NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Updated for 2021-22 Session – Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths for all the exercises from Chapters 1 to 15 are provided here. These NCERT Solutions are curated by our expert faculty to help students in their term wise exam preparations. Students looking for the NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths can download all chapter-wise PDF to find a better approach to solve the problems.
The answers to the questions present in the NCERT books are undoubtedly the best study material a student can get hold of. These CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths 2021-22 will also help students to build a deeper understanding of concepts covered in textbook. Practising the textbook questions will help students analyze their level of preparation and the knowledge of concepts. The solutions to these questions present in the books can help students to clear their doubts quickly.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths ChaptersNCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter DetailsCBSE Class 10 Maths Exam Pattern 2021-2022CBSE Class 10 Chapter-wise Marks WeightageCBSE Question Paper Design

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapters
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths list comprises all the chapter-wise answers to the questions present in the NCERT Book for Class 10 Maths written in a very precise and lucid manner, maintaining the objective of textbooks. The students can refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 as their additional references and study materials. Practising NCERT textbook exercise solutions will surely help the students in their preparation for the examination.

NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter Details and Exercises
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers – Term I
In Chapter 1 of Class 10, students will explore real numbers and irrational numbers. The chapter starts with the Euclid’s Division Lemma which states that “Given positive integers a and b, there exist unique integers q and r satisfying a = bq + r, 0≤r<b”. The Euclid’s Division algorithm is based on this lemma and is used to calculate the HCF of two positive integers. Then, the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic is defined which is used to find the LCM and HCF of two positive integers. After that, the concept of an irrational number, a rational number and decimal expansion of rational numbers are explained with the help of theorem.
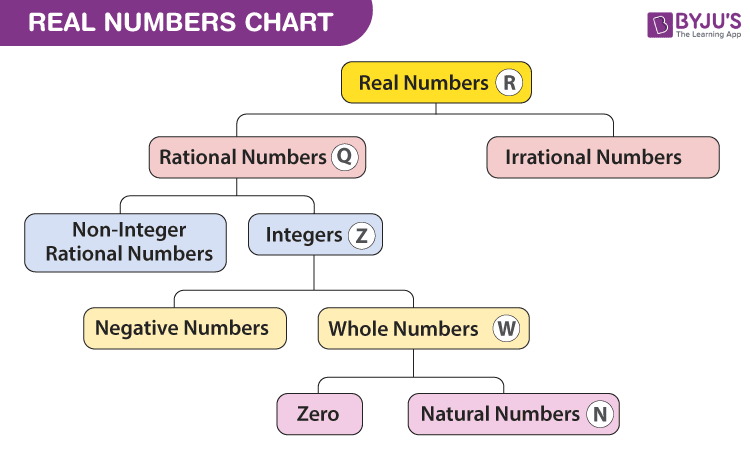
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers for Term I:
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic – statements after reviewing work done earlier and after illustrating and motivating through examples. Decimal representation of rational numbers in terms of terminating/non-terminating recurring decimals.
Important Steps –
To obtain the HCF of two positive integers, say c and d, with c > d, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Apply Euclid’s division lemma, to c and d. So, we find whole numbers, q and r such that c = dq + r, 0 ≤ r < d.
Step 2: If r = 0, d is the HCF of c and d. If r ≠ 0, apply the division lemma to d and r.
