Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System is the most preferred study material due to its unique description of the concepts. In this Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10, Chapter 12, a distinctive attempt is made to build an understanding of the function of hormones. Pursuing this chapter would ensure that you develop a piece of in-depth knowledge about the properties and functions of the hormones.
Our main objective is to help students by providing the solutions. These Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 are prepared by our expert tutors with neat descriptions. To download these Selina solutions, click on the respective links.
Download PDF of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System
Access Answers of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System
Review questions Page: 162
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
(Selective the most appropriate option in each case)
1. A gland having endocrine as well as exocrine function is
(a) Pituitary (b) Thyroid
(c) Pancreas (d) adrenal
Solution:-
(c) Pancreas
2. Exophthalmic goitre is caused due to the overactivity of
(a) thymus (b) thyroid
(c) parathyroid (d) adrenal cortex
Solution:-
(b) thyroid
3. The deficiency of ADH causes:
(a) diabetes mellitus (b) diabetes insipidus
(c) dwarfism (d) acromegaly
Solution:-
(b) diabetes insipidus
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Name the following:
(a) The three hormones produced by pancreas.
Solution:-
The three hormones produced by pancreas are insulin, glucagon and somatostatin.
(b) The hormone produced by adrenal medulla.
Solution:-
Adrenaline is the hormone produced by adrenal medulla.
(c) The condition caused by the over secretion of insulin.
Solution:-
Hypoglycemia is the condition caused by the over secretion of insulin.
(d) The hormone secreted by beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Solution:-
Insulin is the hormone secreted by beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
(e) The hormone which increases blood pressure.
Solution:-
Adrenaline is the hormone which increases blood pressure.
(f) The hormone causing more urine formation.
Solution:-
Anti-diuretic hormone (vasopressin) is the hormone causing more urine formation.
(g) The hormone which stimulates the entire sympathetic nervous system.
Solution:-
Adrenaline is the hormone which stimulates the entire sympathetic nervous system.
2. What would a child suffer from, if there was hypo secretion from his thyroid?
Solution:-
The symptoms of hypothyroidism in children are different than in adults. The following are the late symptoms of the disorder. However, each child may experience symptoms differently, and often the symptoms are not seen at all.
Congenital hypothyroidism is associated with an increased risk for congenital abnormalities of the cardiovascular, genitourinary, and skeletal systems.
3. Choose the odd one out from each series:
(a) The glands – thyroid, adrenal, pituitary, prostate
Solution:-
Prostate
(b) The conditions – cretinism, myxoedema, goiter, scurvy
Solution:-
Scurvy
(c) The hormones- insulin, glucagon, cretinism, thyroxine
Solution:-
Cretinism
(d) The hormonal sources – adrenal cortex, adrenal medulla, cortisone, pituitary
Solution:-
Cortisone
4. Match the items of column I with those of column II.
Column I Column II
1. ‘b’ (beta) cells of islets (a) Condition due to undersecretion of
of Langerhans thyroxine in adults
2. Thyroid (b) Undersecretion of glucocorticoids
3. Cretinism (c) Exophthalmic goitre
4. Addison’s diseases (d) Increases heart beat
5. Hyperthyroidism (e) Thyroxine
6. Myxoedema (f) Adrenal cortex
7. Adrenaline (g) Insulin
8. Cortisone (h) Undersecretion of thyroxine in a child
Solution:-
Column I Column II
1. ‘b’ (beta) cells of islets (g) Insulin
of Langerhans
2. Thyroid (c) Exophthalmic goitre
3. Cretinism (h) Undersecretion of thyroxine in a child
4. Addison’s diseases (b) Undersecretion of glucocorticoids
5. Hyperthyroidism (e) Thyroxine
6. Myxoedema (a) Condition due to undersecretion of
thyroxine in adults
7. Adrenaline (d) Increases heartbeat
8. Cortisone (f) Adrenal cortex
5. Match the conditions in column A with the cause in column B.
A (Condition) B (Cause)
(a) Dwarfism and mental (i) Excess of glucose in blood.
retardation
(b) Diabetes mellitus (ii) Oversecretion of growth hormone.
(c) Shortage of glucose in blood (iii) Insulin shock.
(d) Gigantism (iv) oversecretion of thyroxine.
(e) Enlargement of breasts (v) Hypothyroidism in a child.
in adult males
(f) Exophthalmic goitre (vi) Oversecretion of cortical hormones.
