Students can download JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper 1 with solutions for Physics section from this page. The questions have been solved by our expert teachers and the solutions have been prepared in a detailed manner. This has been done to address the need of students to find the right answer to each of the questions asked in JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1. The questions and solutions can be either viewed on our page directly or the document which is available in a PDF format can be downloaded for offline use.
Practising JEE Advanced 2019 Physics Question Paper 1 will help the candidates to study productively and at the same time analyze their performance in a more practical manner. Ultimately, aspirants will be able to face the exam with higher confidence and score more marks in IIT JEE Advanced exam.
Paper 1 - Physics
Question 1: A current carrying wire heats a metal rod. The wire provides a constant power P to the rod. The metal rod is enclosed in an insulated container. It is observed that the temperature (T) in the metal rod changes with time (t) as T(t) = T0 (1 + βt1/4) where β is a constant with appropriate dimension of temperature. The heat capacity of metal is:
- a) \(\frac{4P(T(t) - T_0)^3}{\beta^4 T_o^4}\)
- b) \(\frac{4P(T(t) - T_0)^2}{\beta^4 T_o^3}\)
- c) \(\frac{4P(T(t) - T_0)^4}{\beta^4 T_o^5}\)
- d) \(\frac{4P(T(t) - T_0)}{\beta^4 T_o^2}\)
Solution:
- Heat capacity = dQ/dt
H = dQ/dT ⇒ dQ/dt = H dT/dt
P = H dT/dt
= (HT0/4 ) β t-3/4
⇒ 4P/T0 β = Ht-3/4
⇒ t-3/4 =\((\frac{T-T_0}{T_0 \beta})^3\)
⇒ H =\(\frac{4P(T-T_0)^3}{T_0^4 \beta^4}\)
Question 2: In a capillary tube of radius 0.2 mm the water rises up to height of 7.5 cm with angle of contact equal to zero. If another capillary with same radius but of different material dipped in the same liquid. The height of water raised in capillary will be, if angle of contact becomes 60°.
- a) 7.5 cm
- b) 15 cm
- c) 3.75 cm
- d) 30 cm
Solution:
T = Rhρg/2cosθ
h/cosθ = constant
7.5/1 = h’/(1/2)
⇒ h’ = 3.75 cm
Question 3: A sample of 19K40 disintegrates into two nuclei Ca & Ar with decay constant λCa = 4.5 x 10-10 S-1 and λAr = 0.5 x 10-10 S-1 respectively. The time after which 99% of 19K40 gets decayed is:
- a) 6.2 × 109 sec
- b) 9.2 × 109 sec
- c) 7.2 × 109 sec
- d) 4.2 × 109 sec
Solution:
λ = λ
(1/100) N0 = N0 e-λt
ln(1/100) = -( λ1 + λ2)t + ln 100 = +( λ1 + λ2)t2
⇒ (2.303x2)/(5x10-10) = t
Or t = 9.2 x 109 sec
Question 4: Consider a spherical gaseous cloud of mass density ρ(r) in a free space where r is the radial distance from its centre. The gaseous cloud is made of particles of equal mass m moving in circular orbits about their common centre with the same kinetic energy K. The force acting on the particles is their mutual gravitational force. If ρ(r) is constant with time. The particle number density n(r) = ρ(r)/m is:
(g = universal gravitational constant)
