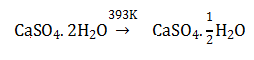JEE Main is an examination conducted for admission to some of the reputed institutions in the country. It is the dream of many students to crack this examination. One of the best ways to prepare for the examination is by practising previous years’ question papers. On this page, JEE Main 2020 Chemistry paper is solved. Practise these questions to get an excellent score in the examination.
January 8 Shift 1 - Chemistry
1. The number of bonds between sulphur and oxygen atoms in S2O82− and number of bonds between sulphur and sulphur atoms in rhombic sulphur, respectively, are:
- a. 8 and 6
- b. 4 and 6
- c. 8 and 8
- d. 4 and 8
Solution:
-
Here, we have to count S − O single bonds as well as S = O in S2O82–, as each double bond also has one sigma bond. The structure of S2O82- and S8 is shown below:

2. The predominant intermolecular forces present in ethyl acetate, a liquid, are:
- a. London dispersion, dipole-dipole and hydrogen bonding
- b. hydrogen bonding and London dispersion
- c. dipole-dipole and hydrogen bonding
- d. London dispersion and dipole-dipole
Solution:
-
London dispersion forces (also called as induced dipole - induced dipole interactions), exist because of the generation of temporary polarity due to collision of particles and for this very reason, they are present in all molecules and inert gases as well.
Because of the presence of a permanent dipole, there will be dipole-dipole interactions present here.
There is no H that is directly attached to an oxygen atom, so H-bonding cannot be present.
3. For the Balmer series in the spectrum of H-atom,
v̅ = RH [ (1/n12) – (1/n22)]
The correct statements among (A) to (D) are:
A) The integer n1= 2.
B) The ionization energy of hydrogen can be calculated from the wave number of these lines.
C) The lines of longest wavelength corresponds to n2= 3.
D) As wavelength decreases, the lines of the series converge.
- a. B, C, D
- b. A, B, D
- c. A, C, D
- d. A, B, C
Solution:
-
- is correct since the series studied in H-spectrum, including Balmer series, are de-excitation series or emission series. So, electrons get de-excited to n= 2 which means that nlower= 2.
- It is possible to obtain I.E. from the formula above, but since the question has stated the formula for the Balmer series, nlower has been fixed as 2. So, it is not possible to calculate I.E. from it. To calculate I.E., we’ll have to put nlower= 1, which isn’t possible here.
- ΔE = hc/λ
With nlower fixed as 2, ΔE increases as nhigher is increased. So, the last line of the Balmer series,i.e. from infinity to n= 2, will have the maximum energy in the series and thus, the lowest wavelength. Similarly, the first line in the series, i.e. from n= 3 to n= 2 will have the lowest energy in the series and thus, the highest wavelength. Which makes this statement correct. - As orbits with higher orbit number or those that are further away from the nucleus are considered, the energy gap in-between subsequent orbits decrease. Now, consider the following for example and with nlower fixed as 2.
Energy of a photon released on transition from n= 100 to n= 2 will have similar energy to that of the photon that gets released on transition from n= 101 to n= 2, because energy of the 100th and the 101th orbit will be very close in value. That means they will also have very close values of wavelengths, which further implies that these two lines will be situated quite close to each other on the photographic plate.
In a similar fashion, we can see that as the nhigher increases, the lines start to converge together. And since, increasing the nhigher will indeed lead to an increase in the energy of the photon released, it will end up releasing photons of shorter wavelengths. Combining these two statements we can easily see that as the wavelength decreases, the spectral lines start to converge.
4. The first ionization energy (in kJ/mol) of Na, Mg, Al and Si, respectively,
- a. 496, 737, 577, 786
- b. 496, 577, 737, 786
- c. 496, 577, 786, 737
- d. 786, 737, 577, 496
Solution:
-
The expected order is Na < Mg < Al < Si.
But the actual/experimental order turns out to be Na < Al < Mg < Si, because of the fully filled s- sub shell of magnesium and the s2p1 configuration of Al which makes it relatively easy for Al to lose its outermost electron.
