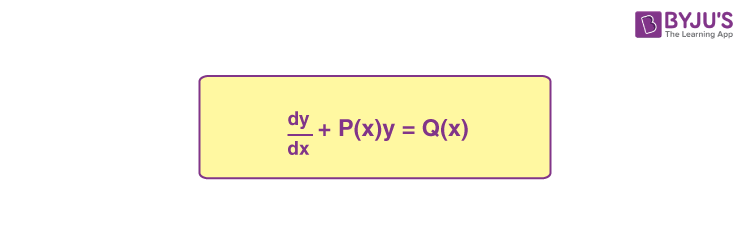| Unit 1: Sets, Relations, and Functions |
- Sets and their representation.
- Union, intersection, and complement of sets and their algebraic properties.
- Powerset.
- Relation, Types of relations, equivalence relations.
- Functions; one-one, into and onto functions, the composition of functions.
|
| Unit 2: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations |
- Complex numbers as ordered pairs of reals.
- Representation of complex numbers in the form (a+ib) and their representation in a plane, Argand diagram.
- Algebra of complex numbers, modulus and argument (or amplitude) of a complex number, square root of a complex number.
- Triangle inequality.
- Quadratic equations in real and complex number system and their solutions.
- The relation between roots and coefficients, nature of roots, the formation of quadratic equations with given roots.
|
| Unit 3: Matrices and Determinants |
- Matrices: Algebra of matrices, types of matrices, and matrices of order two and three.
- Determinants: Properties of determinants, evaluation of determinants, the area of triangles using determinants.
- Adjoint and evaluation of inverse of a square matrix using determinants and elementary transformations.
- Test of consistency and solution of simultaneous linear equations in two or three variables using determinants and matrices.
|
| Unit 4: Permutations and Combinations |
- The fundamental principle of counting.
- Permutation as an arrangement and combination as a selection.
- The meaning of P (n,r) and C (n,r). Simple applications.
|
| Unit 5: Mathematical Induction |
| The principle of Mathematical Induction and its simple applications. |
| Unit 6: Binomial Theorem |
- Binomial theorem for a positive integral index.
- General term and middle term.
- Properties of Binomial coefficients and simple applications.
|
| Unit 7: Sequence and Series |
- Arithmetic and Geometric progressions, insertion of arithmetic.
- Geometric means between two given numbers.
- The relation between A.M. and G.M.
- Sum up to n terms of special series: Sn, Sn2, Sn3.
- Arithmetico Geometric progression.
|
| Unit 8: Limit, Continuity and Differentiability |
- Real-valued functions, algebra of functions, polynomials, rational, trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential functions, inverse functions.
- Graphs of simple functions.
- Limits, continuity, and differentiability.
- Differentiation of the sum, difference, product, and quotient of two functions.
- Differentiation of trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential, composite and implicit functions; derivatives of order up to two.
- Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems.
- Applications of derivatives: Rate of change of quantities, monotonic increasing and decreasing functions, Maxima, and minima of functions of one variable, tangents, and normals.
|
| Unit 9: Integral Calculus |
- Integral as an antiderivative.
- Fundamental integrals involving algebraic, trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions.
- Integration by substitution, by parts, and by partial fractions.
- Integration using trigonometric identities.
- Integral as limit of a sum.
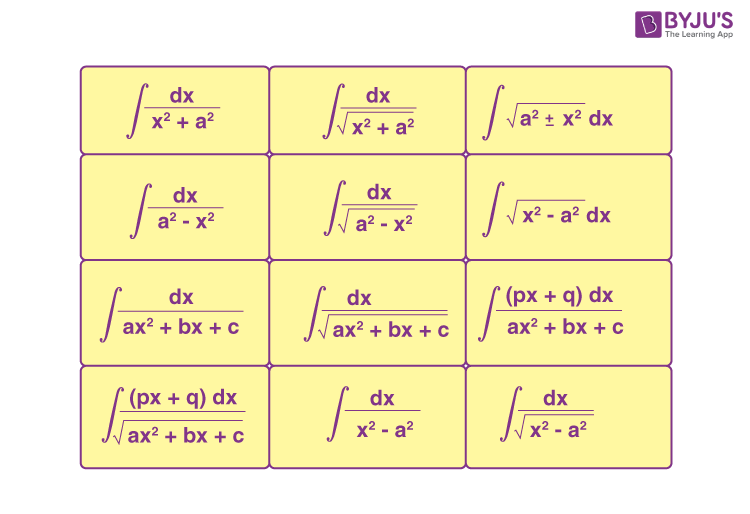
- Evaluation of simple integrals:

- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
- Properties of definite integrals, evaluation of definite integrals, determining areas of the regions bounded by simple curves in standard form.
|
| Unit 10: Differential Equations |
- Ordinary differential equations, their order, and degree.
- Formation of differential equations.
- The solution of differential equations by the method of separation of variables.
- The solution of homogeneous and linear differential equations of the type:

|
| Unit 11: Coordinate Geometry |
- Cartesian system of rectangular coordinates in a plane, distance formula, section formula, locus, and its equation, translation of axes, the slope of a line, parallel and perpendicular lines, intercepts of a line on the coordinate axes.
- Straight lines: Various forms of equations of a line, intersection of lines, angles between two lines, conditions for concurrence of three lines.
- Distance of a point from a line, equations of internal and external bisectors of angles between two lines, coordinates of the centroid, orthocentre, and circumcentre of a triangle, equation of the family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines.
- Circles, conic sections: Standard form of the equation of a circle, the general form of the equation of a circle, its radius and centre, equation of a circle when the endpoints of a diameter are given, points of intersection of a line and a circle with the centre at the origin and condition for a line to be tangent to a circle, equation of the tangent.
- Sections of cones, equations of conic sections (parabola, ellipse, and hyperbola) in standard forms, condition for y = mx + c to be a tangent and point (s) of tangency.
|
| Unit 12: 3D Geometry |
- Coordinates of a point in space, the distance between two points.
- Section formula, direction ratios and direction cosines, the angle between two intersecting lines.
- Skew lines, the shortest distance between them and its equation.
- Equations of a line and a plane in different forms, the intersection of a line and a plane, coplanar lines.
|
| Unit 13: Vector Algebra |
- Scalars and Vectors. Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of vectors.
- Vector’s Components in 2D and 3D space.
- Scalar products and vector products, triple product.
|
| Unit 14: Statistics and Probability |
- Measures of Dispersion: Calculation of mean, mode, median, variance, standard deviation, and mean deviation of ungrouped and grouped data.
- Probability: Probability of events, multiplication theorems, addition theorems, Baye’s theorem, Bernoulli trials, Binomial distribution and probability distribution.
|
| Unit 15: Trigonometry |
- Identities of Trigonometry and Trigonometric equations.
- Functions of Trigonometry.
- Properties of Inverse trigonometric functions.
- Problems on Heights and Distances.
|
| Unit 16: Mathematical Reasoning |
- Statements and logical operations: or, and, implied by, implies, only if and if.
- Understanding of contradiction, tautology, contrapositive and converse.
|