Step 3: Continue the process till the remainder is zero. The divisor at this stage will be the required HCF. This algorithm works because HCF (c, d) = HCF (d, r) where the symbol HCF (c, d) denotes the HCF of c and d, etc.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 1 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions Real Numbers Class 10 Exercise 1.1 – 5 Questions (4 Long Answers, 1 Short Answer) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Real Numbers Class 10 Exercise 1.2 – 7 Questions (4 Long Answers, 3 Short Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Real Numbers Class 10 Exercise 1.3 – 3 Questions (3 Short Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Real Numbers Class 10 Exercise 1.4 – 3 Questions (3 Short Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 1 Real Numbers at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Real Numbers Class 10 Notes
- Real Numbers Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Real Numbers
- RD Sharma Solutions Real Numbers Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials – Term I
In Polynomials, the chapter begins with the definition of degree of the polynomial, linear polynomial, quadratic polynomial and cubic polynomial. This chapter has a total of 4 exercises including an optional exercise. Exercise 2.1 includes the questions on finding the number of zeroes through a graph. It requires the understanding of Geometrical Meaning of the Zeroes of a Polynomial. Exercise 2.2 is based on the Relationship between Zeroes and Coefficients of a Polynomial where students have to find the zeros of a quadratic polynomial and in some of the questions they have to find the quadratic polynomial. In Exercise 2.3, the concept of division algorithm is defined and students will find the questions related to it. The optional exercise, 2.4 consists of the questions from all the concepts of Chapter 2.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials for Term I:
Zeroes of a polynomial. Relationship between zeroes and coefficients of quadratic polynomials only.
Important Steps –
We first arrange the terms of the dividend and the divisor in the decreasing order of their degrees. Recall that arranging the terms in this order is called writing the polynomials in standard form.
Step 1: To obtain the first term of the quotient, divide the highest degree term of the dividend by the highest degree term of the divisor. Then carry out the division process.
Step 2: Now, to obtain the second term of the quotient, divide the highest degree term of the new dividend by the highest degree term of the divisor. Again, carry out the division process.
Step 3: Now, the degree of the remainder is less than the degree of the divisor. So, we cannot continue the division any further.
Here again, we see that Dividend = Divisor × Quotient + Remainder What we are applying here is an algorithm which is similar to Euclid’s division algorithm that you studied in Chapter 1.
This says that
If p(x) and g(x) are any two polynomials with g(x) ≠ 0, then we can find polynomials q(x) and r(x) such that
p(x) = g(x) × q(x) + r(x),
where r(x) = 0 or degree of r(x) < degree of g(x).
This result is known as the Division Algorithm for polynomials.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 2 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions Polynomials Class 10 Exercise 2.1 – 1 Question (1 Short Answer) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Polynomials Class 10 Exercise 2.2 – 2 Questions (2 Short Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Polynomials Class 10 Exercise 2.3 – 5 Questions (2 Short Answers, 3 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Polynomials Class 10 Exercise 2.4 – 5 Questions (2 Short Answers, 3 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 2 Polynomials at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Polynomials Class 10 Notes
- Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Polynomials
- RD Sharma Solutions Polynomials Class 10
NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables – Term I
This chapter explains the concept of Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables. This chapter has a total of 7 exercises, and in these exercises, different methods of solving the pair of linear equations are described. Exercise 3.1 describes how to represent a situation algebraically and graphically. Exercise 3.2 explains the methods of solving the pair of the linear equation through Graphical Method. Exercises 3.3, 3.4, 3.5 and 3.6 describe the Algebraic Method, Elimination Method, Cross-Multiplication Method, Substitution Method, respectively. Exercise 3.7 is an optional exercise which contains all types of questions. Students must practise these exercises to master the method of solving the linear equations.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables for Term I:
Pair of linear equations in two variables and graphical method of their solution, consistency/inconsistency. Algebraic conditions for number of solutions. Solution of a pair of linear equations in two variables algebraically – by substitution and by elimination. Simple situational problems. Simple problems on equations reducible to linear equations.
