NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions is provided here for the benefit of students of Class 9. Geometry is a fundamental concept that is useful in many fields. Therefore, it is necessary to learn the concept and understand its applications. The best way to learn this concept is by referring to the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions. These solutions are designed by teachers who can articulate concepts in an efficient manner to help students ace their second term CBSE Class 9 Maths examination.
Hence, NCERT Solutions is the guide you should adopt for your studies as the content is presented in a comprehensive format. We ensure that the instructions provided are simple and clear cut. Moreover, we ensure that our content is updated as per the latest term-wise CBSE Syllabus 2021-22 and guidelines.
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions
List of Exercises in class 9 Maths Chapter 11:
Access Answers of NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 – Constructions
Exercise 11.1 Page: 191
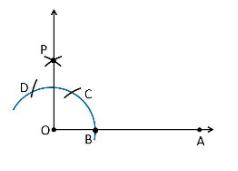
1. Construct an angle of 90° at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction.
Construction Procedure:
To construct an angle 90°, follow the given steps:
1. Draw a ray OA
2. Take O as a centre with any radius, draw an arc DCB is that cuts OA at B.
3. With B as a centre with the same radius, mark a point C on the arc DCB.
4. With C as a centre and the same radius, mark a point D on the arc DCB.
5. Take C and D as centre, draw two arcs which intersect each other with the same radius at P.
6. Finally, the ray OP is joined which makes an angle 90° with OP is formed.
Justification
To prove ∠POA = 90°
In order to prove this, draw a dotted line from the point O to C and O to D and the angles formed are:
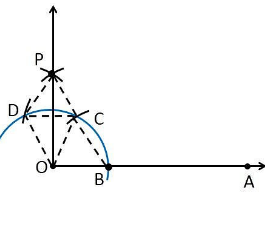
From the construction, it is observed that
OB = BC = OC
Therefore, OBC is an equilateral triangle
So that, ∠BOC = 60°.
Similarly,
OD = DC = OC
Therefore, DOC is an equilateral triangle
So that, ∠DOC = 60°.
From SSS triangle congruence rule
△OBC ≅ OCD
So, ∠BOC = ∠DOC [By C.P.C.T]
Therefore, ∠COP = ½ ∠DOC = ½ (60°).
∠COP = 30°
To find the ∠POA = 90°:
∠POA = ∠BOC+∠COP
∠POA = 60°+30°
∠POA = 90°
Hence, justified.