5. The stoichiometry and solubility product of a salt with the solubility curve given below is, respectively: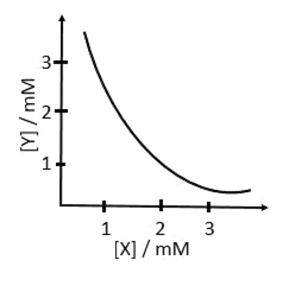
- a. X2Y, 2 x 10−9M3
- b. XY2, 1 x 10−9M3
- c. XY2, 4 x 10−9M3
- d. XY, 2 x 10−6M3
Solution:
-
(a) X2Y(s) ⇌ 2X+ + Y2−
Ksp = [X+]2[Y2−] = 4 × 10−6 × 10−3 = 4 × 10−9
(b) XY2(s) ⇌ X2+ + 2Y−
Ksp = [X2+][Y−]2 = 10−3 × 4 × 10−6 = 4 × 10−9
(c) XY2(s) ⇌ X2+ + 2Y−
Ksp = [X2+][Y−]2 = 10−3 × ( 2 × 10−3)2 = 4 × 10−9
(d) XY(s) ⇌ X+ + Y−
Ksp = [X+][Y−] = 10−3 × 10−3 = 10−6
6. The complex that can show fac- and mer-isomers is:
- a. [Co(NO2)3(NH3)3]
- b. [PtCl2(NH3)2
- c. [Co(NH3)4Cl2]
- d. [CoCl2(en)2]
Solution:
-
Facial and meridional geometrical isomerism is observed only in [MA3B3] type complexes which is given in option a.
7. A graph of vapour pressure and temperature for three different liquids X, Y and Z is shown below: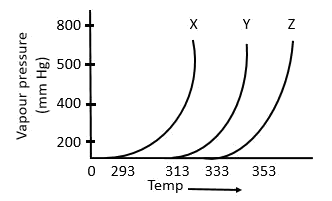
The following inferences are made:
A) X has higher intermolecular interactions compared to Y
B) X has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y
C) Z has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y The correct inference(s) is/are:
- a. C
- b. A
- c. B
- d. A and C
Solution:
-
As shown in the plot below, for the same T, the vapour pressure of X is the highest and of Z is the lowest. Now, that means with the same average K.E. of X, Y and Z molecules, the X molecules are able to compensate their respective intermolecular forces better. So, X molecules have the highest vapour pressure. This implies that the intermolecular forces in X are the weakest among the three. The opposite could be said for Z as well.

8. As per Hardy-Schulze formulation, the flocculation values of the following for ferric hydroxide sol are in the order:
- a. AlCl3 > K3[Fe(CN)6] > K2CrO4 > KBr = KNO3
- b. K3 [Fe(CN)6 ] < K2CrO4 < AlCl3 < KBr < KNO3
- c. K3 [Fe(CN)6 ] < K2CrO4 < KBr = KNO3 = AlCl3
- d. K3 [Fe(CN)6 ] > AlCl3 > K2CrO4 > KBr > KNO3
Solution:
- The minimum concentration of an electrolyte which is required to cause the coagulation or flocculation of a sol is known as flocculation value. Flocculation value is inversely proportional to coagulation power (coagulation power is directly proportional to the valency of the ions causing coagulation). Fe(OH)3 sol is a positive sol and thus we have to consider the valency of the anions in the given electrolytes.
9. The rate of a certain biochemical reaction at physiological temperature (T) occurs 106 times faster with enzyme than without. The change in activation energy upon adding enzyme is:
- a. − 6RT
- b. – 6 × 2.303 RT
- c. + 6RT
- d. +6 × 2.303 RT
Solution:
-
K1 = Ae−Ea1/RT ....(1)
K2 = Ae−Ea2/RT ....(2)
Dividing equation 1 with equation 2, we get
K1/K2 = e (Ea2−Ea1)/RT
10−6 = e (Ea2−Ea1)/RT
Taking loge on both sides, we get
∆E = Ea2 − Ea1 = – 6 × 2.303 RT
10. When gypsum is heated to 393K, it forms:
- a. CaSO4. 1/2 H2O
- b. Dead burnt plaster
- c. CaSO4 5H2O
- d. Anhydrous CaSO4
Solution:
11. The third ionization enthalpy is minimum for:
- a. Mn
- b. Co
- c. Ni
- d. Fe
Solution:
Consider an element E
E2+ → E3+ would be the 3rd I.E. of the element E.
