According to Hooke’s law, the force required to compress or extend a spring is directly proportional to the distance it is stretched.
Formula of Spring Constant
The formula of spring constant is given as:
| Formula | F=-k x |
| SI unit | N.m-1 |
Where,
- F is the restoring force of the spring directed towards the equilibrium
- k is the spring constant in N.m-1
- x is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position
In other words, the spring constant is the force applied if the displacement in the spring is unity. If a force F is considered that stretches the spring so that it displaces the equilibrium position by x.
Spring Constant Dimensional Formula
We know that,
F=-kx
Therefore,
Dimension of F=[MLT-2]
Dimension of x= [L]
Therefore, dimension of k=
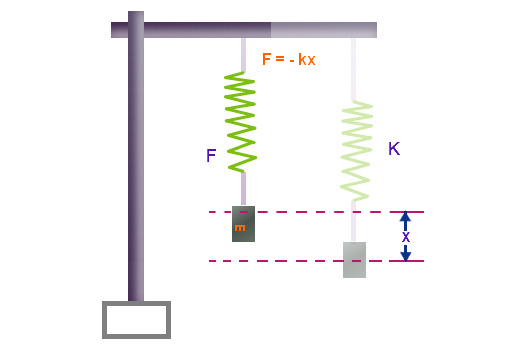
The Spring Constant Formula is given as,
- F = Force applied,
- x = displacement by the spring
- The negative sign shows that the restoring force is opposite to the displacement
It is expressed in Newton per meter (N/m).
Solved Examples
Example 1 A spring with load 5 Kg is stretched by 40 cm. Determine its spring constant.
Solution:
Given:
Mass m = 5 Kg
Displacement x = 40 cm
We know that,
Force F = m a = 5 × 0.4 = 2 N
The spring constant is given as:
= – 2 / 0.4= – 5 N/m
Example 2 A boy weighing 20 pounds stretches a spring by 50 cm. Determine the spring constant of the spring.
Solution:
Given:
Mass m = 20 lbs = 20 / 2.2 = 9.09 Kg
Displacement x = 50 cm
The force F = ma = 9.09 × 9.8 = 89.082 N
The spring constant formula is given by:
= – 89.082 / 0.5 = – 178.164 N/m.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about other Physics related concepts.


Comments