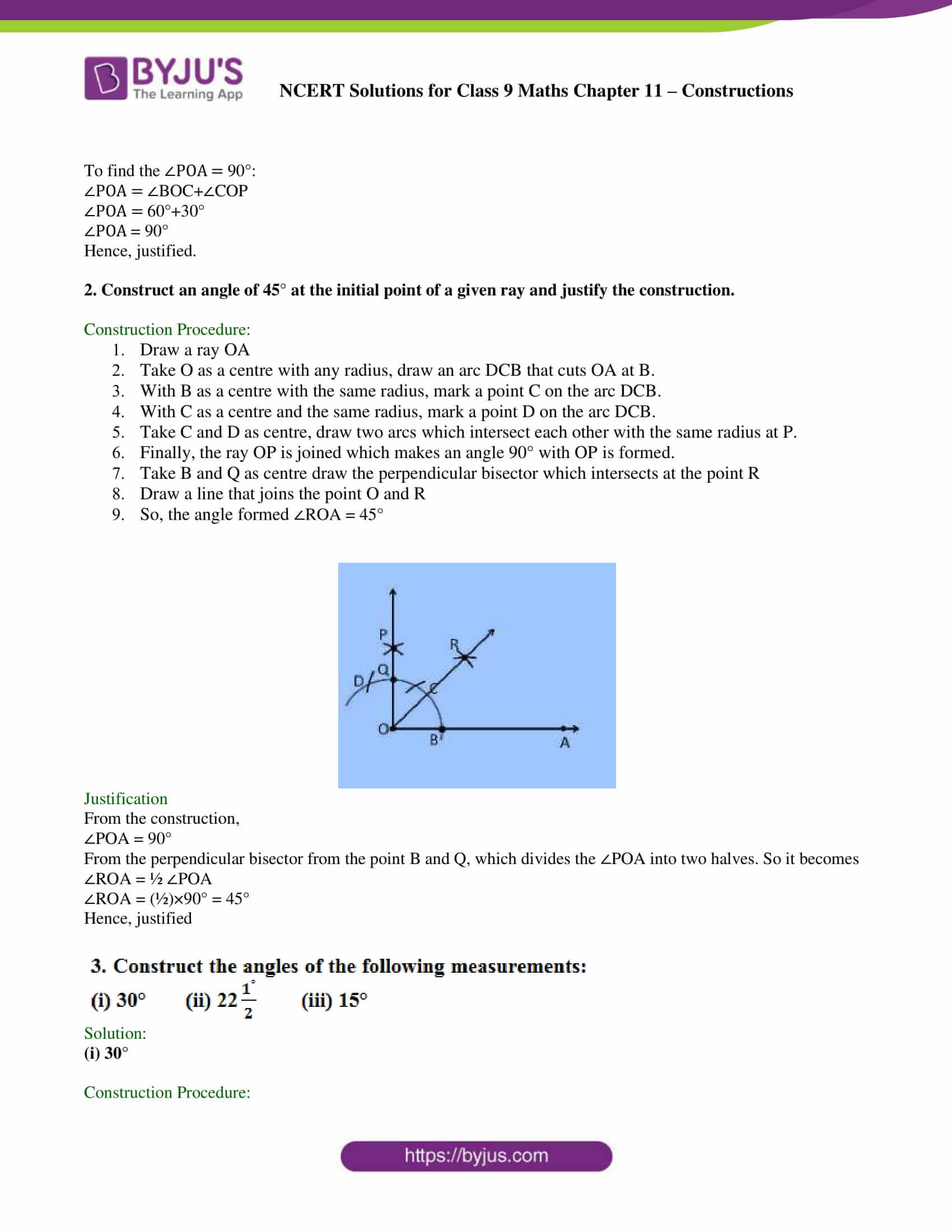
2. Construct an angle of 45° at the initial point of a given ray and justify the construction.
Construction Procedure:
1. Draw a ray OA
2. Take O as a centre with any radius, draw an arc DCB that cuts OA at B.
3. With B as a centre with the same radius, mark a point C on the arc DCB.
4. With C as a centre and the same radius, mark a point D on the arc DCB.
5. Take C and D as centre, draw two arcs which intersect each other with the same radius at P.
6. Finally, the ray OP is joined which makes an angle 90° with OP is formed.
7. Take B and Q as centre draw the perpendicular bisector which intersects at the point R
8. Draw a line that joins the point O and R
9. So, the angle formed ∠ROA = 45°

Justification
From the construction,
∠POA = 90°
From the perpendicular bisector from the point B and Q, which divides the ∠POA into two halves. So it becomes
∠ROA = ½ ∠POA
∠ROA = (½)×90° = 45°
Hence, justified

Solution:
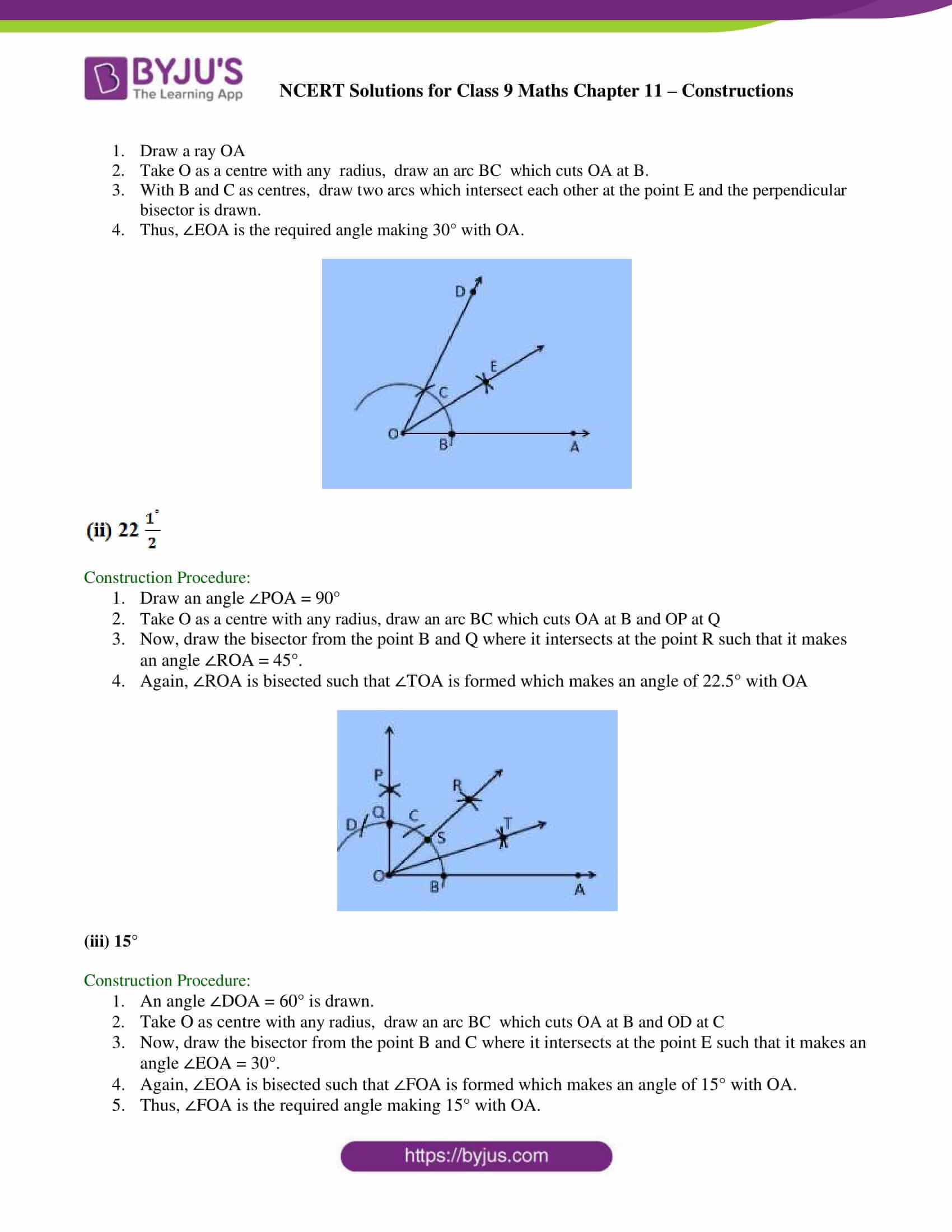
(i) 30°
Construction Procedure:
1. Draw a ray OA
2. Take O as a centre with any radius, draw an arc BC which cuts OA at B.
3. With B and C as centres, draw two arcs which intersect each other at the point E and the perpendicular bisector is drawn.