- a) 3K/πr2m2G
- b) K/2πr2m2G
- c) K/πr2m2G
- d) K/6πr2m2G
Solution:
GMm/r = mv2/r = 2/r x ½ x mv2 = 2k/r
M = 2kr/Gm
4πr2 dr ρ = 2k dr/Gm
Or ρ = k/2πGmr2
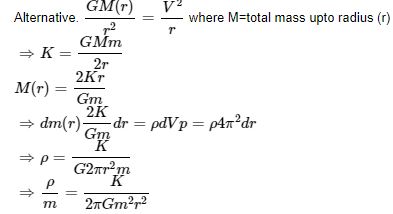
Question 5: A thin spherical insulating shell of radius R caries a uniformly distributed charge such that the potential at its surface is V0. A hole with small area α4πR2 (α <<<1) is made in the shell without effecting the rest of the shell. Which one of the following is correct.
- a) The magnitude of Vector E at a point located on a line passing through the hole and shell’s centre on a distance 2R from the centre of spherical shell will be reduced by αV0/2R
- b) Potential at the centre of shell is reduced by 2αV0
- c) The magnitude of vector E at the centre of shell reduced by αV0/2R
- d) The ratio of potential at the centre of the shell to that of the point at (1/2) R from centre towards the hole will be (1-α)/(1-2α)
Solution:
dq = Q/4πR2 - dA = Qα
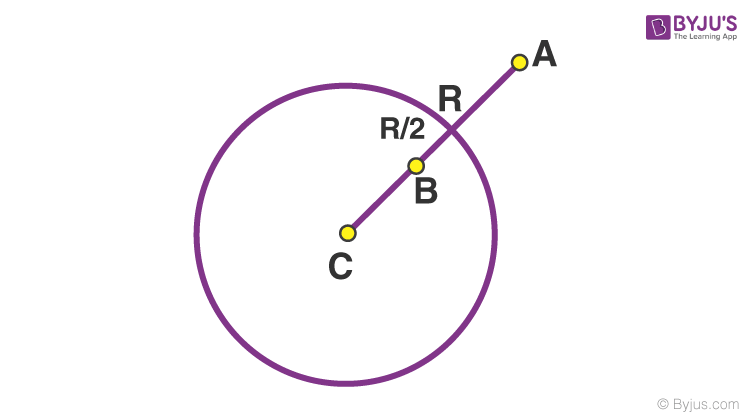
Vc = KQ/R - KαQ/R = V0(1- α)
VB = KQ/R - KαQ/[R/2] = V0(1 - 2α)
Therefore, VC / VB = 1 - α / 1 - 2α
Question 6: A charged shell of radius R carries a total charge Q. Given ϕ as the flux of electric field through a closed cylindrical surface of height h, radius r & with its center same as that of the shell. Here center of cylinder is a point on the axis of the cylinder which is equidistant from its top & bottom surfaces. Which of the following are correct.
- a) If h > 2R and r > R then ϕ = Q/Єo
- b) If h > 2R and r = 4R/5 then ϕ = Q/5Єo
- c) If h < 8R/5 and r = 3R/5 then ϕ = 0
- d) If h > 2R and r = 3R/5 then ϕ = Q/5Єo
Solution:
a, b and d
a.
\(h > 2Rr> R\)<img class="img-responsive" src="https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/JEE-Advanced-2019-Physics-Paper-1-Question-6.jpg" alt="JEE Main 2019 Jan Shift 2 Physics Solutions" />
\(\phi = \frac{Q}{\varepsilon _{o}} \: clearly \: from \: Gauss's \: Law\)b. Suppose,
\(h = \frac{8R}{5}r = \frac{3R}{5}\)<img class="img-responsive" src="https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/JEE-Advanced-2019-Physics-Paper-1-Question-6-2.jpg" alt="JEE Main 2019 Jan Shift 1 Physics Solutions" />
\(\phi = 0\)So for
\(h < \frac{8R}{5}, \;\phi = 0\)c. For h = 2R
r = 4R / 5
<img class="img-responsive" src="https://cdn1.byjus.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/JEE-Advanced-2019-Physics-Paper-1-Question-6-3.jpg" alt="JEE Main 2019 Jan Shift 1 Physics Solutions" />
Shaded charge =
\(2\pi\frac{1 - cos53^{o}\times (Q)}{4\pi }\)∴ = Q/5
∴
\(q_{enclosed} = \frac{2Q}{5}\)∴
\(\phi = \frac{2Q}{5_{\varepsilon_{o} }}\)For h > 2Rr = 4R / 5
∴
\(\phi = \frac{2Q}{5_{\varepsilon_{o} }}\)d. Similar to option c for h = 2R
r = 3R / 5
\(q_{enclosed} = 2 \times 2\pi (1 - cos 37^{o})\frac{Q}{4\pi } = \frac{Q}{5}\)∴
\(\phi = \frac{Q}{5_{\varepsilon_{o} }}\)
Question 7: Which statements is/are corect:

- a) At time t = 0, the S1 is closed instantaneous current in the closed circuit will be 25 mA
- b) The key S1 is kept closed for long time such that capacitors are fully charged. Now key S2 is closed at this time the instantaneous current across 30Ω resistor between P & Q will be 0.2A.
- c) If key S1 is kept closed for long time such that capacitors are fully charged the voltage across C1 will be 4V.
- d) If S1 is kept closed for long time such that capacitors are fully charged the voltage difference between P & Q will be 10V.
Solution:
When S1 is closed then charge on capacitor is zero.
While replacing all capacitors with wire, we have
i = t/[70+100+30] = 5/200 = 25 mA
When circuit is in steady state, q/10 + q/80 + q/80 - 5 = 0
or q = 40 μC
Therefore, voltage across C1 = 40/10 = 4 volt
Just after closing of S2, charge on capacitor remain same, KVL
-10+30x+40/10+y×70=0
or 30x + 70y = 6
Again, -40/80 + 5 + (x-y)30 - 40/80 + (x - y) 100 - 10 + 30x = 0
⇒ 160x - 130y - 6 = 0
Solving both the equations, we have x = 0.05 amp and y = 96/1510
Option (b) and (c) are correct.
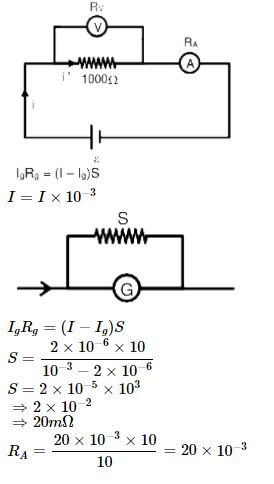
Question 8: A galvanometer of resistance 10 ohm and maximum current of 2μA is converted into voltmeter of range 100 mV and when converted into ammeter then range is 1mA. When these voltmeter and ammeter are connected by a (ideal) battery in series with a resistance of R = 1000 Ω, then
- a) Measured value of R is between 978Ω and 996Ω
- b) Resistance of voltmeter 105Ω
- c) Shunt resistance is 20mΩ
- d) If the ideal battery is replaced by non-ideal battery with internal resistance of 5Ω then R will be > 1000 Ω
Solution:
c
Question 9: Conducting wire of parabolic shape, initially y = x2 is moving with velocity

