- The new study shows that subsidence and uplift are found to be associated with seasonal changes in groundwater, apart from the normal, common reasons.
- Water acts as a lubricating agent, and hence when there is water in the dry season, the rate of slip of the fault in this region is reduced.
- In the Himalaya, seasonal water from glaciers, as well as monsoon precipitation, plays a key role in the deformation of the crust and the seismicity associated with it. The subsidence rate is associated with groundwater consumption.
- The researchers have made the combined use of Global Positioning System (GPS) and Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE) data, which has made it possible for them to quantify the variations of hydrologic mass.
- The GRACE satellites, launched by the US in 2002, monitor changes in water and snow stores on the continents. This made it possible for the IIG team to study terrestrial hydrology.
- According to the researchers, the combined GPS and GRACE data suggest a 12% reduction in the rate of the subsurface slip. This slip refers to how fast the fault is slipping relative to the foot and hanging wall.
- The slip occurs at the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT), due to hydrological variations and human activities, over which there is the periodic release of accumulated strain.
22. Scientists pave way for potential new therapy for tongue cancer
What’s in News?
A new therapy for tongue cancer could be in the offing, with a team of scientists at the Department of Biotechnology coming out with a new insight into the mechanism by which an anti-cancer protein helps in the development of cancer when it mutates.
- Human cells carry a protein called p53.
- It is very helpful as it controls several fundamental processes including cell division and repair of damaged DNA.
- It functions by binding directly to DNA leading to the production of proteins needed for regular cellular functions as well as effectively blocking cancer development.
- However, its ability to prevent cancer is significantly compromised, if it mutates.
- More importantly, recent studies have reported that some specific and common mutated p53 forms even activate cancer growth.
- In a new study, scientists have identified rare p53 mutant forms unique to Indian tongue cancer and the likely means by which these mutant p53 cause cancer.
- By using state of the art technologies, they identified target genes of the mutant p53 protein. Of these, a gene called SMARCD1 was the most prominent.
- SMARCD1 encodes a protein that along with several other proteins constitutes a multi-protein complex involved in changing the structure of DNA enabling the production of proteins from genes.
- The scientists found that SMARCD1 was an exclusive target of mutations observed in Indian tongue cancer patients.
- Further studies showed the ability of SMARCD1 to increase cancerous features in tongue cancer cells.
- Notably, this is the first time that SMARCD1 has been shown to be a possible driver of any form of cancer.
- The results of the study can be employed to develop therapies to treat tongue cancer.
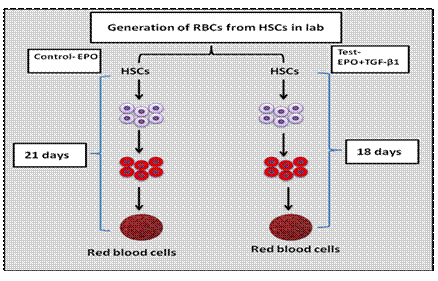
23. New approach to speed up red blood cells generation in the lab
What’s in News?
A team of researchers at the Department of Biotechnology’s National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS) at Pune have found a new approach to speed up red blood cells generation in the lab.
Details:
- Transfusion of red blood cells (RBCs) is a life-saving treatment for numerous conditions such as severe anaemia, injury-related trauma, supportive care in cardiovascular surgery, transplant surgery, pregnancy-related complications, solid malignancies and blood-related cancers.
- However, blood banks, particularly in developing countries, often face a severe shortage of whole blood as well as components of blood like red blood cells.
- Researchers across the world are exploring possibilities to generate RBCs outside the body (in vitro) from haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
- These HSCs have the capability to give rise to the different types of cells found in the blood.
- Various groups have been able to produce RBCs in the laboratory from HSCs.
- However, the process takes a long time – around twenty-one days.
- The resources required to grow cells in the laboratory over such a long duration can be very expensive for the generation of RBCs on a large scale for clinical purposes.
Recently, it has been found that the process can be speeded up by adding a very low concentration of a small protein molecule called `transforming growth factor β1’ (TGF-β1), along with a hormone called `erythropoietin’ (EPO), to the growth medium. They could cut down the process time by three days.
24. National Biopharma Mission
- The National Biopharma Mission (NBM) is an industry-Academia Collaborative Mission for accelerating biopharmaceutical development in the country.
- Under this Mission, the Government has launched Innovate in India (i3) programme to create an enabling ecosystem to promote entrepreneurship and indigenous manufacturing in the sector.
- The mission will be implemented by the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The mission was approved in 2017 at a total cost of Rs 1500 crore and is 50% co-funded by World Bank loan.
- Together with National and International experts, the most promising projects are selected in response to open Request for Applications issued by the PMU.
- The program is promoting entrepreneurship by supporting small and medium enterprises for indigenous product development (Novel Cell lines, indigenously developed Biologics, devices and Raw materials for Biologics manufacturing) and through establishment of shared facilities and Technology Transfer Offices.
This scientifically driven enterprise aims at developing an ecosystem for affordable product development and is focused on the following 4 verticals:
- Development of product leads for Vaccines, Biosimilars and Medical Devices that are relevant to the public health need by focussing on managed partnerships.
- Presently the mission is supporting the development of candidate vaccines for Cholera, Influenza, Dengue, Chikungunya and Pneumococcal disease;
- Biosimilar products for Diabetes, Psoriasis, emergency situations & Oncology;
- Products for development of MedTech Devices for Imaging, Pumps for dialysis, MRI and Molecular Biology devices.
- Upgradation of shared infrastructure facilities and establishing them as centres of product discovery/discovery validations and manufacturing.
- Support is being extended by the Mission for establishing shared facilities.
- 15 facilities have been funded for – Biopharmaceuticals development (7), MedTech device development (6) and Vaccine Development (2).
- Develop human capital by providing specific training to address the critical skills gap among the nascent biotech companies across the product development value chain in areas such as product development, intellectual property registration, technology transfer and regulatory standards.
- Technology Transfer Offices: To help enhance industry academia inter-linkages and provide increased opportunities for academia, innovators and entrepreneurs to translate knowledge into products and technologies, 5 Technology Transfer Offices are being considered for funding under NBM.
National Creche Scheme (earlier named as Rajiv Gandhi National Creche Scheme) is being implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme through States/UTs to provide day care facilities to children (age group of 6 months to 6 years) of working mothers.
The salient features of the National Creche Scheme are as follows:
-
- Daycare Facilities including Sleeping Facilities
- Early Stimulation for children below 3 years and pre-school Education for 3 to 6 years old children.
- Supplementary Nutrition ( to be locally sourced)
- Growth Monitoring
- Health Check-up and Immunization
March 13th, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
Related Links:
| UPSC 2020 | How to apply for UPSC 2020? |
| Monthly Magazine for UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Current Affairs Quiz |
| Government Exams | UPSC Prelims Exam |
Read more PIB articles here.


Comments