4. Thus, ∠EOA is the required angle making 30° with OA.


Construction Procedure:
1. Draw an angle ∠POA = 90°
2. Take O as a centre with any radius, draw an arc BC which cuts OA at B and OP at Q
3. Now, draw the bisector from the point B and Q where it intersects at the point R such that it makes an angle ∠ROA = 45°.
4. Again, ∠ROA is bisected such that ∠TOA is formed which makes an angle of 22.5° with OA

(iii) 15°
Construction Procedure:
1. An angle ∠DOA = 60° is drawn.
2. Take O as centre with any radius, draw an arc BC which cuts OA at B and OD at C
3. Now, draw the bisector from the point B and C where it intersects at the point E such that it makes an angle ∠EOA = 30°.
4. Again, ∠EOA is bisected such that ∠FOA is formed which makes an angle of 15° with OA.
5. Thus, ∠FOA is the required angle making 15° with OA.

4. Construct the following angles and verify by measuring them by a protractor:
(i) 75° (ii) 105° (iii) 135°
Solution:
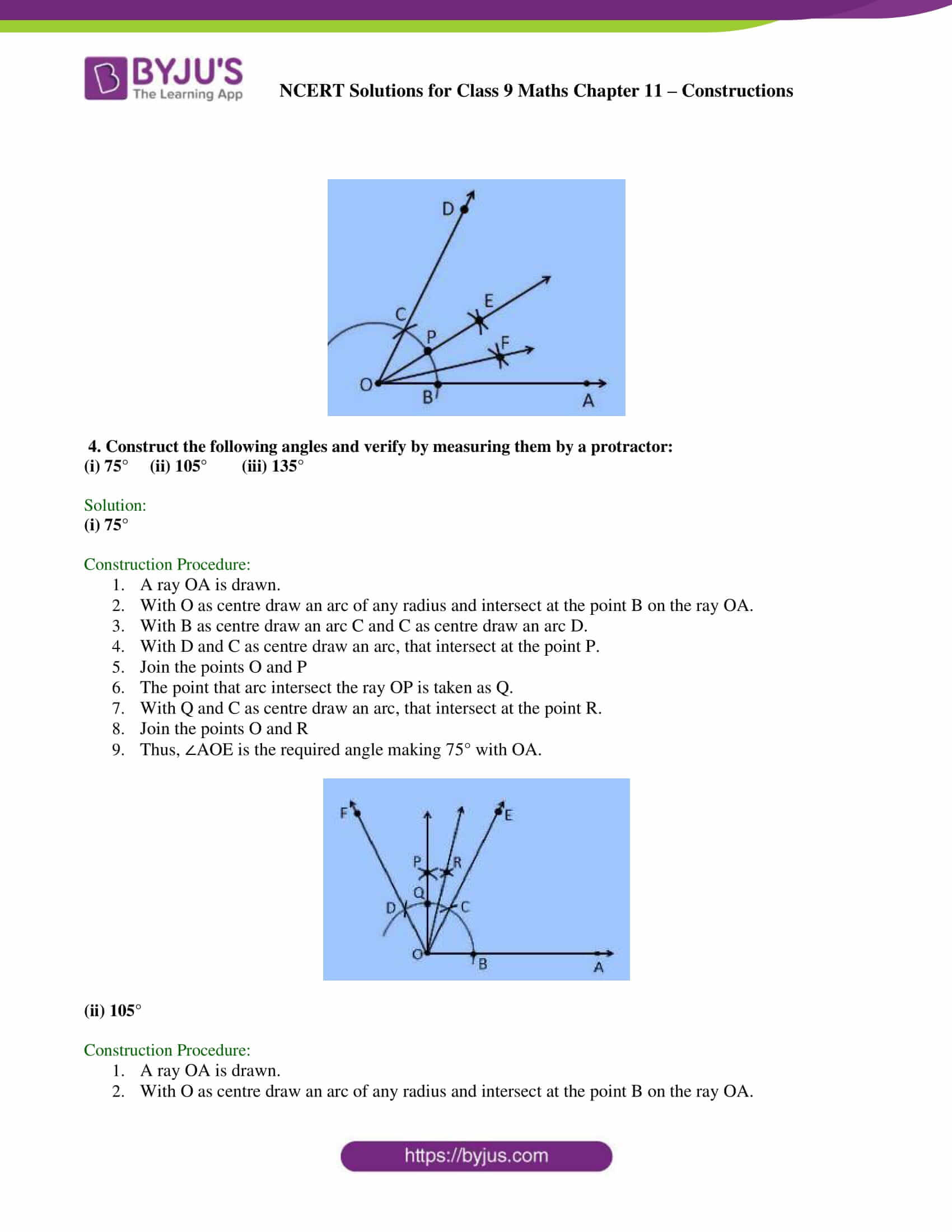
(i) 75°
Construction Procedure:
1. A ray OA is drawn.
2. With O as centre draw an arc of any radius and intersect at the point B on the ray OA.
3. With B as centre draw an arc C and C as centre draw an arc D.
4. With D and C as centre draw an arc, that intersect at the point P.
5. Join the points O and P
6. The point that arc intersect the ray OP is taken as Q.
7. With Q and C as centre draw an arc, that intersect at the point R.
8. Join the points O and R
9. Thus, ∠AOE is the required angle making 75° with OA.

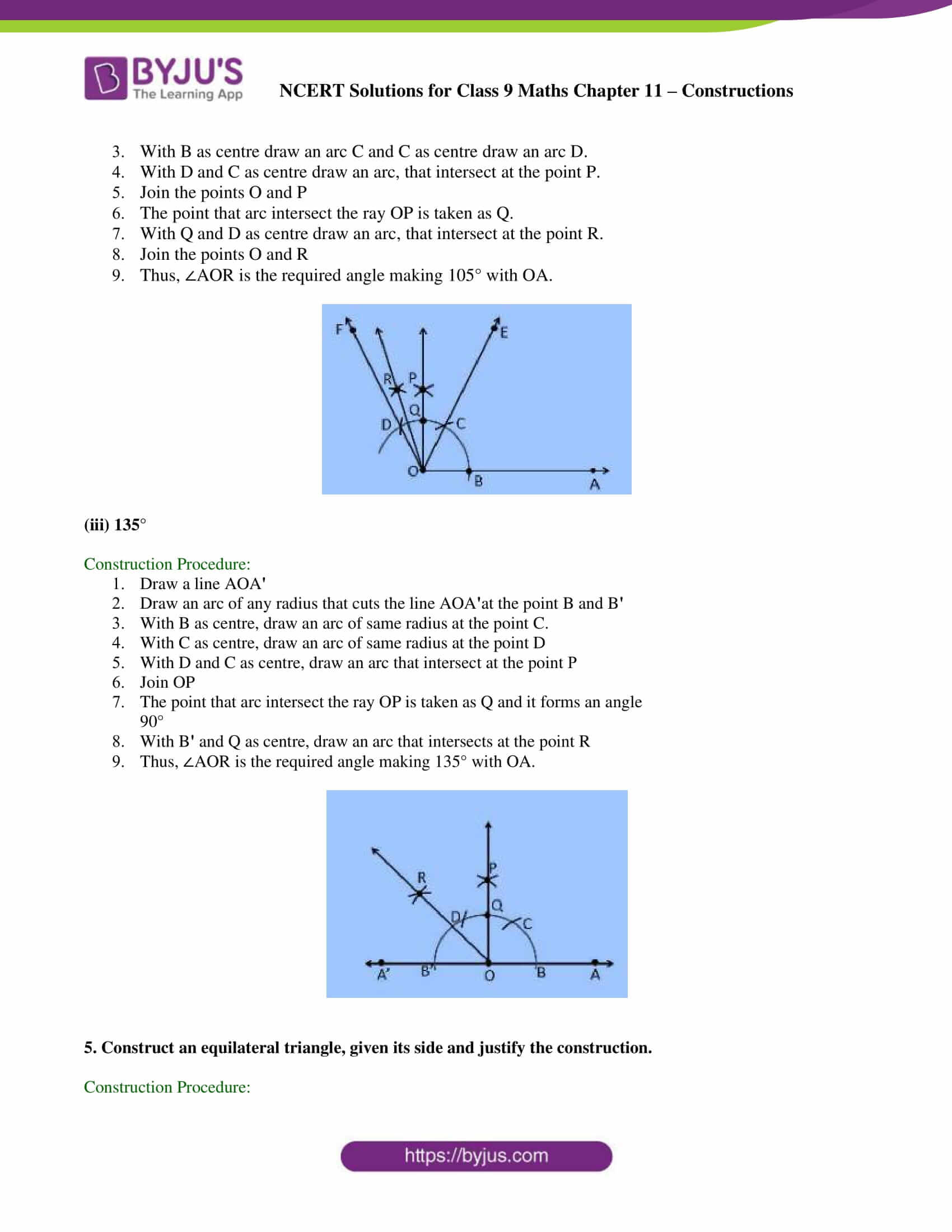
(ii) 105°
Construction Procedure:
1. A ray OA is drawn.
2. With O as centre draw an arc of any radius and intersect at the point B on the ray OA.
3. With B as centre draw an arc C and C as centre draw an arc D.
4. With D and C as centre draw an arc, that intersect at the point P.
5. Join the points O and P
6. The point that arc intersect the ray OP is taken as Q.
7. With Q and D as centre draw an arc, that intersect at the point R.
8. Join the points O and R
9. Thus, ∠AOR is the required angle making 105° with OA.

(iii) 135°
Construction Procedure:
1. Draw a line AOA‘
2. Draw an arc of any radius that cuts the line AOA‘at the point B and B‘
3. With B as centre, draw an arc of same radius at the point C.
4. With C as centre, draw an arc of same radius at the point D
5. With D and C as centre, draw an arc that intersect at the point P
6. Join OP
7. The point that arc intersect the ray OP is taken as Q and it forms an angle 90°
8. With B‘ and Q as centre, draw an arc that intersects at the point R
9. Thus, ∠AOR is the required angle making 135° with OA.

