Read the daily PIB update and stay up-to-date on current affairs for the UPSC exam.
January 21st, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PRAGATI 2. Integrated Check Post (ICP) 3. e-National Agriculture Market (e-Nam) 4. National Startup Advisory Council 5. Startup India 6. Geological Survey of India (GSI) 7. Round-table of UNAIDS
1. PRAGATI
Context:
PM will chair the 32nd interaction through PRAGATI.
About PRAGATI:
- The Prime Minister had launched the multi-purpose and multi-modal governance platform, PRAGATI in 2015.
- PRAGATI is an integrating and interactive platform, aimed at addressing the common man’s grievances.
- PRAGATI also helps in simultaneously monitoring and reviewing important programmes and projects of the Government of India, as well as projects flagged by various State governments.
- PRAGATI stands for ‘Pro Active Governance and Timely Implementation’.
For more on PRAGATI, click on the linked article.
2. Integrated Check Post (ICP)
Context:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Prime Minister of Nepal K P Sharma Oli jointly Inaugurate Integrated Check Post at Jogbani-Biratnagar.
About Integrated Check Post (ICP):
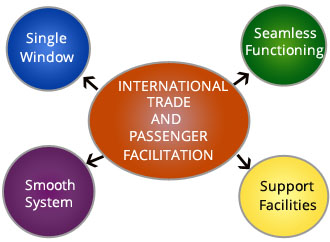
- An ICP is a one-stop solution that houses all regulatory agencies, such as immigration, customs and border security.
- Concerned at inadequate infrastructure for cross border movement of persons, vehicles and goods, the Committee of Secretaries in 2003 recommended setting up of Integrated Check Posts (ICPs) at major entry points on India’s land borders which would house all the regulatory agencies like immigration, customs, border security, etc. together with support facilities in a single complex equipped with all modern amenities and serve as a single-window facility as is prevalent at Airports and Seaports.
- ICPs are managed by the Land Ports Authority of India (LPAI), which was set up specifically for this purpose in 2012.
- An ICP not only gives many services under one roof but also offers facilities such as cargo process building, cargo inspection sheds, warehouse, cold storage, currency exchange counters, Internet hubs, clearing agents, banks, vehicle scanners, isolation bay and parking.
- ICPs facilitate legitimate trade between the neighbouring countries.
- Major stakeholders at ICPs:
- Customs
- Immigration
- Border guarding force
- Plant quarantine
- Human quarantine
- ICPs are needed because the country should be secured against hostile parties. There is a need to develop integrated infrastructure at the entry points on the country’s borders.
- The development of the ICP infrastructure has been planned in two phases: seven have been developed in Phase-1, of which six are now operational; the rest are to be developed in Phase-2. Totally, 20 border checkpoints have been designated as ICPs.
The following tables give a few numbers related to ICPs in India:
| ICPs Border-wise | |
| Border | No. of ICPs |
| Bangladesh | 10 |
| Nepal | 7 |
| Bhutan | 1 |
| Myanmar | 1 |
| Pakistan | 1 |
| Total | 20 |
| ICPs State-wise | |
| State | No. of ICPs |
| West Bengal | 8 |
| Bihar | 3 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 2 |
| Uttarakhand | 1 |
| Assam | 1 |
| Manipur | 1 |
| Meghalaya | 1 |
| Mizoram | 1 |
| Punjab | 1 |
| Tripura | 1 |
| Total | 20 |
3. e-National Agriculture Market (e-Nam)
Context:
First National Consultative Workshop on Strengthening Agri-Logistics in e-National Agriculture Market (e-Nam) held in New Delhi.
About e-Nam:
To know more about e-NAM, click on the linked article.
4. National Startup Advisory Council
Context:
Central Government Notifies National Startup Advisory Council.
About the National Startup Advisory Council:
- The Council will advise the government on measures needed to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups in the country to drive sustainable economic growth and generate large scale employment opportunities.
- The Council will:
- Suggest measures to foster a culture of innovation amongst citizens and students in particular.
- Promote innovation in all sectors of the economy across the country, including semi-urban and rural areas.
- Support creative and innovative ideas through incubation and research and development to transform them into valuable products, processes or solutions to improve productivity and efficiency.
- Create an environment of absorption of innovation in industry.
- Suggest measures to facilitate public organizations to assimilate innovation with a view to improving public service delivery.
- Promote creation, protection and commercialization of intellectual property rights.
- Make it easier to start, operate, grow and exit businesses by reducing regulatory compliances and costs.
- Promote ease of access to capital for startups, incentivize domestic capital for investments into startups, mobilize global capital for investments in Indian startups.
- Keep control of startups with original promoters.
- Provide access to global markets for Indian startups.
- Members of the Council:
- The Council will be chaired by the Minister for Commerce & Industry.
- The Council will consist of non-official members, to be nominated by the Central Government, from various categories like founders of successful startups, veterans who have grown and scaled companies in India, persons capable of representing interests of investors into startups, persons capable of representing interests of incubators and accelerators and representatives of associations of stakeholders of startups and representatives of industry associations. The term of the non-official members of the Council will be for a period of two years.
- The nominees of the concerned Ministries/Departments/Organisations, not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India, will be ex-officio members of the Council.
- The Joint Secretary, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade will be the Convener of the Council.
Context:
The Department for Promotion of Industry & Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry will showcase a tableau on Startup India in the Republic Day Parade 2020 at Rajpath in New Delhi.
About Startup India:
To know all about Startup India, click on the linked article.
6. Geological Survey of India (GSI)
Context:
Indian Navy Signs MoU for offshore Data with Geological Survey of India.
Details:
- The MoU is for ‘Sharing of seabed sediments data, products and expertise for Naval Application in Meteorology and Oceanography’.
- GSI’s Marine and Coastal Survey Division based at Mangaluru has mapped most of India’s 2.1 Million km2 Exclusive Economic Zone and has a vast repository of offshore data.
About the Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) was set up in 1851 primarily to find coal deposits for the Railways.
- Over the years, it has not only grown into a repository of geo-science information required in various fields in the country, but has also attained the status of a geo-scientific organisation of international repute.
- The main functions of GSI relate to creation and updation of national geoscientific information and mineral resource assessment.
- These objectives are achieved through ground surveys, air-borne and marine surveys, mineral prospecting and investigations, multi-disciplinary geoscientific, geo-technical, geo-environmental and natural hazards studies, glaciology, seismotectonic study, and carrying out fundamental research.
- It is headquartered in Kolkata and has six regional offices in other parts of the country.
Major National Survey Organisations of India:
- GSI: Geology
- Archaeological Survey of India: Archaeology
- Botanical Survey of India: Botany
- Fishery Survey of India: Fisheries
- Forest Survey of India: Forest
- Indian Institute of Ecology and Environment: Ecology & Environment
- National Institute of Oceanography: Oceanography
- Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India: Population & Language
- Survey of India: Cartography
- Zoological Survey of India: Zoology
Context:
The Union Minister of State for Shipping (I/C) and Chemical & Fertilizers participated in the High-level roundtable of UNAIDS (The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS).
Details:
- The theme of the Round-table was “Access for all: Leveraging Innovations, Investments and Partnerships for Health”.
- It was held at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland.
To know more about UNAIDS, click on the linked article.
January 21st, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
Related Links:
| UPSC 2020 | UPSC Current Affairs |
| Monthly Magazine for UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Current Affairs Quiz |
| Government Exams | UPSC Prelims Exam |
Read more PIB articles here.

Comments