Important Formulas –
The general form for a pair of linear equations in two variables x and y is
a1 x + b1 y + c1 = 0
and a2 x + b2 y + c2 = 0,
where a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 are all real numbers and a1 2 + b1 2 ≠ 0, a2 2 + b2 2 ≠ 0.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 3 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.1 – 3 Questions (2 Short Answers, 1 Long Answer) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.2 – 7 Questions (5 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.3 – 3 Questions (2 Short Answers, 1 Long Answer) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.4 – 2 Questions (2 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.5 – 4 Questions (4 Short Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.6 – 2 Questions (2 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Maths Exercise 3.7 – 8 Questions (1 Short Answer, 7 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Notes
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 Important Questions,
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- RD Sharma Solutions Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10
NCERT Solutions of Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations – Term II
In this chapter, students will get to know the standard form of writing a Quadratic Equation. The chapter goes on to explain the method of solving the quadratic equation through the factorization method and completing the square method. The chapter ends with the topic on finding the nature of roots which states that, a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 has
- Two distinct real roots, if b² – 4ac > 0
- Two equal roots, if b² – 4ac = 0
- No real roots, if b² – 4ac < 0
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations for Term II:
Standard form of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, (a ≠ 0). Solutions of quadratic equations (only real roots) by factorization, and by using quadratic formula. Relationship between discriminant and nature of roots. Situational problems based on quadratic equations related to day to day activities (problems on equations reducible to quadratic equations are excluded)
Important Formulas –
If b 2 – 4ac > 0, we get two distinct real roots
[latex]-\frac{b}{2a}+\frac{\sqrt{b^{2}-4ac}}{2a}\: and\: -\frac{b}{2a}-\frac{\sqrt{b^{2}-4ac}}{2a}[/latex]If b 2 – 4ac = 0, then
[latex]\\x=-\frac{b}{2a}\pm 0 \\ \\x=-\frac{b}{2a}\: or-\frac{b}{2a}[/latex]So, the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are both -b/2a.
Therefore, we say that the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has two equal real roots in this case.
If b 2 – 4ac < 0, then there is no real number whose square is b 2 – 4ac. Therefore, there are no real roots for the given quadratic equation in this case.
Since b 2 – 4ac determines whether the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has real roots or not, b 2 – 4ac is called the discriminant of this quadratic equation.
So, a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has
(i) two distinct real roots, if b 2 – 4ac > 0,
(ii) two equal real roots, if b 2 – 4ac = 0,
(iii) no real roots, if b 2 – 4ac < 0.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 4 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions Maths Quadratic Equations Class 10 Exercise 4.1 – 2 Questions (1 Short Answer, 1 Long Answer) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Maths Quadratic Equations Class 10 Exercise 4.2 – 6 Questions (6 Short Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Maths Quadratic Equations Class 10 Exercise 4.3 – 11 Questions (8 Short Answers, 3 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Maths Quadratic Equations Class 10 Exercise 4.4 – 5 Questions (2 Short Answers, 3 Long Answer) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Quadratic Equations Class 10 Notes
- Quadratic Equations Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations
- RD Sharma Solutions Quadratic Equations Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions – Term II
This chapter introduces students to a new topic that is Arithmetic Progression, i.e. AP. The chapter constitutes a total of 4 exercises. In Exercise 5.1, students will find the questions related to representing a situation in the form of AP, finding the first term and difference of an AP, finding out whether a series is AP or not. Exercise 5.2 includes the questions on finding out the nth term of an AP by using the following formula;
an = a + (n-1) d
The next exercise i.e., 5.3, contains the questions on finding the sum of first n terms of an AP. The last exercise includes higher-level questions based on AP to enhance students’ analytical and problem-solving skills.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions for Term II:
Motivation for studying Arithmetic Progression Derivation of the nth term and sum of the first n terms of A.P. and their application in solving daily life problems.
(Applications based on sum to n terms of an A.P. are excluded)
Important Formulas –
If a1, a2, a3, a4, a5, a6,… are the terms of AP and d is the common difference between each term, then we can write the sequence as; a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, a+4d, a+5d,….,nth term… where a is the first term. Now, nth term for arithmetic progression is given as;
nth term = a + (n-1) d
Sum of the first n terms in Arithmetic Progression;
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n-1) d]
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 5 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 5.1 – 4 questions (1 Short Answer, 3 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 5.2 – 20 questions (10 Short Answers, 10 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 5.3 – 20 Questions (7 Short Answer, 13 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 5.4 – 5 Questions (5 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Arithmetic Progressions Class 10 Notes
- Arithmetic Progressions Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Arithmetic Progressions
- RD Sharma Solutions Arithmetic Progressions Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles – Term I
In Chapter 6 of Class 10 CBSE Maths, students will study those figures which have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. The chapter Triangles starts with the concept of a similar and congruent figure. It further explains the condition for the similarity of two triangles and theorems related to the similarity of triangles. After that, the areas of similar triangles have been explained with a theorem. At the end of this chapter, the Pythagoras Theorem and converse of Pythagoras Theorem is described.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 6 Triangles for Term I:
Definitions, examples, counter examples of similar triangles.