5. Construct an equilateral triangle, given its side and justify the construction.
Construction Procedure:
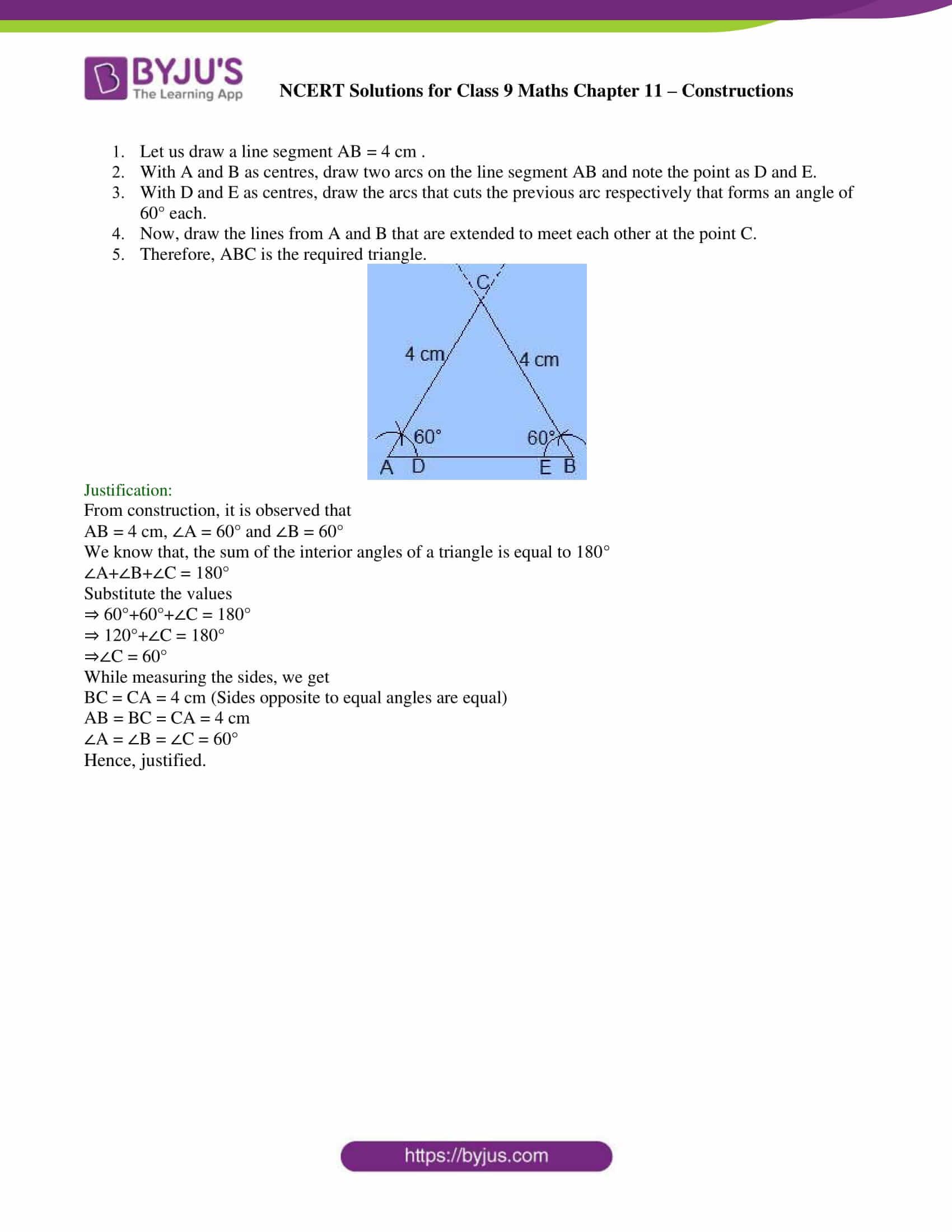
1. Let us draw a line segment AB = 4 cm .
2. With A and B as centres, draw two arcs on the line segment AB and note the point as D and E.
3. With D and E as centres, draw the arcs that cuts the previous arc respectively that forms an angle of 60° each.
4. Now, draw the lines from A and B that are extended to meet each other at the point C.
5. Therefore, ABC is the required triangle.

Justification:
From construction, it is observed that
AB = 4 cm, ∠A = 60° and ∠B = 60°
We know that, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180°
∠A+∠B+∠C = 180°
Substitute the values
⇒ 60°+60°+∠C = 180°
⇒ 120°+∠C = 180°
⇒∠C = 60°
While measuring the sides, we get
BC = CA = 4 cm (Sides opposite to equal angles are equal)
AB = BC = CA = 4 cm
∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
Hence, justified.
Exercise 11.2 Page: 195
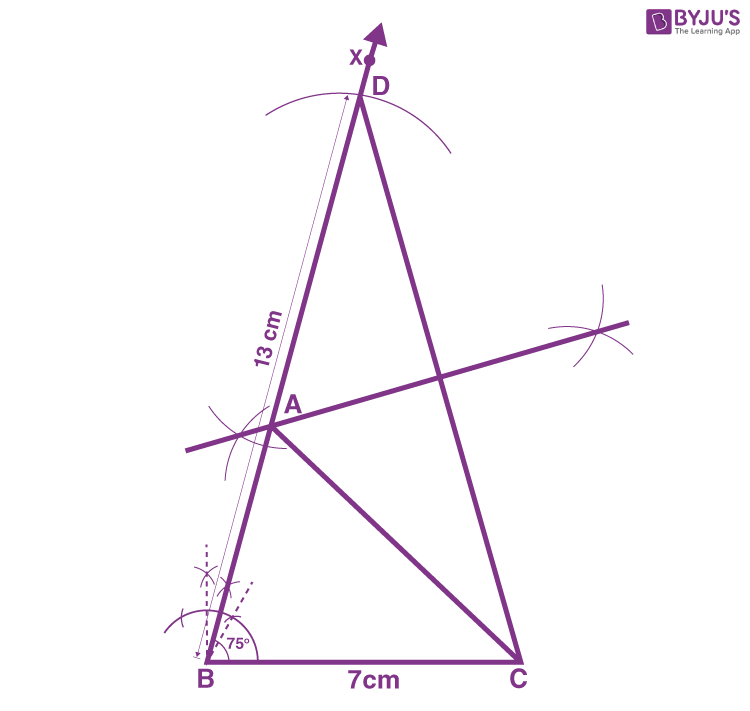
1. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 7cm, ∠B = 75° and AB+AC = 13 cm.
