What is Heat Engine?
A heat engine is a device that converts heat to work. It takes heat from a reservoir then does some work like moving a piston, lifting weight etc and finally discharges some heat energy into the sink. Schematically it can be represented as:
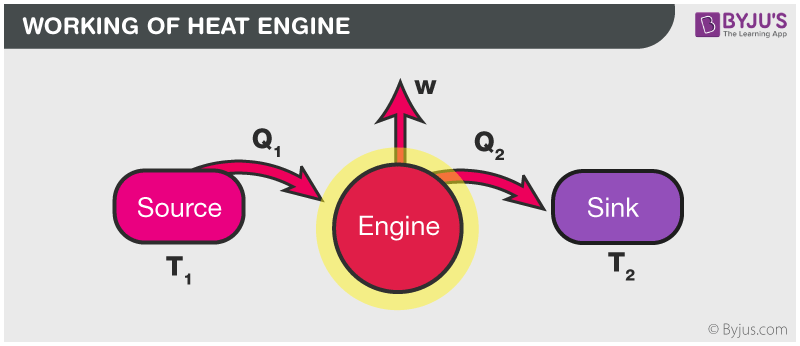
Heat Engine Efficiency
Let us derive an expression for the efficiency of a heat engine. We can define heat engine efficiency as:
Where,
After each cycle, the engine returns to its initial state so,
So from the figure, it is clear that,
Hence the heat engine efficiency is:
So for

Types of Heat Engine
Following are the two types of heat engine:
- Internal combustion engine
- External combustion engine
External combustion engine
In these heat engines, the fuel burns outside and away from the main engine where force and motion are produced. A steam engine is an example of external combustion engine.
Internal combustion engine
In these heat engines, the fuel burns inside the cylinder. A car engine is an example of internal combustion engine.
The internal combustion engine is more efficient than external combustion engine as there is no energy wasted during heat transfer between the boiler and the cylinder.
Following is the table explaining related concepts of heat engine:
| Carnot’s Theorem |
| Heat Pump And Refrigerator: Applications |
What is Heat Pump?
A heat pump is a device that extracts heat from one piece and transfers it to another. Heat pumps transfer heat by circulating a substance known as refrigerant through a cycle of evaporation and condensation.
Refrigerators and air conditioners are examples of heat pumps. A refrigerator is essentially an insulated box with a heat pump system connected to it. The evaporator coil is located inside the box, usually in the freezer compartment. Heat is absorbed from this location and transferred outside, usually behind or underneath the unit where the condenser coil is located.
A refrigerator takes out heat from a lower temperature

In this case, we define the coefficient of performance as:
Where,
- Q2 is the heat taken from the system
- W is the work done on the refrigerator
Similar to heat engine after a cycle the refrigerator returns to its original state hence ∆U = 0. So from the figure,
Therefore,
A refrigerator will not be able to function without external work so its coefficient of performance can never be infinite.




Nice post
Find the efficiency in carnot engine.
You can read about the efficiency of the Carnot engine here.
Very essential and useful for revision at all times
What is the difference between a heat engine and a refrigerator?
In a heat engine, heat is transferred from a higher temperature level (source) to lower temperature level(sink). Work is obtained during this process.
In a refrigerator, the heat is transferred from a lower temperature level to a higher temperature level by applying external work to maintain the temperature below atmospheric temperature.
Both these devices work on the basis of heat flow.