1. (Prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
2. (Motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side.
3. (Motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar.
4. (Motivate) If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their corresponding angles are equal and the two triangles are similar.
5. (Motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar.
6. (Motivate) If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse, the triangles on each side of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other.
7. (Motivate) The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides.
8. (Prove) In a right triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides.
9. (Motivate) In a triangle, if the square on one side is equal to sum of the squares on the other two sides, the angle opposite to the first side is a right angle.
Important Theorems –
Theorem 6.1: If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Theorem 6.2: If a line divides any two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, then the line is parallel to the third side.
Theorem 6.3: If in two triangles, corresponding angles are equal, then their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion) and hence the two triangles are similar.
Theorem 6.4: If in two triangles, sides of one triangle are proportional to (i.e., in the same ratio of ) the sides of the other triangle, then their corresponding angles are equal and hence the two triangles are similar.
Theorem 6.5: If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of the other triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, then the two triangles are similar.
Theorem 6.6: The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Theorem 6.7: If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse, then triangles on both sides of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other.
Theorem 6.8: In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Theorem 6.9: In a triangle, if square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite the first side is a right angle.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 6 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.1 – 3 Questions (3 Short Answers) |
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.2 – 10 Questions (9 Short Answers, 1 Long Answer) |
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.3 – 16 Questions (12 Short Answers, 4 Long Answers) |
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.4 – 9 Questions (7 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.5 – 17 Questions (15 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞Triangles Class 10 Exercise 6.6 – 10 Questions (5 Short Answers, 5 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 6 Triangles at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Triangles Class 10 Notes
- Triangles Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Triangles
- RD Sharma Solutions Triangles Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry – Term I
In this chapter, students will learn how to find the distance between two points whose coordinates are given, and to find the area of the triangle formed by three given points. Along with this, students will also study how to find the coordinates of the point which divides a line segment joining two given points in a given ratio. For this purpose, students will get introduced to Distance Formula, Section Formula and Area of a Triangle in this chapter of Coordinate Geometry.

Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry for Term I:
LINES (In two-dimensions)
Review: Concepts of coordinate geometry, graphs of linear equations. Distance formula. Section formula (internal division)
Important Formulas –
Distance Formula
[latex]PQ=\sqrt{(x_{2}-x_{1})^{2}+(y_{2}-y_{1})^{2}}[/latex]Section Formula
[latex]m_{1}:m_{2}=(\frac{m_{1}x_{2}+m_{2}x_{1}}{m_{1}+m_{2}},\frac{m_{1}y_{2}+m_{2}y_{1}}{m_{1}+m_{2}})[/latex] [latex]Area\: of\: Triangle=\frac{1}{2}[x_{1}(y_{2}-y_{3})+x_{2}(y_{3}-y_{1})+x_{3}(y_{1}-y_{2})][/latex]| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 7 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Exercise 7.1 – 10 Questions (3 Short Answers, 7 Long Answer) |
| ☞Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Exercise 7.2 – 10 Questions (2 Short Answers, 8 Long Answer) |
| ☞Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Exercise 7.3 – 5 Questions (2 Short Answers, 3 Long Answer) |
| ☞Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Exercise 7.4 – 8 Questions (3 Short Answers, 5 Long Answer) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Notes
- Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Coordinate Geometry
- RD Sharma Solutions Coordinate Geometry Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry – Term I
This chapter will introduce students to Trigonometry. They will study some ratios of a right triangle with respect to its acute angles, called trigonometric ratios of the angles. The chapter also defines the trigonometric ratios for angles of 00 and 900. Further, students will also know how to calculate trigonometric ratios for some specific angles and establish some identities involving these ratios, called trigonometric identities.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry for Term I:
Trigonometric ratios of an acute angle of a right-angled triangle. Proof of their existence (well defined). Values of the trigonometric ratios of 300, 450 and 600. Relationships between the ratios.
TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
Proof and applications of the identity sin2A + cos2A = 1. Only simple identities to be given
Important Formulas –
Trigonometry Maths formulas for Class 10 cover three major functions Sine, Cosine and Tangent for a right-angle triangle. Let a right-angled triangle ABC is right-angled at point B and have ∠θ.
Sin θ= [latex]\frac{Side\, opposite\, to\, angle\, \theta}{Hypotenuse}[/latex]=[latex]\frac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}[/latex] = P/H
Cos θ = [latex]\frac{Adjacent\, side\, to\, angle\, \theta}{Hypotenuse}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{Base}{Hypotenuse}[/latex] = B/H
Tan θ = [latex]\frac{Side\, opposite\, to\, angle\, \theta}{Adjacent\, side\, to\, angle\, \theta}[/latex] = P/B
Sec θ = [latex]\frac{1}{cos\, \theta }[/latex]
Cot θ = [latex]\frac{1}{tan\, \theta }[/latex]
Cosec θ = [latex]\frac{1}{sin\, \theta }[/latex]
Tan θ = [latex]\frac{Sin\, \theta }{Cos\, \theta }[/latex]
Trigonometry Table
| Angle | 0° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
| Sinθ | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 |
| Cosθ | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | ½ | 0 |
| Tanθ | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | Undefined |
| Cotθ | Undefined | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 |
| Secθ | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | Undefined |
| Cosecθ | Undefined | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 |
Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
sin (90° – A) = cos A,
cos (90° – A) = sin A,
tan (90° – A) = cot A,
cot (90° – A) = tan A,
sec (90° – A) = cosec A,
cosec (90° – A) = sec A
sin2 A + cos2 A = 1,
sec2 A – tan2 A = 1 for 0° ≤ A < 90°,
cosec2 A = 1 + cot2 A for 0° < A ≤ 90°
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 8 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Exercise 8.1 – 11 Questions (8 Short Answers, 3 Long Answers) |
| ☞Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Exercise 8.2 – 4 Questions (2 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Exercise 8.3 – 7 Questions (5 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Exercise 8.4 – 5 Questions (3 Short Answers, 2 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 8 Trigonometry at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Introduction to Trigonometry
- RD Sharma Solutions Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry – Term II
This chapter is the continuation of the previous chapter as here the students will study the applications of trigonometry. It is used in geography, navigation, construction of maps, determining the position of an island in relation to the longitudes and latitudes. In this chapter, students will see how trigonometry is used for finding the heights and distances of various objects, without actually measuring them. They will get introduced to the term line of sight, angle of elevation, angle of depression.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry for Term II:
HEIGHTS AND DISTANCES-Angle of elevation, Angle of Depression.
Simple problems on heights and distances. Problems should not involve more than two right triangles. Angles of elevation / depression should be only 30°, 45°, 60°.
Important Points –
The line of sight is the line drawn from the eye of an observer to the point in the object viewed by the observer.
The angle of elevation of the point viewed is the angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level, i.e., the case when we raise our head to look at the object.
The angle of depression of a point on the object being viewed is the angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point is below the horizontal level, i.e., the case when we lower our head to look at the point being viewed.

You would need to know the following:
(i) the distance DE at which the student is standing from the foot of the minar
(ii) the angle of elevation, ∠ BAC, of the top of the minar
(iii) the height AE of the student.
Assuming that the above three conditions are known, how can we determine the height of the minar?
In the figure, CD = CB + BD. Here, BD = AE, which is the height of the student.
To find BC, we will use trigonometric ratios of ∠ BAC or ∠ A.
In ∆ ABC, the side BC is the opposite side in relation to the known ∠ A. Our search narrows down to using either tan A or cot A, as these ratios involve AB and BC.