Solution:-
A (Condition) B (Cause)
(a) Dwarfism and mental (v) Hypothyroidism in a child.
retardation
(b) Diabetes mellitus (i) Excess of glucose in the blood.
(c) Shortage of glucose in blood (iii) Insulin shock.
(d) Gigantism (ii) Oversecretion of growth hormone.
(e) Enlargement of breasts (vi) Oversecretion of cortical hormones.
in adult males
(f) Exophthalmic goitre (iv) oversecretion of thyroxine.
6. Identify the odd one in each of the following and mention what the rest are:
(a) Larynx; glucagon; testosterone; prolactin
Solution:-
Larynx
Glucagon; testosterone; prolactin are hormones and larynx is the soundbox.
(b) Adrenaline; penicillin; insulin; thyroxin
Solution:-
Penicillin
Adrenaline; insulin; thyroxin are hormones and penicillin is an antibiotic.
(c) Stomach; ileum; liver; adrenaline
Solution:-
Adrenaline
Stomach; ileum; liver are the organs of the digestive system and adrenaline is a hormone.
(d) TSH; GH; ADH; insulin
Solution:-
Insulin
TSH; GH; ADH are the hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and insulin is secreted by the pancreas.
(e) Iodine; cretinism; goiter; myxoedema
Solution:-
Iodine
Cretinism; goiter; myxoedema are the deficiencies occur due to the deficiency of thyroxine. Iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroxine hormone.
C. SHORT ANSWER TYPE
1. Mention which of the statements are true (T) and which are false (F). Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) Adrenaline is often described as an emergency hormone. (T/F)
Solution:-
True
Adrenaline is a hormone, which prepares the body to meet any emergency situation, for “fight” i.e. to face danger or for “flight”, to run away from it.
(b) There are two kinds of diabetes (mild and severe) related with two different hormones. (T/F)
Solution:-
False
There are two different kinds of diabetes – diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus which are related to two different hormones ADH and insulin respectively.
(c) Simple goitre can be prevented by using iodised salt in food. (T/F)
Solution:-
True
Simple goitre is due to an insufficient quantity of iodine in food. This can be prevented by use of iodised salt in food because iodine is the active ingredient in the production of thyroxine.
(d) Pituitary is popularly called the master gland. (T/F)
Solution:-
True.
Pituitary is popularly called as the master gland because it seems to control practically all other endocrine glands.
(e) Hormones “obey” the commands like “enough, slow down” or “too little, speed up”. (T/F)
Solution:-
True
The body has a mechanism to maintain a normal state. Whenever there is a change in this state there are “messages” through the body systems to “increase” if there is a fall below the normal, or to “decrease” if there is a rise above the normal.
(f) Gigantism and dwarfism in humans basically depend on the quality and quantity of the food eaten during early growing age. (T/F)
Solution:-
False
Gigantism and dwarfism are caused due to oversecretion and under secretion of growth hormones from pituitary respectively in childhood.
2. How do endocrine glands differ from other glands?
Solution:-
Endocrine glands are also called ductless glands because their secretions are poured directly into the blood and not through any special duct.
Other glands are called duct glands or exocrine glands where secretions are carried through ducts.
3. Mention any two differences between a hormone and an enzyme.
Solution:-
| Hormone | Enzyme |
| 1. Hormones are the chemical messenger that provide signals to the cell for performing the particular function. | 1. Enzymes are the catalyst, which enhance the biochemical reactions. |
| 2. Hormones are carried by the blood to different part of the body for giving signals to the cell. | 2. Enzymes act at the place where they are formed. |
4. Do you agree with the statement- “All hormones are chemical signals”? Yes/No. Justify your answer.
Solution:-
Yes, I agree with the statement- “All hormones are chemical signals”.
Some hormones are peptides (proteins such as insulin) which are water-soluble, some are amines (derived from amino acids such as adrenaline) again water-soluble and some are steroids (derived from cholesterol such as testosterone) which are lipid-soluble.
5. Why is iodine as a nutrient, important to our body?
Solution:-
Use of iodised salt (containing iodine) in food is recommended because iodine is the active ingredient in the production of thyroxine. Thyroxine hormone is a very essential hormone for our body. In case of its abnormal secretions, a person may suffer certain severe disorders. So, iodine as a nutrient is important to our body.
6. If you stand to make your maiden speech before a large audience, your mouth dries up and heart rate increases. What brings about these changes?