Construction Procedure:
The steps to draw the triangle of given measurement is as follows:
1. Draw a line segment of base BC = 7 cm
2. Measure and draw ∠B = 75° and draw the ray BX
3. Take a compass and measure AB+AC = 13 cm.
4. With B as the centre, draw an arc at the point be D
5. Join DC
6. Now draw the perpendicular bisector of the line DC and the intersection point is taken as A.
7. Now join AC
8. Therefore, ABC is the required triangle.
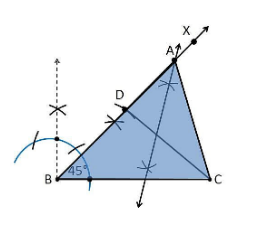
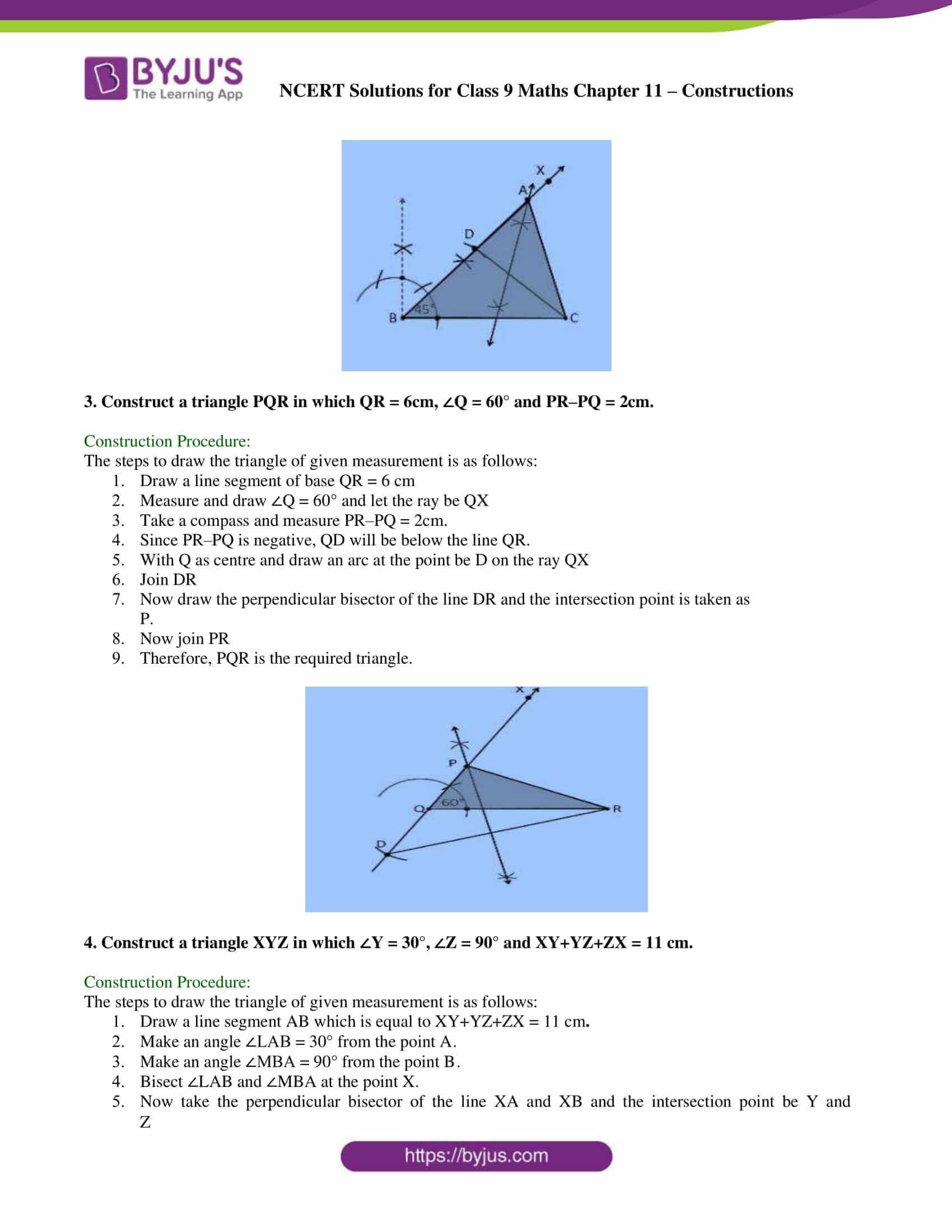
2. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 8cm, ∠B = 45° and AB–AC = 3.5 cm.
Construction Procedure:
The steps to draw the triangle of given measurement is as follows:
1. Draw a line segment of base BC = 8 cm
2. Measure and draw ∠B = 45° and draw the ray BX
3. Take a compass and measure AB-AC = 3.5 cm.
4. With B as centre and draw an arc at the point be D on the ray BX
5. Join DC
6. Now draw the perpendicular bisector of the line CD and the intersection point is taken as A.
7. Now join AC
8. Therefore, ABC is the required triangle.
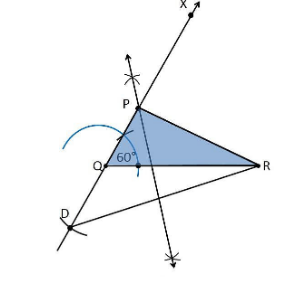
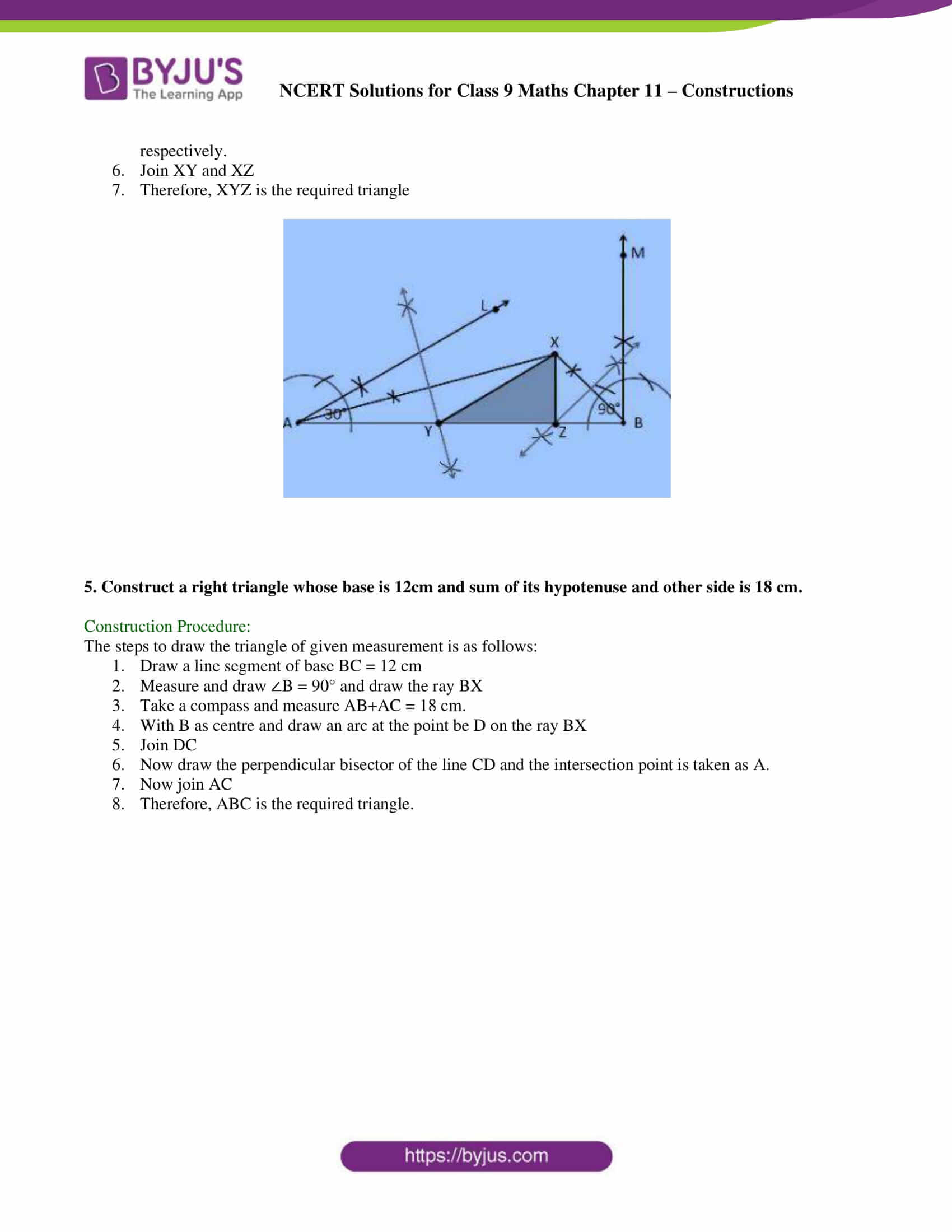
3. Construct a triangle PQR in which QR = 6cm, ∠Q = 60° and PR–PQ = 2cm.
Construction Procedure:
The steps to draw the triangle of given measurement is as follows:
1. Draw a line segment of base QR = 6 cm
2. Measure and draw ∠Q = 60° and let the ray be QX
3. Take a compass and measure PR–PQ = 2cm.
4. Since PR–PQ is negative, QD will be below the line QR.
5. With Q as centre and draw an arc at the point be D on the ray QX
6. Join DR
7. Now draw the perpendicular bisector of the line DR and the intersection point is taken as P.
8. Now join PR
9. Therefore, PQR is the required triangle.
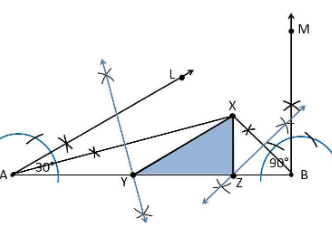
4. Construct a triangle XYZ in which ∠Y = 30°, ∠Z = 90° and XY+YZ+ZX = 11 cm.
Construction Procedure:
The steps to draw the triangle of given measurement is as follows:
1. Draw a line segment AB which is equal to XY+YZ+ZX = 11 cm.
2. Make an angle ∠LAB = 30° from the point A.
3. Make an angle ∠MBA = 90° from the point B.
4. Bisect ∠LAB and ∠MBA at the point X.
5. Now take the perpendicular bisector of the line XA and XB and the intersection point be Y and Z, respectively.
6. Join XY and XZ
7. Therefore, XYZ is the required triangle
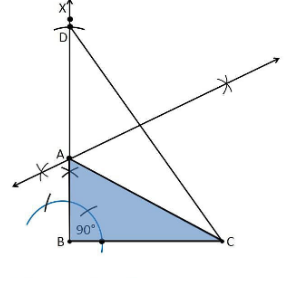
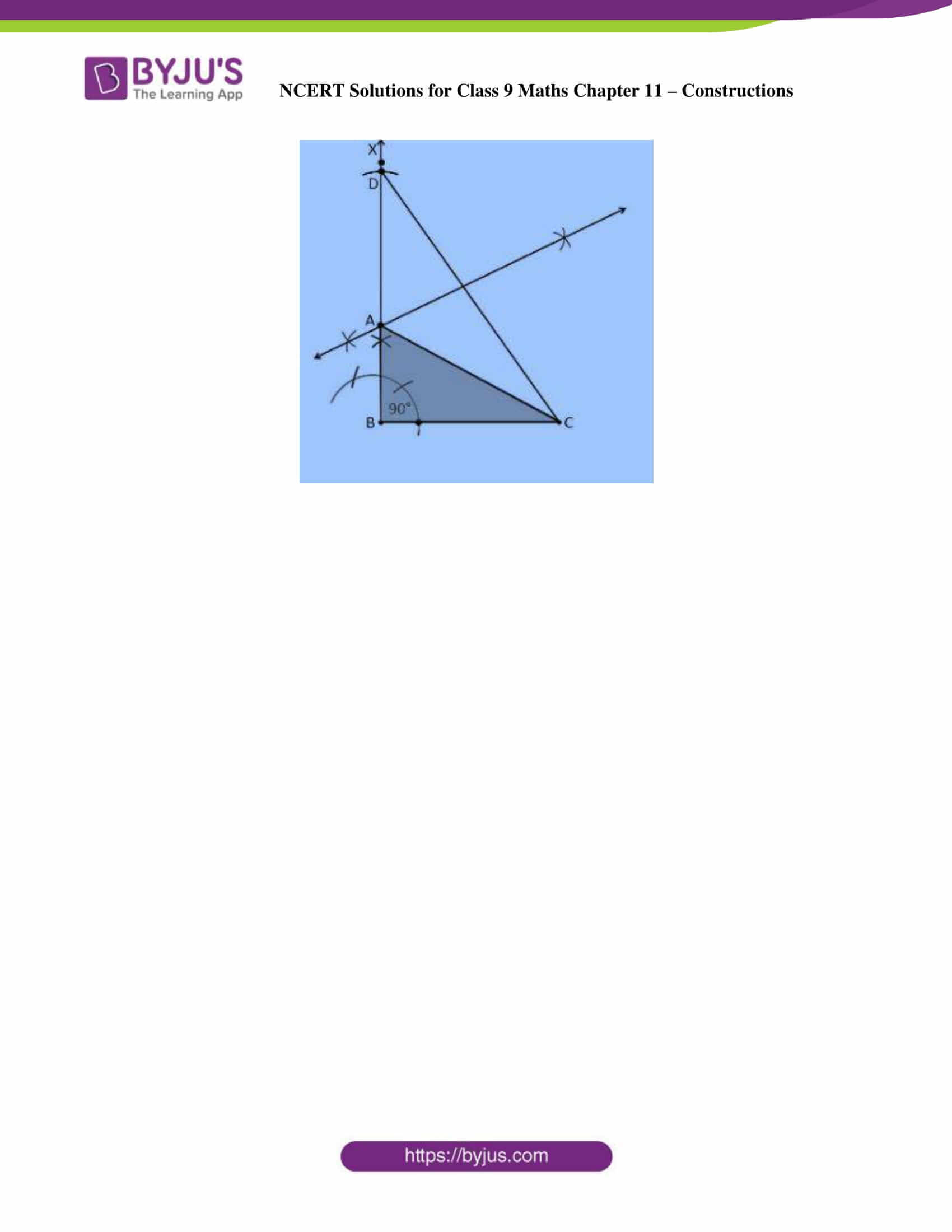
5. Construct a right triangle whose base is 12cm and sum of its hypotenuse and other side is 18 cm.
Construction Procedure:
The steps to draw the triangle of given measurement is as follows:
1. Draw a line segment of base BC = 12 cm
2. Measure and draw ∠B = 90° and draw the ray BX
3. Take a compass and measure AB+AC = 18 cm.
4. With B as centre and draw an arc at the point be D on the ray BX
5. Join DC
6. Now draw the perpendicular bisector of the line CD and the intersection point is taken as A.
7. Now join AC
8. Therefore, ABC is the required triangle.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Exemplar for class 9 Maths Chapter 11 |
| CBSE Notes for class 9 Maths Chapter 11 |
Chapter 11 Constructions belongs to Unit 4: Geometry. This unit carries a total of 28 marks out of 100. Therefore, this chapter should be studied thoroughly as a majority of the questions could appear from this unit. The important topics that are covered under this chapter are:
- Basic Construction
- Construction of triangles
Constructions is an important chapter included in the second term of Class 9 Maths that helps the students to understand how different shapes are made. It also teaches their implications and their academic relevance. Learn how to construct a bisector, a perpendicular bisector and much more. Explore more about Constructions and learn to solve various kinds of problems only on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths. It is also one of the best academic resources to revise for your second term exams.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions
- Formulas are explained
- Comprehensive format and jargon-free language
- Constant addition of new questions with solutions
- Additional key tips and tricks are provided.
- Access other important learning resources like sample papers.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11
How NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 helpful for second term exam preparation?
Which is the best source for Class 9 Maths second term exam preparation?
What are the main concepts covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 11?
1. Basic Construction
2. Construction of triangles


It was very helpful!!
Very helpful thank you so much
Very good