Therefore, tan A = BC/AB or cot A = AB/BC, which on solving would give us BC.
By adding AE to BC, you will get the height of the minar.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 9 Exercise |
|---|
| ☞Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Exercise 9.1 – 16 Questions (16 Long Answers) |

Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- RD Sharma Solutions Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles – Term II
In earlier classes, students have studied about a circle and various terms related to a circle such as a chord, segment, arc, etc. In this chapter, students will study the different situations that arise when a circle and a line are given in a plane. So, they will get thorough with the concept of Tangent to a Circle and Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles for Term II:
Tangent to a circle at, point of contact
1. (Prove) The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
2. (Prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Important Theorems –
Theorem 10.1: The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
Theorem 10.2: The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle
Case 1: There is no tangent to a circle passing through a point lying inside the circle.
Case 2: There is one and only one tangent to a circle passing through a point lying on the circle.
Case 3: There are exactly two tangents to a circle through a point lying outside the circle.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 10 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Circles Class 10 Exercise 10.1 – 4 Questions (2 Short Answer, 2 Long Answers) |
| ☞Circles Class 10 Exercise 10.2 – 13 Questions (2 Short Answers, 14 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 10 Circles at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Circles Class 10 Notes
- Circles Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Circles
- RD Sharma Solutions Circles Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions – Term II
This chapter consists of a total of 2 exercises. Whatever students have learned about construction in earlier classes will also help them. In Exercise 11.1, students will study how to divide a line segment, whereas in Exercise 11.2 they will study the construction of tangents to a circle. Methods and steps for construction are explained and also some examples are additionally given to make it clearer to the students.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions for Term II:
1. Division of a line segment in a given ratio (internally).
2. Tangents to a circle from a point outside it.
Important Points –
Construction 11.1: To divide a line segment in a given ratio.
Construction 11.2: To construct a triangle similar to a given triangle as per given scale factor.
Construction 11.3: To construct the tangents to a circle from a point outside it.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 11 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Constructions Class 10 Exercise 11.1 – 7 Questions (7 Long Answers) |
| ☞Constructions Class 10 Exercise 11.2 – 7 Questions (7 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 11 Constructions at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Constructions Class 10 Notes
- Constructions Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Constructions
- RD Sharma Solutions Constructions Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles – Term I
This chapter begins with the concepts of perimeter and area of a circle. Using this concept, the chapter further explains how to find the area of sector and segment of a circular region. Moreover, students will get clarity on finding the areas of some combinations of plane figures involving circles or their parts.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles for Term I:
Motivate the area of a circle; area of sectors and segments of a circle. Problems based on areas and perimeter / circumference of the above said plane figures. (In calculating area of segment of a circle, problems should be restricted to central angle of 60° and 90° only. Plane figures involving triangles, simple quadrilaterals and circle should be taken.)
Important Formulas –
circumference = 2πr
area of the circle = πr 2
Area of the sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × π r2
Length of an arc of a sector of angle θ = (θ/360) × 2 π r where r is the radius of the circle
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 12 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Exercise 12.1 – 5 Questions (5 Short Answers) |
| ☞Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Exercise 12.2 – 14 Questions (9 Short Answers, 5 Long Answers) |
| ☞Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Exercise 12.3 – 16 Questions (9 Short Answers, 7 Long Answers) |

Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Notes
- Areas Related to Circles Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Areas Related to Circles
- RD Sharma Solutions Areas Related to Circles Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes – Term II
In Chapter 13, there are a total of 5 exercises. The first exercise consists of the questions based on finding the surface area of an object formed by combining any two of the basic solids, i.e cuboid, cone, cylinder, sphere and hemisphere. In Exercise, 13.2 questions are based on finding the volume of objects formed by combining any two of a cuboid, cone, cylinder, sphere and hemisphere. Exercise 13.3 deals with the questions in which a solid is converted from one shape to another. Exercise 13.4 is based on finding the volume, curved surface area and total surface area of a frustum of a cone. The last exercise is optional and has high-level questions based on all the topics of this chapter.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes for Term II:
1. Surface areas and volumes of combinations of any two of the following: cubes, cuboids, spheres, hemispheres and right circular cylinders/cones.