Solution:-
If you stand to make your maiden speech before a large audience, your mouth dries up and heart rate increases because, Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline. Adrenaline is a hormone, which prepares the body to meet any emergency situation, for “fight” i.e. to face danger or for “flight”, to run away from it. Extra energy and strength are provided to the body in that situation. The extra hormone is released into the blood at the time of emotional stress. When excited or angry, our adrenals produce a lot of adrenaline. The gland itself is stimulated by the nerve endings of the autonomic nervous system.
7. If one adrenal gland is removed, the other one gets enlarged to some extent. How do you explain this change?
Solution:-
If one adrenal gland is removed, the other one gets enlarged to some extent because to meet the requirement of secretion of hormones that are required by our body for correct functioning.
8. Name the two kinds of diabetes? Mention their symptoms and the causes.
Solution:-
The two kinds of diabetes are diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus.
Diabetes mellitus caused due to insufficient secretion of insulin. The symptoms are high concentration of sugar in the blood, excretes a great deal of urine loaded with sugar, the person feels thirsty and loses weight.
Diabetes insipidus caused due to no sugar in the urine. The symptoms are Urination is frequent and copious, Loss of water from the body due to frequent urination.
9. People living in the low Himalayan hilly regions often suffer from goitre. What could be the possible reason for it?
Solution:-
People living in the low Himalayan hilly regions often suffer from goitre, it is the enlargement of the thyroid and is visible as a swelling in the neck. This is due to an insufficient quantity of iodine in food. This condition is common in the people living in hilly regions where iodine is deficient in the soil and hence in the food grown there.
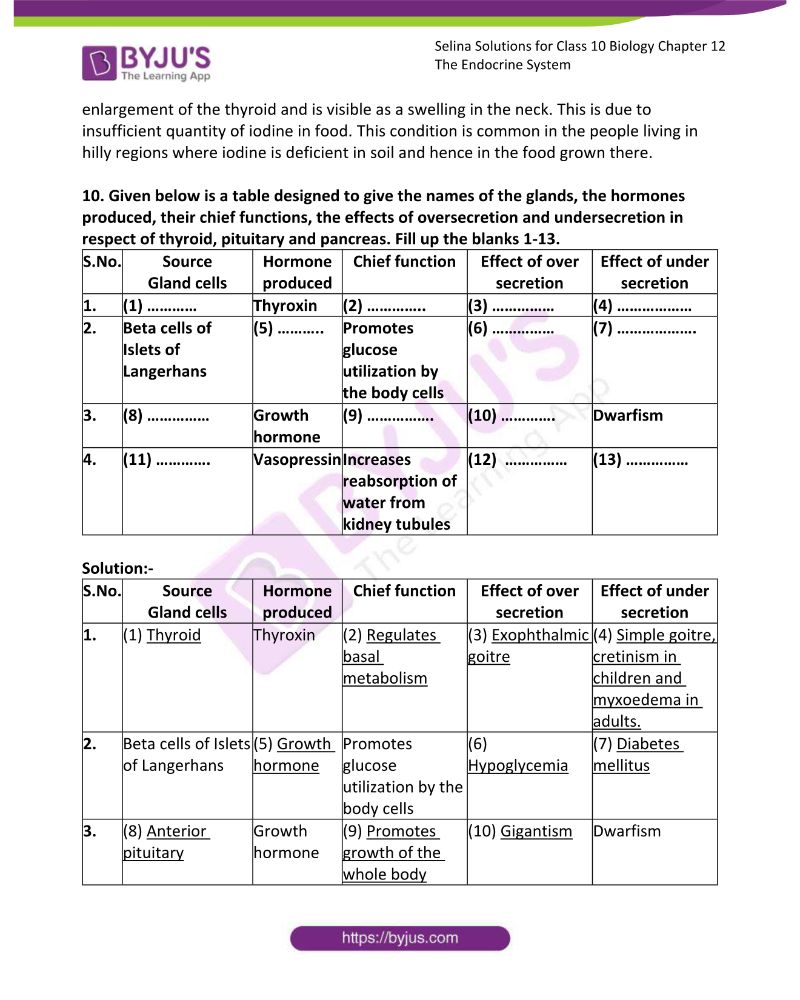
10. Given below is a table designed to give the names of the glands, the hormones produced, their chief functions, the effects of oversecretion and undersecretion in respect of thyroid, pituitary and pancreas. Fill up the blanks 1-13.