- a) |Δφ| = (1/2) B0V0L for β = 0
- b) |Δφ| = (4/3) B0V0L for β = 2
- c) |Δφ| is proportional to the length of wire projected on y-axis.
- d) |Δφ| remains same if the parabolic wire is replaced by a straight wire, y = x, initially of length √2l
Solution:

B, C is correct
D is also correct because projection of wire on y axis is same.
Question 10: If in a hypothetical system if the angular momentum and mass are dimensionless. Then which of the following is true.
- a) The linear momentum varies as L-1
- b) The energy varies as L-2
- c) The power varies as L-4
- d) The force varies as L-5
Solution:
[M] = [M0L0T0]
[J] = [ML2T-1]
[ML2T-1] = [M0L0T0]
⇒ [L2] = [T]
Momentum:
[P] = [MLT-2 . LT-1] = [ML2T-3] = [L2L-6] = [L-4]
[E] = [MLT-2 . L] = [L2L-4] = [L-2]
[F] = [LL-4] = [L-3]
Linear Momentum = MLT<sup>-1</sup>
M<sup>o</sup> LL<sup>-2</sup> = Lsup>-1</sup>
Options A,B,C are correct.
Question 11: V – T diagram for n mol monoatomic gas is given below:


- c) Work done in cyclic process is ΔW = nRT0/2
- d) There are only adiabatic and isochoric processes are involved
Solution:
Corresponding PV entraps


(d) There are no adiabatic process is involved.
Only Options (a) and (b) are correct.
Question 12: Apparent depth for point object x in all three cases are H1, H2 & H3 respectively when seen from below given H = 30 cm, n = 1.5 & R = 3m, then

- a) 0.8 < H2 - H1 < 0.9
- b) H2 > H1
- c) H2 > H3
- d) H3 > H1
Solution:
Case 1:
\(\frac{n_2}{n_1} = \frac{d^1}{d}\)⇒ 1/n = d1/(3Q)
⇒ d1 = (30/3) x 2 = 20 cm
Case 2:
\(\frac{n_2}{v} - \frac{n_1}{u}= \frac{n_2-n_1}{R}\)\(\frac{1}{H_2} - \frac{3}{-2 \times 30} = \frac{1-3/2}{-300}\)H2 = 20.684
Case 3:
\(\frac{n_2}{v} - \frac{n_1}{u}= \frac{n_2-n_1}{R}\)\(\frac{1}{H_3} - \frac{3}{-2 \times 30} = \frac{1-\frac{3}{2}}{-300}\)\(H_{3} = \frac{600}{31} = 19.354 cm\)V3 = 19.354
Question 13:
Consider the following nuclear fission reaction

In this fission reaction. Kinetic energy of α-particle emitted is 4.44 MeV. Find the energy emitted as γ – radiation in keV in this reaction.
m(88Ra226) = 226.005 amu
m(2He4) = 4.000 amu
Solution:
Δm = 0.005 amu

Question 14: N dielectrics are introduced in series in a capacitor of thickness D. Each dielectric have width d = D/N &
dielectric constant of mth dielectric is given by Km = K(1 + m/N) : [N >> 103, Area of plates = A]
Net capacitance is given by [KЄoA]/[αDln2]. Find value of α.
Solution:
x/m = Δ/N

Integrating we get
Ceq = [KЄoA]/[Dln2]
Therefore, α = 1
Question 15: If at angle θ the light takes maximum time to travel in optical fiber. Then the maximum time is x (10-8), calculate x.
Solution:

1.5 sin θC = 1.44 sin 900
sin θC = 24/25
and sin θC = x/d
⇒ d = 25x/24
Now,
t = L/(C/n2) = 5 x 10-8s
Putting: C = 3 x 108, n2 = 1.5 and L = 10
Question 16: The source S1 is at rest. The observer and the source S2 are moving towards S1 as shown in figure. The roof beats observed by the observer if both sources have frequency 120 Hz and speed of sound 330 m/s in is

Solution:
Question 17: A weight of 100 N is suspended by two wires made by steel and copper as shown in figure length of steel wire is 1 m and copper wire is √3 m. Find ratio of change in length of copper wire (Δ l0) to change in length of steel wire (Δ ls). Given Young’s modulus: Ysteel = 2 × 1011 N/m2, Ycopper = 1 × 1011 N/m2.

Solution:
Question 18: An optical bench, to measure the focal length of lens, is 1.5 m long and on the bench marks are with spacing 1/4 cm. Now a lens is placed at 75 cm and pin type object is placed at 45 cm marks on the bench. If its image is formed at 135 cm find maximum possible error in calculation of focal length.
Solution:
V = 30 cm and dv = 0.5 cm
V = 60 cm and dv = 0.5 cm
Now, using lens formula,
1/v - 1/u = 1/f
1/60 + 1/30 = 1/f
⇒ f = 20 cm
⇒
\(\frac{-dv}{v^2} + \frac{-du}{u^2} = \frac{-df}{f^2}\)⇒
\(\frac{df}{f} \times 100 = f[\frac{dv}{v^2} + \frac{du}{u^2}]\)= (20/2)[1/602 + 1/302]
Multiply by 100 both the sides, we get
df/f = 1.38 and 1.39