2. Problems involving converting one type of metallic solid into another and other mixed problems. (Problems with combination of not more than two different solids be taken).
Important Formulas –
TSA of new solid = CSA of one hemisphere + CSA of cylinder + CSA of other hemisphere
Diameter of sphere = 2r
Surface area of sphere = 4 π r2
Volume of Sphere = 4/3 π r3
Curved surface area of Cylinder = 2 πrh
Area of two circular bases = 2 πr2
Total surface area of Cylinder = Circumference of Cylinder + Curved surface area of Cylinder = 2 πrh + 2 πr2
Volume of Cylinder = π r2 h
Slant height of cone = l = √(r2 + h2)
Curved surface area of cone = πrl
Total surface area of cone = πr (l + r)
Volume of cone = ⅓ π r2 h
Perimeter of cuboid = 4(l + b +h)
Length of the longest diagonal of a cuboid = √(l2 + b2 + h2)
Total surface area of cuboid = 2(l×b + b×h + l×h)
Volume of Cuboid = l × b × h
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 13 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞Solutions of NCERT Maths Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.1 – 9 Questions (2 Short Answers, 7 Long Answers) |
| ☞Solutions of NCERT Maths Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.2 – 8 Questions (1 Short Answer, 7 Long Answers) |
| ☞Solutions of NCERT Maths Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.3 – 9 Questions (9 Long Answers) |
| ☞Solutions of NCERT Maths Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.4 – 5 Questions (5 Long Answers) |
| ☞Solutions of NCERT Maths Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 13.5 – 7 Questions (7 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Surface Areas and Volumes Class 10 Notes
- Surface Areas and Volumes Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Surface Areas and Volumes
- RD Sharma Solutions Surface Areas and Volumes Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics – Term II
Here, students will learn the numerical representation of ungrouped data to grouped data and finding the Mean, Mode and Median. Also, the concept of cumulative frequency, cumulative frequency distribution and how to draw cumulative frequency curves will be explained.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics for Term II:
Mean, median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to be avoided). Mean by Direct Method and Assumed Mean Method only.
Important Formulas –
The mean of the grouped data can be found by 3 methods.
- Direct Method: x̅ = [latex]\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i x_i}{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i}[/latex], where ∑fi xi is the sum of observations from value i = 1 to n And ∑fi is the number of observations from value i = 1 to n
- Assumed mean method : x̅ = [latex]a+\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i d_i}{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i}[/latex]
- Step deviation method : x̅ = [latex]a+\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i u_i}{\sum_{i=1}^{n}f_i}\times h[/latex]
The mode of grouped data:
Mode = [latex]l+\frac{f_1 – f_0}{2f_1 – f_0 – f_2} \times h[/latex]
The median for a grouped data:
Median = [latex]l+\frac{\frac{n}{2} – cf}{f} \times h[/latex]
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 14 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Statistics Exercise 14.1 – 9 Questions (9 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Statistics Exercise 14.2 – 6 Questions (6 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Statistics Exercise 14.3 – 7 Questions (7 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Statistics Exercise 14.4 – 3 Questions (3 Long Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 14 Statistics at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Statistics Class 10 Notes
- Statistics Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Statistics
- RD Sharma Solutions Statistics Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability – Term I
The last chapter deals with Probability. The chapter starts with the theoretical approach of probability. Subsequently, the chapter explains the difference between experimental probability and theoretical probability. There are various examples given to explain it in an effective way. So, before going through the exercise problems students must solve the examples of CBSE Maths first.
Topics Covered in Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability for Term I:
Classical definition of probability. Simple problems on finding the probability of an event.
Important Formulas –
- The theoretical probability (also called classical probability) of an event E, written as P(E), is defined as
where we assume that the outcomes of the experiment are equally likely.
- The probability of a sure event (or certain event) is 1.
- The probability of an impossible event is 0.
