Shear modulus also known as Modulus of rigidity is the measure of the rigidity of the body, given by the ratio of shear stress to shear strain. Often denoted by G sometimes by S or μ.
What is Shear Modulus?
Shear Modulus of elasticity is one of the measures of mechanical properties of solids. Other elastic moduli are Young’s modulus and bulk modulus. The shear modulus of material gives us the ratio of shear stress to shear strain in a body.
- Measured using the SI unit pascal or Pa.
- The dimensional formula of Shear modulus is M1L-1T-2.
- It is denoted by G.
It can be used to explain how a material resists transverse deformations but this is practical for small deformations only, following which they are able to return to the original state. This is because large shearing forces lead to permanent deformations (no longer elastic body).
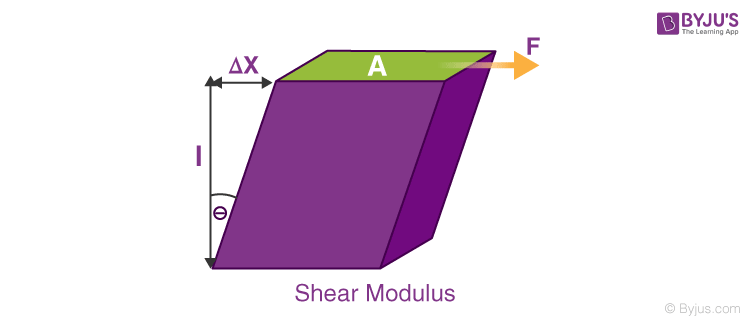
Modulus Of Rigidity Formula
\(\begin{array}{l}G=\frac{\tau _{xy}}{\gamma _{xy}}=\frac{\left ( \frac{F}{A} \right )}{\left ( \frac{\Delta x}{l} \right )}=\frac{Fl}{A\Delta x}\end{array} \) |
Where,
- \(\begin{array}{l}\tau _{xy}=\frac{F}{A}\end{array} \)is shear stress.
- F is the force acting on the object.
- A is the area on which the force is acting.
- \(\begin{array}{l}\gamma _{xy}=\frac{\Delta x}{l}\end{array} \)is the shear strain.
- \(\begin{array}{l}\Delta x\end{array} \)is the transverse displacement.
- l is the initial length.
Units:
- The modulus of rigidity is measured using the SI unit pascal or Pa.
- Commonly it is expressed in terms of GigaPascal (GPa).
- Alternatively, it is also expressed in pounds per square inch(PSI).
Modulus Of Rigidity – Overview:
The modulus of rigidity is the elastic coefficient when a shear force is applied resulting in lateral deformation. It gives us a measure of how rigid a body is. The table given below briefs everything you need to know about rigidity modulus.
| Definition | Shear modulus is the ratio of shear stress to shear strain in a body. |
| Symbol | G or S or μ |
| SI unit | Pascal (Pa), N/m2 |
| Formula | Shear stress/shear strain |
| Dimension formula | M1L-1T-2 |
Example of Modulus Of Rigidity
The following example will give you a clear understanding of how the shear modulus helps in defining the rigidity of any material.
- Shear modulus of wood is 6.2×108 Pa
- Shear modulus of steel is 7.2×1010 Pa
Thus, it implies that steel is a lot more (really a lot more) rigid than wood, around 127 times more!
Calculation:
A block of unknown material kept on a table(The square face is placed on the table.), is under a shearing force. The following data is given, calculate the shear modulus of the material.
Dimensions of the block = 60 mm x 60 mm x 20 mm
Shearing Force = 0.245 N
Displacement = 5 mm
Solution:
Substituting the values in the formula we get-
Shear stress
Shear strain
Thus,
Shear modulus,
= 2450 N/m2.
You may also want to check out these topics given below!
Relation Between Elastic Constants
The elastic moduli of a material, like Young’s Modulus, Bulk Modulus, Shear Modulus are specific forms of Hooke’s law, which states that, for an elastic material, the strain experienced by the corresponding stress applied is proportional to that stress. Thus, we can write the relation between elastic constants by the following equation:
Where,
- G is the Shear Modulus
- E is the Young’s Modulus
- K is the Bulk Modulus
- υ is Poisson’s Ratio
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1) How does rigidity modulus is related to other elastic moduli?
Ans: The shear modulus is related to other elastic moduli as 2G(1+υ) = E = 3K(1−2υ)
where,
G is the Shear Modulus
E is the Young’s Modulus
K is the Bulk Modulus
υ is Poisson’s Ratio
Q2) What happens to shear modulus if applied shear force increases?
Ans: When the shear force is increased, the value of shear modulus also increases.
Q3) If the shear modulus of material 1 is x pascals and Material 2 is 30x pascals. What does it mean?
Ans: If the shear modulus of material 1 is x pascals and Material 2 is 30x pascals. It means that material 2 is more rigid than material 1.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. If you wish to learn more physics concepts with the help of interactive video lessons, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.




Comments