Electronic configuration of Mn is [Ar]4s23d5, Co is [Ar]4s23d7, Fe is [Ar]4s23d6, Ni is [Ar]4s23d8
Electronic configuration of Mn2+ is [Ar]3d5, Co2+ is [Ar]3d7, Fe2+ is [Ar]3d6, Ni2+ is [Ar]3d8
As it is evident from the above configurations of the E2+ for the given elements, Fe2+ would require the least amount of energy for removal of electron as it has the configuration 3d6 4s0. That means that its E3+ form is the most stable among the four elements provided in their respective E3+ states, i.e., when compared, the next electron removal will require least amount of energy.
12. The strength of an aqueous NaOH solution is most accurately determined by titrating: (Note: consider that an appropriate indicator is used)
- a. Aq. NaOH in a pipette and aqueous oxalic acid in a burette
- b. Aq. NaOH in a volumetric flask and concentrated H2SO4 in a conical flask
- c. Aq. NaOH in a burette and concentrated H2SO4 in a conical flask
- d. Aq. NaOH in a burette and aqueous oxalic acid in a conical flask
Solution:
- The standard solution is usually kept in burette. The oxalic acid is a primary standard solution while H2SO4 is a secondary standard solution.
13. The decreasing order of reactivity towards dehydrohalogenation (E1) reaction of the following compounds is:
- a. B > A > D > C
- b. B > D > C > A
- c. B > D > A > C
- d. D > B > C > A
Solution:
- In E1mechanism, the rate determining step is formation of carbocation. So, stability of carbocation formed decides the rate. In option D, the cation formed is resonance stabilised. In option C, the cation formed is a 2 o carbocation. In option A and B, the carbocations formed are 1 o but there is a chance of rearrangement in option b and after the rearrangement, the carbocation formed in option b will be allylic. So, the order of reaction is as follows: D > B > C > A.
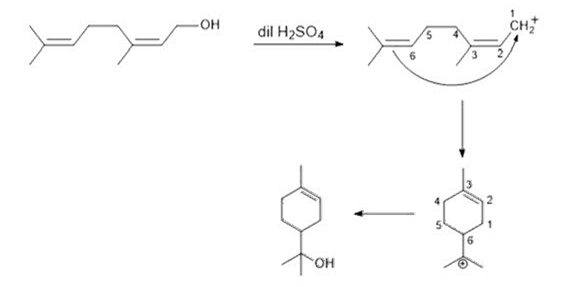
14. Major product in the following reaction is: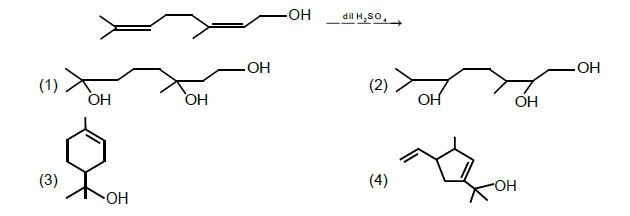
Solution:
15. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of C—OH bond length: methanol, phenol, p-ethoxyphenol
- a. Phenol < methanol < p-ethoxyphenol
- b. methanol < p-ethoxyphenol < phenol
- c. Phenol < p-ethoxyphenol < methanol
- d. methanol < phenol < p-ethoxypheno
Solution:
- In methanol, there is no resonance. In phenol, there is resonance. In p-Ethoxyphenol, there is resonance involved but the involvement of lone pair of oxygen in OH group is poor as compared with phenol due to the presence of lone pair oxygen in OCH3 group which are also involved in resonance. So, partial double bond character develops in C—OH bond of phenol and p-ethoxyphenol but in case of p-ethoxyphenol, resonance is poor as compared to phenol. So, bond length follows the order: methanol > p-ethoxyphenol > phenol
16. Among the gases (i) – (v), the gases that cause greenhouse effect are:
i. ??2
ii. ?2?
iii. ???
iv. ?2
v. ?3
- a. i, ii iii and iv
- b. i, iii, iv and v
- c. i and iv
- d. i, ii, iii and v
Solution:
- ??2, ?3, ?2? vapours and ???′? are green house gases.