- The probability of an event E is a number P(E) such that 0 ≤ P (E) ≤ 1
- An event having only one outcome is called an elementary event. The sum of the probabilities of all the elementary events of an experiment is 1.
| Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions PDF Chapter 15 Exercises |
|---|
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Probability Exercise 15.1 – 25 Questions (22 Short Answers, 3 Long Answers) |
| ☞NCERT Solutions of Maths Class 10 Probability Exercise 15.2 – 5 Questions (5 Short Answers) |
Also access the following resources for NCERT Class 10 Chapter 15 Probability at BYJU’S:
- NCERT Probability Class 10 Notes
- Probability Class 10 Important Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Probability
- RD Sharma Solutions Probability Class 10
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths PDF in English Medium, as well as Hindi Medium (हिंदी मीडियम) for the academic year 2021-22, are not only followed by CBSE but also UP Board, Uttarakhand board and all other boards following NCERT Textbooks.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-wise Marks Weightage for First Term
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Number systems | 06 |
| II | Algebra | 10 |
| III | Coordinate Geometry | 06 |
| IV | Geometry | 06 |
| V | Trigonometry | 05 |
| VI | Mensuration | 04 |
| VII | Statistics and Probability | 03 |
| Total | 40 | |
| Internal Assessment | 10 | |
| Total | 50 |
Internal Assessment Class 9 Term I
| Internal Assessment | Marks |
| Periodic Tests | 03 Marks |
| Multiple Assessments | 02 Marks |
| Portfolio | 02 Marks |
| Student Enrichment Activities-practical work | 03 Marks |
| Total Marks | 10 Marks |
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-wise Marks Weightage for Second Term
| Unit | Unit Name | Marks |
| I | Algebra (Cont.) | 10 |
| II | Geometry (Cont.) | 09 |
| III | Trigonometry (Cont.) | 07 |
| IV | Mensuration (Cont.) | 06 |
| V | Statistics and Probability (Cont.) | 08 |
| Total | 40 | |
| Internal Assessment | 10 | |
| Total | 50 |
Internal Assessment Class 9 Term II
| Internal Assessment | Marks |
| Periodic Tests | 03 Marks |
| Multiple Assessments | 02 Marks |
| Portfolio | 02 Marks |
| Student Enrichment Activities-practical work | 03 Marks |
| Total Marks | 10 Marks |
Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths:
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions of Maths given here in PDFs have several benefits which include:
- The solutions given here are very easy to understand.
- Solutions are provided in steps for better understanding.
- Diagrams are given to help the students in visualizing the solutions.
- All the questions from each chapter are covered.
Students are advised to prepare all the chapters covered in the solution modules, which will eventually help them to gain a deeper knowledge of concepts. For effective preparations, it is essential for students to understand all the steps provided in the solutions.
How are CBSE Class 10 Maths Solutions of NCERT Helpful for Term Wise Exams?
CBSE Class 10 Maths is an important subject for students. Here, we have provided complete assistance to students for its preparation. Class 10 is the first benchmark for any student that will reflect in the future records of achievement. CBSE always prescribes the NCERT books for term wise exam preparation.
Exam preparation is a rigorous process that requires an overall understanding of individual chapters. This process demands hard work towards studies and an effective approach to getting through the solutions. This significant role is played by NCERT 10 Class Maths Solutions to equip students in the preparation of competitive entrance exams. NCERT books are best known for putting forth the concepts in a simple way for better understanding. NCERT Class 10 Books for Mathematics are written in the most lucid and clear manner that helps to break the complex problems in the most efficient way.
Keep visiting to get complete chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths PDF free download for all the classes. Students can also find the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science, at BYJU’S. Students can download BYJU’S App to get a personalized learning experience and prepare for the exams more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
How to grasp the important concepts covered in the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths?
Will the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths help me to solve the problems easily?
Where will I get the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths PDF?
Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths useful for the students under the CBSE board?
1. It builds a strong foundation of fundamental concepts and improves confidence to face the term wise exams.
2. The method of solving complex problems can be learnt easily.
3. It is a perfect study material for the students to finish their assignments on time and to score more marks in the term wise exams.