| S.No. | Source
Gland cells |
Hormone produced | Chief function | Effect of over secretion | Effect of under secretion |
| 1. | (1) ………… | Thyroxin | (2) ………….. | (3) …………… | (4) ……………… |
| 2. | Beta cells of Islets of Langerhans | (5) ……….. | Promotes glucose utilization by the body cells | (6) …………… | (7) ………………. |
| 3. | (8) …………… | Growth hormone | (9) ……………. | (10) …………. | Dwarfism |
| 4. | (11) …………. | Vasopressin | Increases reabsorption of water from kidney tubules | (12) …………… | (13) …………… |
Solution:-
| S.No. | Source
Gland cells |
Hormone produced | Chief function | Effect of over secretion | Effect of under secretion |
| 1. | (1) Thyroid | Thyroxin | (2) Regulates basal metabolism | (3) Exophthalmic goitre | (4) Simple goitre, cretinism in children and myxoedema in adults. |
| 2. | Beta cells of Islets of Langerhans | (5) Growth hormone | Promotes glucose utilization by the body cells | (6) Hypoglycemia | (7) Diabetes mellitus |
| 3. | (8) Anterior pituitary | Growth hormone | (9) Promotes growth of the whole body | (10) Gigantism | Dwarfism |
| 4. | (11) Posterior pituitary | Vasopressin | Increases reabsorption of water from kidney tubules | (12) More concentrated and less amount of urine | (13) Diabetes insipidus |
11. Complete the following table by filling in the blanks numbered 1 to 7.
| Gland | Hormone secreted | Effect on body |
| (1) ……………….. | (2) ……………. | Regulates basal metabolism |
| Pancreas (“beta” cells) | (3) ……………. | Controls blood sugar |
| (4) ……………. | (5) ……………. | Increases heart beat |
| (6) ……………. | Thyroid stimulating hormone | (7) …………….. |
Solution:-
| Gland | Hormone secreted | Effect on body |
| (1) Thyroid | (2) Thyroxin | Regulates basal metabolism |
| Pancreas (“beta” cells) | (3) Insulin | Controls blood sugar |
| (4) Adrenal gland | (5) Adrenaline | Increases heartbeat |
| (6) Anterior pituitary | Thyroid-stimulating hormone | (7) Stimulates thyroxin secretion |
12. Complete the following table by filling in the blank spaces numbered 1 to 8.
| Gland | Secretions | Effect on body |
| (1)……………. | Oestrogen | (2) ……………… |
| Alpha cells of islets of Langerhans | (3) ……………… | (4) ……………… |
| (5) ……………. | (6) ……………… | Protruding eyes |
| (7) ……………. | (8) ……………… | Gigantism |
Solution:-
| Gland | Secretions | Effect on body |
| (1) Ovary | Oestrogen | (2) development of secondary sexual characteristics |
| Alpha cells of islets of Langerhans | (3) Glucagon | (4) Raises blood level |
| (5) Thyroid | (6) Hypersecretion of thyroxin | Protruding eyes |
| (7) Anterior pituitary | (8) Hypersecretion of growth hormone | Gigantism |
D. LONG ANSWER TYPE
1. Compare the hormonal response with the nervous response with respect to their speed, transmission and the general nature of changes brought about.
Solution:-
| Hormonal response | Nervous response |
| 1. Hormonal response is usually slow | 1. The nervous response is immediate/Rapid |
| 2. Transmitted chemically through the blood. | 2. Transmitted electro chemically through the nerve fibres and chemically across synapses. |
| 3. Affects different organs. | 3. Affects only the particular muscles or the gland. |
| 4. Effect is short term or long-lasting | 4. Effect only short-lived. |
2. Mention three important differences between the action of hormones and that of nerves in the regulatory mechanism of our body.
Solution:-
| Action of Hormones | Action of Nerves |
| 1. Hormones can bring about specific chemical changes and regulates metabolism. | 1. Nerves do not influence chemical changes and cannot regulate metabolism. |
| 2. Affects different organs (wide spread in body) | 2. Affects only the particular muscles or the gland (local) |
| 3. Hormones cannot be modified by learning from previous experience. | 3. Nerves can be modified to some extent by learning from previous experience. |
E. STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
1. Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:

(a). Name the cells of the pancreas that produce (1) glucagon (2) insulin.
Solution:-
The pancreas that produces glucagon is alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans.
The pancreas that produces insulin is beta cells of the islets of Langerhans.
(b). State the main function of (1) glucagon and (2) insulin.