17. The major products A and B in the following reactions are:


Solution:
18. A flask contains a mixture of isohexane and 3-methylpentane. One of the liquids boils at 63 °C while the other boils at 60 °C. What is the best way to separate the two liquids and which one will be distilled out first?
- a. Fractional distillation, isohexane
- b. Simple distillation, 3-methylpentane
- c. Fractional distillation, 3-methylpentane
- d. Simple distillation, isohexane
Solution:
- When the difference between the B.P. of the two liquids is less than around 40 ??, fractional distillation is more efficient. The difference between the boiling points of isohexane and 3-methylpentane is only 3 degrees. So, fractional distillation is the best suitable method. Since, isohexane has a lower boiling point, it comes out first.
19. Which of the given statement is not true for glucose?
- a. The pentacetate glucose does not react with hydroxylamine to give oxime
- b. Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form oxime.
- c. Glucose gives Schiff's test for aldehyde.
- d. Glucose exists in two crystalline forms alpha and beta.
Solution:
-
Glucose exists in two crystalline forms alpha and beta which are anomers of each other.
Glucose does not react with Schiff’s reagent because after the internal cyclisation, it forms either alpha- anomer or beta-anomer. In these forms, free aldehydic group is not present.
Glucose forms open chain structure in aqueous solution which contains aldehyde at chain end. This aldehydic group reacts with NH4OH to form oxime. On the other hand, glucose penta acetate being a cyclic structure even in aqueous form does not have terminal carbonyl group. Therefore it will not react with ??4??.
20. The reagent used for the given conversion is: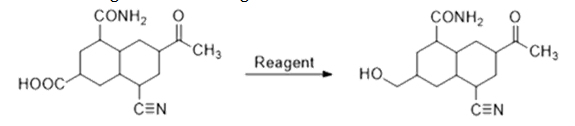
- a. ?2?6
- b. ?????4
- c. ????4
- d. ?2, ??
Solution:
- ?2?6 does not reduce amide, carbonyl group and cyanide. It selectively reduces carboxylic acid to alcohol. So, for this conversion, it is the best suitable reagent.
21. The volume (in mL) of 0.125 M ????3 required to quantitatively precipitate chloride ions in 0.3 g of [?(??3 )6 ]??3 is _____.
[??(??3 )6 ]??3 = 267.46 ?/???
?????3 = 169.87 g/mpl
Solution:
To react completely with one mole of [??6]?3 , 3 moles of ????3 is required.
0.3 g [??6 ]?3 means (0.3/267.46) moles of [??6 ]??3.
So, moles of ????3 required will be (0.3×3)/267.46 moles
To find the volume, (0.3×3)/267.46 = 0.125× (?)
(?) = 0.02692
(??) = 26.92
22. What will be the electrode potential for the given half cell reaction at pH= 5?
2?2? → ?2 + 4?+ + 4?–; ?° = – 1.23 ?
(R=8.314 J mol-1K-1; temp.=298 K; oxygen under std. atm. Pressure of 1 bar.)
Solution:
2?2? → ?2 + 4?+ + 4?–; ?° = – 1.23 ?

23. Ferrous sulphate heptahydrate is used to fortify foods with iron. The amount (in grams) of the salt required to achieve 10 ppm of iron in 100 kg of wheat is _______. Atomic weight: Fe=55.85; S=32.00; O=16.00)
Solution:
- 10 ppm of Fe means 10 g of Fe in 106 g of wheat. So, for 100 kg i.e.,105 g of wheat. ?? needed is 1 g. So, for 1 g of Fe, the mass of ????4. 7?2? required is 278/56 = 4.96 g.
24. The magnitude of work done by gas that undergoes a reversible expansion along the path ABC shown in figure is 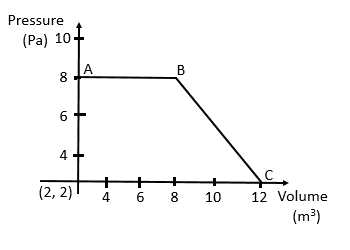
Solution:
Work done by the gas
= The area under the curve
= (Area of the square) + (Area of the triangle)
= 48 J
25. The number of chiral centres in Penicillin is ____.
Solution:
The structure of penicillin is shown below:

So, the number of chiral centers= 3