We have come across different types of motions in our previous sessions. Rotatory motion, rectilinear motion, oscillatory motion, uniform circular, and periodic motion are some types of motion. Movement of an object while rotating along a circular path is known as circular motion. Circular motion can be either uniform or non-uniform. In this article, let us discuss in brief the uniform circular motion along with examples.
| Table of Contents: |
What is Uniform Circular Motion?
The movement of a body following a circular path is called a circular motion. Now, the motion of a body moving with constant speed along a circular path is called Uniform Circular Motion. Here, the speed is constant but the velocity changes.
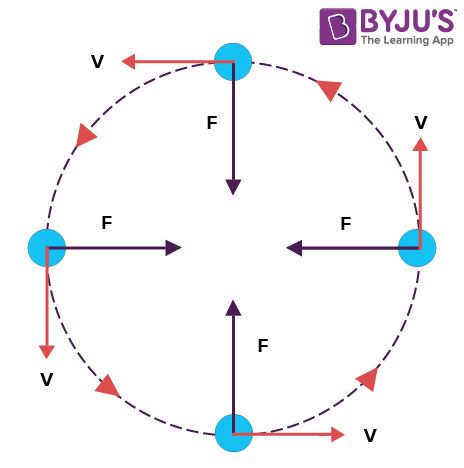
If a particle is moving in a circle, it must have some acceleration acting towards the centre which is making it move around the centre. Since this acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of a particle at every instant, it is only changing the direction of velocity and not magnitude and that’s why the motion is uniform circular motion. We call this acceleration centripetal acceleration (or radial acceleration), and the force acting towards the centre is called centripetal force.
In the case of uniform circular motion, the acceleration is:
ar = v2r = ω2r
If the mass of the particle is m, we can say from the second law of motion that:
F = ma
mv2r= mω2r
This is not a special force, actually force like tension or friction may be a cause of origination of centripetal force. When the vehicles turn on the roads, it is the frictional force between tyres and ground that provides the required centripetal force for turning.
NOTE
So if a particle is moving in a uniform circular motion:
1) Its speed is constant
2) Velocity is changing at every instant
3) There is no tangential acceleration
4) Radial (centripetal) acceleration = ω2r
5) v=ωr
In case of non-uniform circular motion, there is some tangential acceleration due to which the speed of the particle increases or decreases. The resultant acceleration is the vector sum of radial acceleration and tangential acceleration.
Understanding Uniform Circular Motion

Understanding the Laws of Motion

Uniform Circular Motion Examples
Following are the examples of uniform circular motion:
- Motion of artificial satellites around the earth is an example of uniform circular motion. The gravitational force from the earth makes the satellites stay in the circular orbit around the earth.
- The motion of electrons around its nucleus.
- The motion of blades of the windmills.
- The tip of second’s hand of a watch with circular dial shows uniform circular motion.
In the video, you will learn the difference between uniform circular motion and non-uniform circular motion.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the tendency to overturn by a cyclist if he turns around a curve at 15 miles/hour and if he doubles the speed?
From formula, we know that
Name the device used for measuring speed of rotation.
The tachometer is a device that is used for measuring the speed of rotation.
What happens to the velocity vector of a particle, if the particle is moving in a circle, at equal angles in equal times.
The velocity vector of a particle will change its direction. This is because it is always directed in the direction of the tangent to the circle.
Which property is conserved when a particle is moving with constant angular velocity?
When a particle is moving with constant angular velocity, the energy of the particle is conserved. This is because in a uniform circular motion, kinetic energy remains unchanged and the momentum of the particle varies with change in velocity.
What happens to the direction when a vector is multiplied by a positive number?
The work done by the body when it moves along a circle with a constant speed is zero. This means that the work done by the centripetal force is zero.




Nice