Solution:-
The main function of insulin is checking the rise of sugar level in blood.
The main function of glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver to glucose, thus it raises sugar level in the blood.
c. Why is the pancreas referred to as an exo-endocrine gland?
Solution:-
The pancreas referred to as an exo-endocrine gland because, it has a special group of hormone-secreting cells called islets of Langerhans, which are scattered in the entire gland. The islet cells produce three hormones insulin, glucagon and somatostatin from delta cells respectively. Thus behaves like an endocrine gland. It also behaves as an exocrine gland by secreting enzymes which are carried through ducts and help in digestion.
d. Why is insulin not given orally but is injected into the body?
Solution:-
Insulin is not given orally but is injected into the body because insulin is chemically protein in nature and thus it gets digested by protein digestive enzymes.
e. What is the technical term for the cells of the pancreas that produce endocrine hormones?
Solution:-
Islets of Langerhans is the technical term for the cells of the pancreas that produce endocrine hormones.
f. Where in the body is the pancreas located?
Solution:-
The pancreas is located in the abdomen behind the stomach.
2. Given below is a portion from the human body showing some important structure in ventral (front) view.

(a) Where is this portion located in the body?
Solution:-
This portion is located in the neck region above the sternum.
(b) Name the structures numbered 1-3.
Solution:-
Structure 1 represents Larynx
Structure 2 represents Thyroid gland
Structure 3 represents Trachea
(c) State one main function of each of the structures named above.
Solution:-
Larynx – The larynx commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The larynx houses the vocal folds and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation.
Thyroid gland – The thyroid gland is a vital hormone gland: It plays a major role in the metabolism, growth and development of the human body. It helps to regulate many body functions by constantly releasing a steady amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream.
Trachea – The vital function of providing airflow to and from the lungs for respiration
(d) Is there any duct to carry the secretions from the structure numbered 2? If so, give its name.
Solution:-
No, the thyroid gland has no duct as it is a ductless gland. It pours its secretion directly into the bloodstream.
3. Given below is an outline diagram of human body showing position of certain organs.

(a) Name the parts numbered 1 to 4.
Solution:-
Part 1 represents pituitary gland.
Part 2 represents thyroid gland.
Part 3 represents pancreas.
Part 4 represents adrenal glands.
(b) What is common to all these parts in regard to the nature of their functions?
Solution:-
The common to all these parts in regard to the nature of their function is all the glands are endocrine glands. They pour their secretions directly into the bloodstream.
(c) Name the nutrient element which is essential for the normal working of part 2.
Solution:-
The nutrient element which is essential for the normal working of part 2 thyroid gland is iodine.
4. Given below are two diagrams (one is correct, the other one is somewhat incorrect) showing the transport of a hormone from its source gland/cell to the target organ/cell.

(a) Which one has the error- A or B?
Solution:-
By observing the figure we can say that figure A has the error.
(b) What is the error?
Solution:-
By observing the figure we can say that in figure B hormones secreted by the endocrine gland is carried to all parts as they may have one or more target sites at a time which is correct. But in figure A hormones secreted by the endocrine gland is moving in a single direction towards the target cell.
The given solutions are as per the 2019-20 Concise Selina textbook. The Selina Solutions for the academic year 2020-21 will be updated soon..
Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System, Endocrine glands secrete certain chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are extremely important secretions for the regulation of body activities. Concepts covered in this chapter are needed for the regulation of body activities, general properties of hormones, endocrine glands and control of hormonal secretions.
List of subtopics covered in Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System
| Number | Subtopic |
| 12.1 | Need for the regulations of body activities |
| 12.2 | General properties of hormones |
| 12.3 | Endocrine Glands |
| 12.4 | Control of hormonal secretions |
| 12.5 | The Hormones at a glance |
Contents of Exercise
| Name of the exercise | Number of questions | Question Type | Page number |
| Review questions | 3 | MCQ | 162 |
| 6 | Very short | 162 and 163 | |
| 12 | Short | 163 and 164 | |
| 2 | Long | 164 | |
| 4 | Structured/Skill | 164 and 165 |
Key Features of Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 Chapter 12 The Endocrine System
- Solutions are answered with the help of relevant analogies.
- Solutions contain suitable and relevant examples to explain the concepts effectively.
- Diagrams are used in this chapter, wherever required.
- Selina solutions are readily accessible and free to download.
















Comments