Tangential velocity is the linear speed of any object moving along a circular path. A point on the outside edge of a turntable moves a greater distance in one complete rotation than a point near to the center. When a body moves in a circular path at a distance r from the center, the body’s velocity is directed tangentially at any instant. This is known as tangential velocity. In other words, the linear velocity is its tangential velocity at any instant.
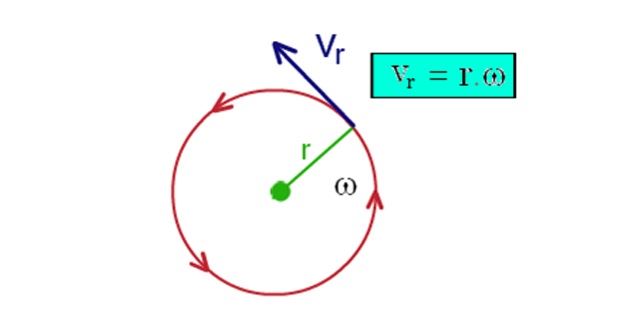
Formula of Tangential Velocity
The tangential velocity formula is given by,
Where,
- r is the radius of the circular path and
- ω is the angular velocity
The tangential velocity formula is applied in calculating the tangential velocity of any object moving in a circular path.
It is expressed in meter per second (m/s).
Solved Examples
Example 1
If the angular velocity of a wheel is 40 rad/s, and the wheel diameter is 60 cm, calculate the tangential velocity.
Solution:
Given:
Radius, r = ½ of diameter of 60 cm
r = 30 cm = 0.30 m
Angular velocity, ω = 40 rad/s.
The tangential velocity formula is given by,
= 40 x 0.30
Vr = 12 m/s
Example 2
If a wheel moves at 10 m/sec, and its angular velocity is 5 radians/sec, calculate the radius of the wheel.
Solution:
Given:
Tangential velocity, Vr= 10 m/sec
Angular velocity, ω, = 5 radians/sec.
the formula for tangential velocity is given by,
Vr = ω r
Vr / ω = r
10/5= r
r = 2 m


Comments