According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, the total energy of an isolated system always remains constant. The first law explains about the relationship between the work done by the system or by the system and the heat absorbed without putting any limitation on the direction of heat flow.
Table of Contents
- What is Spontaneity?
- Recommended Videos
- Predicting the spontaneity of a reaction
- Gibbs Equation
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
However, all processes which occur naturally tend to proceed spontaneously in one direction only. What does spontaneity mean here? What factors determine the direction in a spontaneous change?
What is Spontaneity?
Let us try to understand the meaning of spontaneity. A spontaneous process is an irreversible process and it could only be reversed by some external agents. The entropy of any system is defined as the degree of randomness in it.
Recommended Videos

Predicting the spontaneity of a reaction
Generally, total entropy change is the essential parameter which defines the spontaneity of any process. Since most of the chemical reactions fall under the category of a closed system and open system; we can say there is a change in enthalpy too along with the change in entropy. Since, change in enthalpy also increases or decreases the randomness by affecting the molecular motions, entropy change alone cannot account for the spontaneity of such a process. Therefore, for explaining the spontaneity of a process we use the Gibbs energy change. Gibbs’ energy is a state function and an extensive property. The general expression for Gibbs energy change at constant temperature is expressed as:
Gibbs Equation ⇒
ΔGsys = ΔHsys – TΔSsys
Where,
ΔGsys = Gibbs energy change of the system
ΔHsys = enthalpy change of the system
ΔSsys = entropy change of the system
T = Temperature of the system
This is known as the Gibbs equation.
For a spontaneous process, the total entropy change, ΔStotal is always greater than zero.
ΔStotal=ΔSsys + ΔSsurr
Where,
ΔStotal= total entropy change for the process
ΔSsys = entropy change of the system
ΔSsurr = entropy change of the surrounding
The change in temperature between the system and the surrounding in the case of thermal equilibrium between system and surrounding is 0, i.e. DT= 0. Thus, enthalpy lost by the system is gained by the surrounding. Hence, the entropy change of the surrounding is given as,
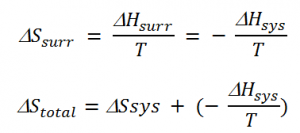
ΔHsurr = change in enthalpy of the surrounding
ΔHsys = change in enthalpy of the system
Also, for a spontaneous process, the total change in entropy is 0, i.e. ΔStotal> 0.
Therefore;
TΔSsys – ΔHsys>0
ΔHsys– TΔSsys<0
Using the Gibbs equation, it can be said that
ΔGsys< 0
Thus, it can be inferred that any process is spontaneous if the change in Gibbs energy of the system is less than zero or else the process is not spontaneous.
Therefore, with the help of the above relation, spontaneity of a reaction can be easily predicted.
- In the case of exothermic reactions, enthalpy of the system is negative thereby making all exothermic reactions spontaneous.
- In the case of endothermic reactions, Gibbs free energy becomes negative only when the temperature is very high or the entropy change is very high.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How is a reaction spontaneous?
Reactions are favorable when they result in a decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy of the system. When both of these conditions are met, the reaction occurs naturally. A spontaneous reaction is a reaction that favors the formation of products at the conditions under which the reaction is occurring.
Which chemical reaction is always spontaneous?
A reaction which is exothermic (ΔH negative) and results in an increase in the entropy of the system (ΔS positive) will always be spontaneous.
Which process is spontaneous?
A spontaneous process is one that occurs on its own, without any energy input from the outside. For example, a ball will roll down an incline; water will flow downhill; ice will melt into water; radioisotopes will decay; and iron will rust.
What two factors favor a spontaneous reaction?
Enthalpy- Reactions that give off energy tend to be spontaneous. Entropy- Entropy is a measure of the randomness or disorder in a system. Generally reactions that increase the randomness of the system are spontaneous.
What is spontaneous and non spontaneous reaction?
A spontaneous process is capable of proceeding in a given direction without needing to be driven by an outside source of energy. An endergonic reaction (also called a nonspontaneous reaction) is a chemical reaction in which the standard change in free energy is positive and energy is absorbed.
To learn more about spontaneity and thermodynamics, register with BYJU’S and download our app – BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Comments